Related Research Articles

The Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad was a railroad that operated in the Midwestern United States. Commonly referred to as the Burlington Route, the Burlington, or as the Q, it operated extensive trackage in the states of Colorado, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Nebraska, Wisconsin, Wyoming, and also in Texas through subsidiaries Colorado and Southern Railway, Fort Worth and Denver Railway, and Burlington-Rock Island Railroad. Its primary connections included Chicago, Minneapolis–Saint Paul, St. Louis, Kansas City, and Denver. Because of this extensive trackage in the midwest and mountain states, the railroad used the advertising slogans "Everywhere West", "Way of the Zephyrs", and "The Way West".
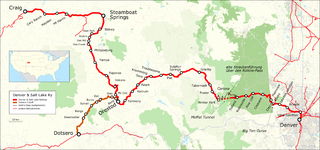
The Denver and Salt Lake Railway (D&SL) was a U.S. railroad company located in Colorado. Originally incorporated in 1902 as the Denver, Northwestern and Pacific (DN&P) Railway, it had as a goal a direct connection of Denver, Colorado, with Salt Lake City, Utah. It underwent numerous reorganizations throughout its financially troubled history and by the time the company was acquired in 1931 by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, it had advanced only as far as Craig, Colorado. After the acquisition the line was connected to the D&RGW main, and the eastern half of the line was used to give the D&RGW a more direct route to Denver. The portions of the railroad still in use today are known as the Moffat Tunnel Subdivision of Union Pacific Railroad's Central Corridor. Amtrak’s California Zephyr service from Denver to Glenwood Springs follows much of the old D&SL route.

The Dakota, Minnesota and Eastern Railroad was a Class II railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway operating across South Dakota and southern Minnesota in the Northern Plains of the United States. Portions of the railroad also extend into Wyoming, Nebraska, Iowa, and Illinois.
Dale Sanders is a prolific railroad photographer and the former editor of CTC Board, a magazine for fans of railroading showcasing high-quality photography and up-to-date news of North American railroading. The magazine frequently featured Sanders' work.

Tennessee Pass elevation 10,424 ft (3,177 m) is a high mountain pass in the Rocky Mountains of central Colorado in the United States. The pass was named after Tennessee, the native state of a group of early prospectors.

The San Diego and Imperial Valley Railroad (SD&IV) is a class III railroad operating freight rail service in the San Diego area, providing service to customers in the region and moving railcars between the end of the BNSF Railway in Downtown San Diego and the Mexico–United States border in San Ysidro. The railroad has exclusive trackage rights to operates over tracks by the San Diego and Arizona Eastern Railway, a subsidiary of the Metropolitan Transit System, the regional public transit service provider. Tracks are shared with the San Diego Trolley, another subsidiary of the Metropolitan Transit System, and freight trains are only operated at nights when passenger service is not in operation. The San Diego & Imperial Valley Railroad was established in October 1984 and is owned and operated by Genesee & Wyoming, a holding company that operates more than 100 shortline railroads like the SD&IV.

The Central Oregon and Pacific Railroad is a Class II railroad operating between Northern California and Eugene, Oregon, United States. It was previously a mainline owned by the Southern Pacific Railroad (SP) between Eugene and Weed, California via Medford, Oregon. SP sold the route on December 31, 1994, in favor of using its route to Eugene via Klamath Falls, Oregon and Cascade Summit.

The Kyle Railroad is a regional railroad line that runs from North Central Kansas into Eastern Colorado. It is based in Phillipsburg, Kansas and runs on 561 miles (903 km) track, mostly the former Rock Island Railroad Chicago to Denver main line. The Kyle was owned by RailAmerica from 2002 to 2012. Genesee & Wyoming Inc. bought RailAmerica in late 2012.

The Arizona Eastern Railway is a Class III railroad that operates 265 miles (426 km) of railroad between Clifton, Arizona, and Miami, Arizona, in the United States. This includes trackage rights over the Union Pacific Railroad between Lordsburg, New Mexico, and Bowie, Arizona. The railroad serves the copper mining region of southeastern Arizona, and the agricultural Gila River Valley. Primary commodities are sulfuric acid, copper concentrate, copper anode and cathode, and copper rod and other copper processing materials. AZER also handles minerals, chemicals, building supplies and lumber. The railroad offers a transload location for lumber, building materials and other consumer commodities at Globe, Arizona.

Railroads Illustrated, formerly known as CTC Board, was a monthly magazine, published by White River Productions (WRP), devoted to railroad photography. WRP purchased CTC Board magazine from Hundman Publishing after the May 2006 issue, and rebranded the magazine as Railroads Illustrated, and used the CTC Board name for the news section. December 2014 marked the final monthly issue, with future expanded editions to be released annually. The news section and some feature content now appears in an expanded Railfan & Railroad, which was acquired by WRP in 2014.
The Texas & New Mexico Railway is a class III short-line railroad operating in west Texas and southeast New Mexico. The railroad line operates on 111 miles of track from a connection with the Union Pacific at Monahans, Texas, and terminates at Lovington, New Mexico. The railroad primarily provides freight service for the oilfields and related industries in the region.

The Southern Ontario Railway is a shortline railroad in the province of Ontario, owned and operated by Genesee & Wyoming Canada Inc., the Canadian subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming Inc.. It operated 69 miles (111 km) of track from Brantford to Nanticoke, Ontario, from 1998 to 2018. The railroad began operations in 1998, and was acquired by RailAmerica two years later. It had interchanges with the Canadian National Railway at Hamilton via trackage rights, Brantford and Paris, and interchanges with the Canadian Pacific Railway at Hamilton.

Ottawa Valley Railway is a Canadian railway that operates 150 miles (240 km) of track in the provinces of Ontario and Quebec, and is owned by Genesee & Wyoming Canada Inc., the Canadian subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming Inc.

Iowa Pacific Holdings was a holding company that owned railroad properties across North America and the United Kingdom, as well as providing services such as railcar repairs, leasing, management and consulting services to other operators. The company was founded in 2001 with headquarters in Chicago, Illinois.
Gale B. Aydelott, better known as "Gus Aydelott," was an American railroad president. He headed the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad for nearly three decades.

The Pacific Imperial Railroad was a company in possession of the SD&AE Desert Line right of way in Southern California, colloquially referred to as the Desert Line. The Desert Line starts at the border crossing at Division, near Campo at Milepost 59.94 in eastern San Diego County, California where it connects with the Baja California Railroad in Mexico, and stretches 70.1 miles through the Jacumba Mountains to El Centro, California, where it connects to Union Pacific Railroad at Milepost 129.61. The significance of the Desert Line is that it provides an alternative rail route to and from the east for servicing the distribution, transportation, and supply chain needs of the Cali-Baja region.

The San Bernardino Transit Center is an intermodal transit center in downtown San Bernardino, California, United States. It is owned and operated by Omnitrans, the area's public transportation agency.
Edward L. Moyers, Jr. was an American railroad executive of the 20th century. He served as president and CEO of several railroads including MidSouth Rail, Illinois Central Railroad and Southern Pacific Railroad. In 1995, Railway Age magazine named Moyers its "Railroader of the Year".
The Uinta Basin Rail project is a proposed 100-mile (160 km) rail line to connect the shale oil rich Uinta Basin region of eastern Utah to the national rail network. Numerous proposals have been made, some as far back as 1902, that are still under consideration. The current effort is a public-private partnership between a coalition of 7 counties in Utah, the Rio Grande Pacific Corporation and Drexel Hamilton Infrastructure Partners. If the rail line is built it will be the first major greenfield rail line built in the United States since the line to the Powder River Basin was built in the 1970s. Construction for this line is projected to begin in 2021; however, environmental groups have filed lawsuits to try to stop construction.
White River Productions is an independent publishing company that specializes in books and magazines targeted to railroad enthusiasts and historians. Kevin EuDaly founded the company in 1992 to published the book Missouri Pacific Diesel Power, which he also authored. Several other titles followed, and the company became his full-time venture beginning in 1996. The company expanded when it took on publishing newsletters and managing membership databases for several railroad historical societies. The company is headquartered in Bucklin, Missouri.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Mark W. Hemphill". Center for Railroad Photography & Art. Archived from the original on March 15, 2012. Retrieved 2011-01-03.
- 1 2 "Freight Rail Thought Leaders". HDR, inc. Archived from the original on 2011-04-14. Retrieved 2011-01-03.
- ↑ "Hemphill Heading Uinta Basin Railway Project". 15 August 2019.