
Yemen is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Its relatively fertile land and adequate rainfall in a moister climate helped sustain a stable population, a feature recognized by the ancient Greek geographer Ptolemy, who described Yemen as Eudaimon Arabia, meaning "Fertile Arabia" or "Happy Arabia". The South Arabian alphabet was developed at latest between the 12th century BC and the 6th century AD, when Yemen was successively dominated by six civilizations that controlled the lucrative spice trade: Ma'in, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, Saba, and Himyar. With the 630 AD arrival of Islam, Yemen became part of the wider Muslim world, where it has remained.

Yemenite Jews, also known as Yemeni Jews or Teimanim, are Jews who live, or once lived, in Yemen, and their descendants maintaining their customs. After several waves of persecution, the vast majority of Yemenite Jews emigrated to Israel in Operation Magic Carpet between June 1949 and September 1950. Most Yemenite Jews now live in Israel, with smaller communities in the United States and elsewhere. As of 2024, only one Jew, Levi Marhabi, remains in Yemen, although Ynet cited local sources stating that the actual number is five.

Zaydism is a branch of Shia Islam that emerged in the eighth century following Zayd ibn Ali's unsuccessful rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate. Zaydism is one of the three main branches of Shi'ism, with the other two being Twelverism and Ismailism. Zaydism is typically considered the Shia branch that is closest to Sunni Islam, although the "classical" form of Zaydism had historically changed its stance on Sunni and Shia traditions multiple times, to the point where Zaydis simply accepting Ali as a rightful successor to Muhammad was enough to consider them Shia. Twelver Shias sometimes consider Zaydism to be a "fifth school" of Sunni Islam. Zaydis regard rationalism as more important than Quranic literalism and historically were quite tolerant towards Sunni Shafi'ism, a religion of about half of the Yemenis.

Yahya Muhammad Hamid ed-Din was the first king of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen from 1918 until his assassination in 1948. He became Imam of the Zaydis, a branch of Shia Islam, in 1904 after the death of his father, Muhammad Al-Mansur, and Imam of Yemen in 1918. His name and title in full was "His Majesty Amir al-Mu'mimin al-Mutawakkil 'Ala Allah Rab ul-Alamin Imam Yahya bin al-Mansur Bi'llah Muhammad Hamidaddin, Imam and Commander of the Faithful".

Yemenite Hebrew, also referred to as Temani Hebrew, is the pronunciation system for Hebrew traditionally used by Yemenite Jews. Yemenite Hebrew has been studied by language scholars, many of whom believe it retains older phonetic and grammatical features lost elsewhere. Yemenite speakers of Hebrew have garnered considerable praise from language purists because of their use of grammatical features from classical Hebrew.

Shalom Shabazi was the son of Yosef ben Avigad, of the family of Mashtā, also commonly known as Abba Sholem Shabazi or Saalem al-Shabazi. He was a Jewish rabbi and poet who lived in 17th century Yemen, often referred to as the arch-poet of Yemen.
Judeo-Yemeni Arabic is a variety of Arabic spoken by Jews living or formerly living in Yemen. The language is quite different from mainstream Yemeni Arabic, and is written in the Hebrew alphabet. The cities of Sana'a, Aden, al-Bayda, and Habban District and the villages in their districts each have their own dialect.
Yemen is an Islamic country. Nearly all Yemenis are Muslims, The U.S. government estimates that more than 99 percent of the population is Muslim with approximately 60-65% belonging to Sunni Islam and 35-40% belonging to Shia Islam. Amongst the native population, there were approximately 1,000 Christians, and 6 remaining Jews in 2016. However, Pew-Templeton estimates the number of Christians to be as high as 40,000, though most do not publicly identify as such, due to fears of religious persecution. According to WIN/Gallup International polls, Yemen has the most religious population among Arab countries and it is one of the most religious populations world-wide.

Sanaa, officially the Sanaa Municipality, is the capital and largest city of Yemen. The city is the capital of the Sanaa Governorate, but is not part of the governorate, as it forms a separate administrative unit. According to the Yemeni constitution, Sanaa is the capital of the country, although the seat of the Yemeni government moved to Aden, the former capital of Democratic Yemen, in the aftermath of the Houthi occupation. Aden was declared the temporary capital by then-president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi in March 2015.

Rabbi Hayyim Habshush was a coppersmith by trade, and a noted nineteenth-century historiographer of Yemenite Jewry. He also served as a guide for the Jewish-French Orientalist and traveler Joseph Halévy. After his journey with Halévy in 1870, he was employed by Eduard Glaser and other later travellers to copy inscriptions and to collect old books.
Al-Mahdi Muhammad bin Ahmed, also known as Ṣāḥib al-Mawāhib, was an Imam of Yemen who ruled in 1689–1718. He belonged to the Qasimid family that was descended from the Islamic prophet Muhammad and dominated the Zaidi imamate in 1597–1962.
Al Makha District is a district of the Taiz Governorate, Yemen. As of 2003, the district had a population of 18,155 inhabitants. The capital lies at Mocha.

Habban District is a district of the Shabwah Governorate in Yemen. As of 2003, the district had a population of 29,846 inhabitants. The district takes its name after the town Habban which lies in As Said District, located at 14o21'N. latitude, 47o04'E. longitude. The town is some 275 km east by northeast of Aden by air, some 75 km inland from the Gulf of Aden.

The Yemen Eyalet was an eyalet (province) of the Ottoman Empire. Although formally an integral part of the empire, the far-flung province was notoriously difficult to administer, and was often lawless. During the early 17th century, the Eyalet was entirely lost to the Zaidi-ruled Qasimid State, only to be recovered by the Ottomans two centuries later. The Yemen Eyalet was reorganized in 1849, upon Ottoman takeover of much of Greater Yemen territories. In 1872, most of it became Yemen Vilayet after a land reform in the empire.
The Orphans' Decree was a law in the Kingdom of Yemen mandating the forced conversion of Jewish orphans to Islam promulgated by the Zaydi. According to one source, the decree has "no parallel in other countries".

The Mawza Exile is considered the single most traumatic event experienced collectively by the Jews of Yemen, in which Jews living in nearly all cities and towns throughout Yemen were banished by decree of the king, Imām al-Mahdi Ahmad, and sent to a dry and barren region of the country named Mawzaʻ to withstand their fate or to die. Only a few communities, viz., those Jewish inhabitants who lived in the far eastern quarters of Yemen were spared this fate by virtue of their Arab patrons who refused to obey the king's orders. Many would die along the route and while confined to the hot and arid conditions of this forbidding terrain. After one year in exile, the exiles were called back to perform their usual tasks and labors for the indigenous Arab populations, who had been deprived of goods and services on account of their exile.

Yemenite Jews in Israel are immigrants and descendants of the immigrants of the Yemenite Jewish communities, who now reside within the state of Israel. They number around 400,000 in the wider definition. Between June 1949 and September 1950, the overwhelming majority of Yemen and Aden's Jewish population was transported to Israel in Operation Magic Carpet.
Yemenite Jewish poetry, often referred to as "paraliturgical poetry" because of its religious nature, has been an integral part of Yemenite Jewish culture since time immemorial. The Jews of Yemen have preserved a well-defined singing arrangement which not only includes the very poetic creation itself, but also involves a vocal and dance performance, accompanied in certain villages outside Sana'a by drumming on an empty tin-can (tanakeh) or a copper tray. The Jews of Yemen, maintaining strict adherence to Talmudic and Maimonidean halakha, observed the gezeirah which prohibited playing musical instruments, and "instead of developing the playing of musical instruments, they perfected singing and rhythm." This arrangement was integrated into the walks of life familiar to the Jews of Yemen. The texts used in the arrangement were put down in writing and later included in separate song collections (dīwāns). The social strictures and norms in Yemenite Jewish culture provide for separate settings for men and for women, where the sexes are never mixed. Men’s song usually expressed the national aspirations of the Jewish people, and it was far removed from the singing associated with the Muslim environment, whereas folk songs of Jewish women were sung by rote memory and expressed the happiness and sorrows inherent in their daily life and was, as a rule, closer to that of Muslim women.
Amram Qorah was the last Chief Rabbi in Yemen, assuming this role in 1934, after the death of Rabbi Yihya al-Abyadh, Resh Methivta, and which role he held for approximately two years. He is the author of the book, Sa'arat Teman, published post-mortem by the author's son, a book that documents the history of the Jews of Yemen and their culture for a little over 250 years, from the Mawza exile to the mass-immigration of Yemenite Jews to Israel in the mid-20th century.
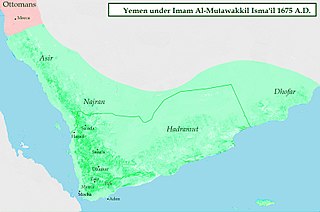
The Qasimid State, also known as the Zaidi Imamate, was a Zaidi-ruled independent state in the Greater Yemen region, which was founded by Imam al-Mansur al-Qasim in 1597, absorbed much of the Ottoman-ruled Yemen Eyalet by 1628, and then completely expelled the Ottomans from Yemen by 1638. The Qasimid State continued to exist into 18th and 19th century, but gradually fractured into separate small states. The most notable of those states was the Sultanate of Lahej; most of those states were submitted by the Ottomans and incorporated into the restored Ottoman province of Yemen Eyalet in 1849.














