
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about 1,100 nautical miles north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about 110 are permanently inhabited—and more than 500 islets, amounting to a total land area of about 18,300 square kilometres (7,100 sq mi). The most outlying island group is Ono-i-Lau. About 87% of the total population of 924,610 live on the two major islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu. About three-quarters of Fijians live on Viti Levu's coasts, either in the capital city of Suva, or in smaller urban centres such as Nadi or Lautoka. The interior of Viti Levu is sparsely inhabited because of its terrain.

Suva is the capital and largest city of Fiji. It is the home of the country's largest metropolitan area and serves as its major port. The city is located on the southeast coast of the island of Viti Levu, in Rewa Province, Central Division.

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
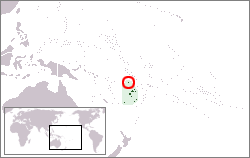
Rotuma is a self-governing heptarchy, generally designated a dependency of Fiji. 'Rotuma' commonly refers to Rotuma Island, the only permanently inhabited and by far the largest of all the islands in the Rotuma Group. Officially, the Rotuma Act declares that Rotuma consists of Rotuma Island as well as its neighbouring islands, rocks, and reefs across the entire Rotuma Group. The dependency is situated around 500 km west of the French islands of Wallis and Futuna and a similar distance north of the Fijian mainland. Its capital is Ahau, a hamlet consisting of a number of colonial-era buildings. Rotuma exists as a dependency of Fiji but itself contains its own socioreligious pene-enclave known traditionally as Faguta where the chiefs and their villages adhere to the practices of worship, festival dates, and French-based writing system of the Marists. Faguta's special character was effectively agreed to by all Rotuma's chiefs in 1871 in the Treaty of Hamelin.
Fiji Airways is the flag carrier of Fiji. It operates international services from its hubs in Fiji to 27 destinations. It has an extended network of 108 international destinations through its codeshare partners. The Fiji Airways Group brings in 64 percent of all visitors who fly to Fiji, employs over 1,000 employees, and earns revenues of over FJD$815 million (US$390m).

Butaritari is an atoll in the Pacific Ocean island nation of Kiribati. The atoll is roughly four-sided. The south and southeast portion of the atoll comprises a nearly continuous islet. The atoll reef is continuous but almost without islets along the north side. Bikati and Bikatieta islets occupy a corner of the reef at the extreme northwest tip of the atoll. Small islets are found on reef sections between channels on the west side. The lagoon of Butaritari is deep and can accommodate large ships, though the entrance passages are relatively narrow. It is the most fertile of the Gilbert Islands, with relatively good soils and high rainfall. Butaritari atoll has a land area of 13.49 km2 (5.21 sq mi) and a population of 3,224 as of 2015. During World War II, Butaritari was known by United States Armed Forces as Makin Atoll, and was the site of the Battle of Makin. Locally, Makin is the name of a separate but closest atoll, 3 kilometres to the northeast of Butaritari, but close enough to be seen. These two atolls share a dialect of the Gilbertese language.
Fijians are a nation and ethnic group native to Fiji, who speak Fijian and English and share a common history and culture.

Viti Levu is the largest island in the Republic of Fiji. It is the site of the nation's capital, Suva, and home to a large majority of Fiji's population.

The Fiji men's national football team is Fiji's national men's team and is controlled by the governing body of football in Fiji, the Fiji Football Association. The team plays most of their home games at the HFC Bank Stadium in Suva.
The culture of Fiji is a tapestry of native Fijian, Indian, European, Chinese, and other nationalities. Culture polity traditions, language, food costume, belief system, architecture, arts, craft, music, dance, and sports will be discussed in this article to give you an indication of Fiji's indigenous community but also the various communities which make up Fiji as a modern culture and living. The indigenous culture is an active and living part of everyday life for the majority of the population.
The Lau Islands of Fiji are situated in the southern Pacific Ocean, just east of the Koro Sea. Of this chain of about sixty islands and islets, about thirty are inhabited. The Lau Group covers a land area of 188 square miles, and had a population of 10,683 at the most recent census in 2007. While most of the northern Lau Group are high islands of volcanic origin, those of the south are mostly carbonate low islands.

Kanacea (Kanathea) is a volcanic island with seven peaks in Fiji's Lau archipelago. It is 15 km west of Vanua Balavu. Covering an area of 12.48 square kilometres, it has a maximum elevation of 259 meters.

Brachylophus fasciatus, the Lau banded iguana, is an arboreal species of lizard endemic to the Lau Islands of the eastern part of the Fijian archipelago. It is also found in Tonga, where it was probably introduced by humans. It is one of the few species of iguanas found outside of the New World and one of the most geographically isolated members of the family Iguanidae. Populations of these iguanas have been declining over the past century due to habitat destruction, and more significantly, the introduction of mongoose and house cats to the islands.

Religiously, Fiji is a mixed society, with Christianity and Hinduism being the main faiths.

Eco-Challenge: The Expedition Race is a multi-day expedition length adventure race in which teams of four competed. It originally aired on TV from April 1995 to April 2002. Based closely on the Raid Gauloises adventure race, the broadcast of Eco-Challenge led to the popularity of the adventure racing.

Fiji has three official languages under the 1997 constitution : English, Fijian and Fiji Hindi. The Fijian language is spoken as the first language by most indigenous Fijians who make up around 54% of the population.

Sir Walter Randolph Carpenter (1877–1954) was an Australian-Canadian pearl hunting, trader, merchant, ship owner, airline industry leader and philanthropist of American ancestry active in the western Pacific from the 1890s through the 1940s.

Camakau are a traditional watercraft of Fiji. Part of the broader Austronesian tradition, they are similar to catamarans, outrigger canoes, or smaller versions of the drua, but are larger than a takia. These vessels were built primarily for the purposes of travelling between islands and for trade. These canoes are single hulled, with an outrigger and a cama, a float, with both ends of the hull being symmetrical. They were very large, capable of travelling open ocean, and have been recorded as being up to 70 ft in length.

William Granger Johnson was a Fijian businessman and politician, serving as a nominated member of the Legislative Council in two spells during the 1940s and 1950s.
Paradise Beverages (Fiji) Limited is a Fijian alcoholic beverage producer based in Suva. It is a publicly listed company on the South Pacific Stock Exchange.














