Related Research Articles
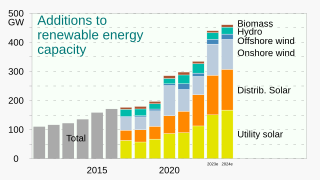
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are considered unsustainable at current rates of exploitation. Renewable energy often provides energy for electricity generation to a grid, air and water heating/cooling, and stand-alone power systems. Renewable energy technology projects are typically large-scale, but they are also suited to rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often crucial in human development. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification, which has several benefits: electricity can move heat or objects efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption. In addition, electrification with renewable energy is more efficient and therefore leads to significant reductions in primary energy requirements.

A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a deviation in their course at a right angle to the wind shear direction.

The Beaufort scale is an empirical measure that relates wind speed to observed conditions at sea or on land. Its full name is the Beaufort wind force scale.

The Legend of Zelda: The Wind Waker is a 2002 action-adventure game developed and published by Nintendo for the GameCube. An installment in The Legend of Zelda series, it was released in Japan in December 2002, in North America in March 2003, and in Europe in May 2003.
The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) classifies hurricanes—which in the Western Hemisphere are tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms—into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds. This measuring system was formerly known as the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, or SSHS.

Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, wind power has been used in sails, windmills and windpumps but today it is mostly used to generate electricity. Wind farms consist of many individual wind turbines, which are connected to the electric power transmission network. New onshore (on-land) wind farms are cheaper than new coal or gas plants, but expansion of wind power is being hindered by fossil fuel subsidies. Onshore wind farms have a greater visual impact on the landscape than some other power stations. Small onshore wind farms can feed some energy into the grid or provide power to isolated off-grid locations. Offshore wind farms deliver more energy per installed capacity with less fluctuations and have less visual impact. Although there is less offshore wind power at present and construction and maintenance costs are higher, it is expanding. Offshore wind power currently has a share of about 10% of new installations.

A wind farm or wind park, also called a wind power station or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turbines covering an extensive area. Wind farms can be either onshore or offshore.

Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local population and civil authorities to make appropriate preparation for the cyclone, including evacuation of vulnerable areas where necessary. It is important that interests throughout the area of an alert make preparations to protect life and property, and do not disregard it on the strength of the detailed forecast track.

The 100 metres, or 100-meter dash, is a sprint race in track and field competitions. The shortest common outdoor running distance, the 100-meter (109.36 yd) dash is one of the most popular and prestigious events in the sport of athletics. It has been contested at the Summer Olympics since 1896 for men and since 1928 for women. The inaugural World Championships were in 1983.

A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for almost one-third of the world's annual tropical cyclones. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern, central, and western. The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclone forecasts is in Japan, with other tropical cyclone warning centers for the northwest Pacific in Hawaii, the Philippines, and Hong Kong. Although the RSMC names each system, the main name list itself is coordinated among 18 countries that have territories threatened by typhoons each year.

Tropical cyclones are ranked on one of five tropical cyclone intensity scales, according to their maximum sustained winds and which tropical cyclone basins they are located in. Only a few scales of classifications are used officially by the meteorological agencies monitoring the tropical cyclones, but other scales also exist, such as accumulated cyclone energy, the Power Dissipation Index, the Integrated Kinetic Energy Index, and the Hurricane Severity Index.
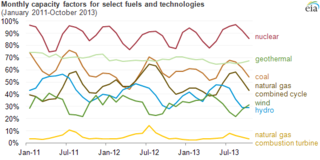
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production.

The United Kingdom is the best location for wind power in Europe and one of the best in the world. By 2022, the UK had over 11 thousand wind turbines with a total installed capacity of over 25 gigawatts (GW): 14 GW onshore and 11 GW offshore, the sixth largest capacity of any country. Wind power generated about 25% of UK electricity, having surpassed coal in 2016 and nuclear in 2018. It is the largest source of renewable electricity in the UK.

A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is referred to by different names, including hurricane, typhoon, tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean, and a typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean, South Pacific, or (rarely) South Atlantic, comparable storms are referred to simply as "tropical cyclones", and such storms in the Indian Ocean can also be called "severe cyclonic storms".

Wind power is a branch of the energy industry that has expanded quickly in the United States over the last several years. From January through December 2021, 379.8 terawatt-hours were generated by wind power, or 9.23% of electricity in the United States. The average wind turbine generates enough electricity in 46 minutes to power the average American home for one month. In 2019, wind power surpassed hydroelectric power as the largest renewable energy source in the U.S.

Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy S.A., formerly Gamesa Corporación Tecnológica S.A. and Grupo Auxiliar Metalúrgico S.A., is a Spanish-German wind engineering company based in Zamudio, Biscay, Spain. It manufactures wind turbines and provides onshore and offshore wind services. It is the world's second largest wind turbine manufacturer.

Wind power generation capacity in India has significantly increased in recent years. As of 30 September 2022, the total installed wind power capacity was 41.666 GW, the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world. Wind power capacity is mainly spread across the Southern, Western, and Northwestern states.

Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet. Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail.

A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy, and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One study claimed that, as of 2009, wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and the most favorable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydro, geothermal, coal and gas energy sources.

The worldwide total cumulative installed electricity generation capacity from wind power has increased rapidly since the start of the third millennium, and as of the end of 2020, it amounts to 733 GW. Since 2010, more than half of all new wind power was added outside the traditional markets of Europe and North America, mainly driven by the continuing boom in China and India. At the end of 2015, China had 145 GW of wind power installed. In 2015, China installed close to half the world's added wind power capacity.
References
- ↑ Faber, Pamela; Rull, Laura Medina. "Written in the Wind: Cultural Variation in Terminology" (PDF). p. 423. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-09-28. Retrieved 9 December 2020.