Related Research Articles

A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and software that store, manage, analyze, edit, output, and visualize geographic data. Much of this often happens within a spatial database, however, this is not essential to meet the definition of a GIS. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system also to include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, the body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations.
A web portal is a specially designed website that brings information from diverse sources, like emails, online forums and search engines, together in a uniform way. Usually, each information source gets its dedicated area on the page for displaying information ; often, the user can configure which ones to display. Variants of portals include mashups and intranet dashboards for executives and managers. The extent to which content is displayed in a "uniform way" may depend on the intended user and the intended purpose, as well as the diversity of the content. Very often design emphasis is on a certain "metaphor" for configuring and customizing the presentation of the content and the chosen implementation framework or code libraries. In addition, the role of the user in an organization may determine which content can be added to the portal or deleted from the portal configuration.

A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discrete global grid. DEMs are used often in geographic information systems (GIS), and are the most common basis for digitally produced relief maps. A digital terrain model (DTM) represents specifically the ground surface while DEM and DSM may represent tree top canopy or building roofs.

Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc., doing business as Esri, is an American multinational geographic information system (GIS) software company headquartered in Redlands, California. It is best known for its ArcGIS products. With a 40% market share, Esri is the world's leading supplier of GIS software, web GIS and geodatabase management applications.
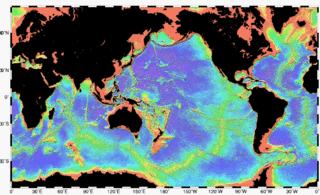
Bathymetry is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors, lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago. Bathymetric charts, are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain as contour lines and selected depths (soundings), and typically also provide surface navigational information. Bathymetric maps may also use a Digital Terrain Model and artificial illumination techniques to illustrate the depths being portrayed. The global bathymetry is sometimes combined with topography data to yield a global relief model. Paleobathymetry is the study of past underwater depths.
A GIS software program is a computer program to support the use of a geographic information system, providing the ability to create, store, manage, query, analyze, and visualize geographic data, that is, data representing phenomena for which location is important. The GIS software industry encompasses a broad range of commercial and open-source products that provide some or all of these capabilities within various information technology architectures.

ArcGIS is a family of client, server and online geographic information system (GIS) software developed and maintained by Esri.
Pennsylvania Spatial Data Access (PASDA) is Pennsylvania's official public access geospatial information clearinghouse. PASDA serves as Pennsylvania's node on the National Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI). PASDA is a cooperative effort of the Pennsylvania Geospatial Technologies Office of the Office of Information Technology and the Pennsylvania State University Institute of Energy and the Environment.

QGIS is a geographic information system (GIS) software that is free and open-source. QGIS supports Windows, macOS, and Linux. It supports viewing, editing, printing, and analysis of geospatial data in a range of data formats. QGIS was previously also known as Quantum GIS.
ArcGIS Server is the core server geographic information system (GIS) software made by Esri. ArcGIS Server is used for creating and managing GIS Web services, applications, and data. ArcGIS Server is typically deployed on-premises within the organization’s service-oriented architecture (SOA) or off-premises in a cloud computing environment.
Geospatial metadata is a type of metadata applicable to geographic data and information. Such objects may be stored in a geographic information system (GIS) or may simply be documents, data-sets, images or other objects, services, or related items that exist in some other native environment but whose features may be appropriate to describe in a (geographic) metadata catalog.

Web mapping or an online mapping is the process of using, creating, and distributing maps on the World Wide Web, usually through the use of Web geographic information systems. A web map or an online map is both served and consumed, thus, web mapping is more than just web cartography, it is a service where consumers may choose what the map will show.
The Arizona Geographic Information Council (AGIC) was established by executive order as Arizona's primary forum and oversight group for coordination efforts related to geographic information systems (GIS). AGIC identifies standards and implementation strategies to provide a framework for optimizing Arizona's investment in GIS. Through cooperation and partnerships, AGIC facilitates the acquisition, exchange and management of geospatial data and technology to benefit State agencies and the Arizona GIS community. AGIC meets on a regular basis and conducts an Annual GIS Conference to address statewide GIS issues, requirements and solutions.
Distributed GIS refers to GI Systems that do not have all of the system components in the same physical location. This could be the processing, the database, the rendering or the user interface. It represents a special case of distributed computing, with examples of distributed systems including Internet GIS, Web GIS, and Mobile GIS. Distribution of resources provides corporate and enterprise-based models for GIS. Distributed GIS permits a shared services model, including data fusion based on Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) web services. Distributed GIS technology enables modern online mapping systems, Location-based services (LBS), web-based GIS and numerous map-enabled applications. Other applications include transportation, logistics, utilities, farm / agricultural information systems, real-time environmental information systems and the analysis of the movement of people. In terms of data, the concept has been extended to include volunteered geographical information. Distributed processing allows improvements to the performance of spatial analysis through the use of techniques such as parallel processing.
The Conservation Geoportal was an online geoportal, intended to provide a comprehensive listing of geographic information systems (GIS) datasets and web map service relevant to biodiversity conservation. It is currently defunct. The site, its contents and functionality were free for anyone to use and contribute to. The Conservation Geoportal was launched on June 28, 2006 at the joint Society for Conservation Biology and Society for Conservation GIS Conference in San Jose, California, USA. As of October 2007, it included metadata for over 3,667 GIS records.
Bhuvan is an Indian web-based utility which allows users to explore a set of geographic content prepared by the Indian Space Research Organisation. The content which the utility serves is mostly restricted to within Indian boundaries and is offered in four regional languages. The content includes thematic maps related to disasters, agriculture, water resources, land cover, and processed satellite data generated by ISRO.
The Wind Energy Data and Information (WENDI) Gateway was established by the Environmental Sciences Division of Oak Ridge National Laboratory in March 2010 to support the United States Department of Energy's Wind and Hydropower Technologies Program. It provided a digital library for wind energy-related data and information from a wide spectrum of sources—including data centers, scientific and technical journals, and geographic information systems (GIS), as well as the websites of government agencies, corporations and trade organizations. The gateway was taken offline after funding ended in August 2012. Much of its content was incorporated into the OpenEI site.

Digimap is a web mapping and online data delivery service developed by the EDINA national data centre for UK academia. It offers a range of on-line mapping and data download facilities which provide maps and spatial data from Ordnance Survey, British Geological Survey, Landmark Information Group and OceanWise Ltd Ltd.,, Getmapping Ltd, the Environment Agency, OpenStreetMap, CollinsBartholomew Ltd, and various other sources.
GeoSUR is a regional initiative led by spatial data producers in Latin America and the Caribbean to implement a regional geospatial network and to help establish the basis of a spatial data infrastructure in the region. GeoSUR supports the development of free access geographic services useful to find, view and analyze spatial information through maps, satellite images, and geographic data.

Web GIS, or Web Geographic Information Systems, are GIS that employ the World Wide Web to facilitate the storage, visualization, analysis, and distribution of spatial information over the Internet. The World Wide Web, or the Web, is an information system that uses the internet to host, share, and distribute documents, images, and other data. Web GIS involves using the World Wide Web to facilitate GIS tasks traditionally done on a desktop computer, as well as enabling the sharing of maps and spatial data. While Web GIS and Internet GIS are sometimes used interchangeably, they are different concepts. Web GIS is a subset of Internet GIS, which is itself a subset of distributed GIS, which itself is a subset of broader Geographic information system. The most common application of Web GIS is Web mapping, so much so that the two terms are often used interchangeably in much the same way as Digital mapping and GIS. However, Web GIS and web mapping are distinct concepts, with web mapping not necessarily requiring a Web GIS.
References
- ↑ "Samples of LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) Derived Elevation Data". Maryland Department of Natural Resources . Retrieved 15 May 2013.