| C3 | |
|---|---|
| ILO Convention | |
| Date of adoption | November 28, 1919 |
| Date in force | June 13, 1921 |
| Classification | Maternity Benefit Maternity Protection |
| Subject | Maternity Protection |
| Previous | Unemployment Convention, 1919 |
| Next | Night Work (Women) Convention, 1919 (shelved) |
Maternity Protection Convention, 1919 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1919:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to "women's employment, before and after childbirth, including the question of maternity benefit",...
The principles contained in the convention were subsequently revised and included in ILO Convention C103, Maternity Protection Convention (Revised), 1952, and in Maternity Protection Convention, 2000.
As of 2013, the convention had been ratified by 34 states. Of the ratifying states, eight have subsequently denounced the treaty.

The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly. Described as an international bill of rights for women, it was instituted on 3 September 1981 and has been ratified by 189 states. Over fifty countries that have ratified the Convention have done so subject to certain declarations, reservations, and objections, including 38 countries who rejected the enforcement article 29, which addresses means of settlement for disputes concerning the interpretation or application of the Convention. Australia's declaration noted the limitations on central government power resulting from its federal constitutional system. The United States and Palau have signed, but not ratified the treaty. The Holy See, Iran, Somalia, and Tonga are not signatories to CEDAW.
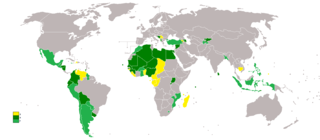
The International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families is a United Nations multilateral treaty governing the protection of migrant workers and families. Signed on 18 December 1990, it entered into force on 1 July 2003 after the threshold of 20 ratifying States was reached in March 2003. The Committee on Migrant Workers (CMW) monitors implementation of the convention, and is one of the seven UN-linked human rights treaty bodies. The convention applies as of August 2021 in 56 countries.
The Valletta Treaty is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe. The 1992 treaty aims to protect the European archaeological heritage "as a source of European collective memory and as an instrument for historical and scientific study". All remains and objects and any other traces of humankind from past times are considered to be elements of the archaeological heritage. The archaeological heritage shall include structures, constructions, groups of buildings, developed sites, moveable objects, monuments of other kinds as well as their context, whether situated on land or under water."
Unemployment Convention, 1919 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Maternity Protection Convention may refer to:
Workmen's Compensation (Agriculture) Convention, 1921 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Protection against Accidents (Dockers) Convention (Revised), 1932 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Maternity Protection Convention (Revised), 1952 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Protection of Wages Convention, 1949 is an International Labour Organization (ILO) Convention.
Seafarers' Identity Documents Convention, 1958 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Prevention of Accidents (Seafarers) Convention, 1970 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Workers with Family Responsibilities Convention, 1981 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Health Protection and Medical Care (Seafarers) Convention, 1987 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Nauru is a small island country in the South Pacific. With a population of 13,649 it is the world's least populous independent republic. Nauru's government operates under its constitution, part two of which contains 'protection of fundamental rights and freedoms.' The Human Rights Council (UNHRC) carried out Nauru's Universal Periodic Review (UPR) in January 2011. The review was generally favourable with only a few areas of concern.
The Conventions concerning Employment of Women during the Night are conventions drafted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) which prohibit women from performing industrial work during the night. The first convention was adopted in 1919 and revised versions were adopted in 1934 and 1948. A protocol to the convention was adopted in 1990 allowing for easing of the restriction under conditions. As of April 2011 the conventions had 27, 15, 46 (undenounced) ratifications respectively. The protocol was ratified 5 and denounced by 2.
The International Congress of Working Women (ICWW), formed in 1919, was an organization formed by female laborers around the world. The ICWW planned to share their concerns around female labor issues at the first Annual International Labor Organization Conference of 1919. The ICWW was successful in creating a document of provisions which was presented to the ILO, and affected decision making in the ILO's Commission on the Employment of Women.

European Convention for the Protection of Animals during International Transport refers to two animal welfare treaties regarding livestock transportation of the Council of Europe: