Related Research Articles

The Dorians were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Hellenes of Classical Greece divided themselves. They are almost always referred to as just "the Dorians", as they are called in the earliest literary mention of them in the Odyssey, where they already can be found inhabiting the island of Crete.

Homer was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history.

Thucydides was an Athenian historian and general. His History of the Peloponnesian War recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of "scientific history" by those who accept his claims to have applied strict standards of impartiality and evidence-gathering and analysis of cause and effect, without reference to intervention by the gods, as outlined in his introduction to his work.
Greek literature dates back from the ancient Greek literature, beginning in 800 BC, to the modern Greek literature of today.

The History of the Peloponnesian War is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War, which was fought between the Peloponnesian League and the Delian League. It was written by Thucydides, an Athenian historian who also served as an Athenian general during the war. His account of the conflict is widely considered to be a classic and regarded as one of the earliest scholarly works of history. The History is divided into eight books.
The Battle of Tanagra was a land battle that took place in 457 BC between Athens and Sparta during the First Peloponnesian War. Tension between Athens and Sparta had built up due the rebuilding of Athens' walls and Spartan rejection of Athenian military assistance. The Athenians were led by Myronides and held a strength of 14,000. The Spartans were led by Nicomedes and had a total of 11,500 soldiers. Both sides suffered losses; however, the Spartans left victorious.

Tonbridge School is a public school in Tonbridge, Kent, England, founded in 1553 by Sir Andrew Judde. It is a member of the Eton Group and has close links with the Worshipful Company of Skinners, one of the oldest London livery companies.
The name Eurymachus is attributed to the following individuals:
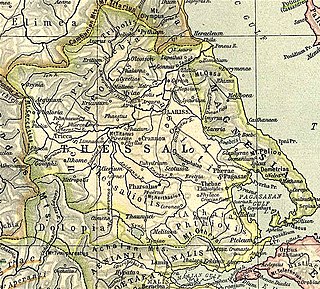
Pherae was a city and polis (city-state) in southeastern Ancient Thessaly. One of the oldest Thessalian cities, it was located in the southeast corner of Pelasgiotis. According to Strabo, it was near Lake Boebeïs 90 stadia from Pagasae, its harbor on the Gulf of Pagasae. The site is in the modern community of Velestino.

Francis Macdonald Cornford was an English classical scholar and translator known for work on ancient philosophy, notably Plato, Parmenides, Thucydides, and ancient Greek religion. Frances Cornford, his wife, was a noted poet. Due to the similarity in their names, he was known in the family as "FMC" and his wife as "FCC".

Meditations is a series of personal writings by Marcus Aurelius, Roman Emperor from AD 161 to 180, recording his private notes to himself and ideas on Stoic philosophy.
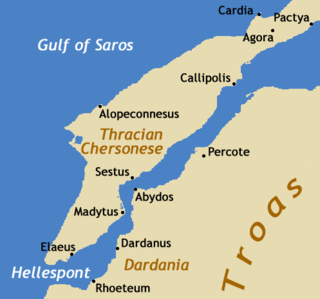
Elaeus, the “Olive City”, was an ancient Greek city located in Thrace, on the Thracian Chersonese. Elaeus was located at the southern end of the Hellespont near the southernmost point of the Thracian Chersonese in modern-day Turkey. According to the geographer Scymnus, Elaeus was founded by settlers from Ionian Teos, while the Pseudo-Scymnus writes that it was a colony of Athens and was founded by Phorbas

Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière Hammond, was a British historian, geographer, classicist and an operative for the British Special Operations Executive (SOE) in occupied Greece during the Second World War.

Heraclea (Herakleia) in Trachis, also called Heraclea Trachinia, was a colony founded by the Spartans in 426 BC, the sixth year of the Peloponnesian War. It was also a polis (city-state).
Peter John Rhodes,, usually cited as P. J. Rhodes, was a British academic and ancient historian. He was Professor of Ancient History at the University of Durham. He specialized in Ancient Greek politics and political institutions.
Epicles (Epiklês) was the name of several prominent Ancient Greeks:

This bibliography of Greece is a list of books in the English language which reliable sources indicate relate to the general topic of Greece.

The Argead dynasty, also known as the Temenid dynasty, was an ancient Macedonian royal house of Dorian Greek provenance. They were the founders and the ruling dynasty of the kingdom of Macedon from about 700 to 310 BC.
Wang Huansheng is a Chinese translator. He has a good command of English, Classical Greek, Latin and Russian. Wang was a researcher of the Chinese Academy of Social Science, he is a member of the Chinese Communist Party and the China Writers Association.
Pteleum or Pteleon was a fortress town in the territory of Erythrae, in Ionia. Pliny the Elder mentions Pteleon, Helos, and Dorium as near Erythrae, but those places are confused by Pliny with the Triphylian towns in Homer's Catalogue of Ships in the Iliad.
References
- 1 2 3 "Tim Haynes – New Headmaster from September 2005". tonbridge-school.co.uk. 7 September 2004.
- ↑ Peter Oborne, The Assault on Truth (London: Simon & Schuster, 2021), p. 107
- ↑ Thucydides, P. J. Rhodes, Martin Hammond, The Peloponnesian War