
The Aztecs were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (altepetl), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Aztec and Aztecs have long been the topic of scholarly discussion ever since German scientist Alexander von Humboldt established its common usage in the early 19th century.

The Nahuas are one of the Indigenous people of Mexico, with Nahua minorities also in El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. They comprise the largest indigenous group in Mexico. They are a Mesoamerican ethnicity. The Mexica (Aztecs) are of Nahua ethnicity, as are their historical enemies, the Tlaxcallans (Tlaxcaltecs). The Toltecs which predated both groups are often thought to have been Nahua as well. However, in the pre-Columbian period Nahuas were subdivided into many groups that did not necessarily share a common identity.

Miguel León-Portilla was a Mexican anthropologist and historian, specializing in Aztec culture and literature of the pre-Columbian and colonial eras. Many of his works were translated to English and he was a well-recognized scholar internationally. In 2013, the Library of Congress of the United States bestowed on him the Living Legend Award.
Classical Nahuatl is any of the variants of Nahuatl spoken in the Valley of Mexico and central Mexico as a lingua franca at the time of the 16th-century Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. During the subsequent centuries, it was largely displaced by Spanish and evolved into some of the modern Nahuan languages in use today. Although classified as an extinct language, Classical Nahuatl has survived through a multitude of written sources transcribed by Nahua peoples and Spaniards in the Latin script.
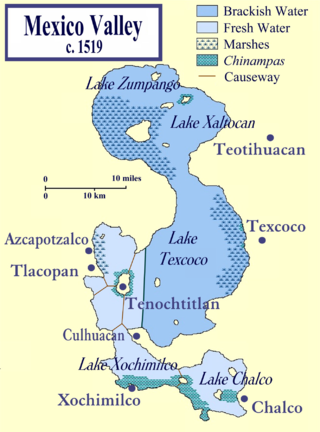
Tlacopan, also called Tacuba, was a Tepanec / Mexica altepetl on the western shore of Lake Texcoco. The site is today the neighborhood of Tacuba, in Mexico City.

The Tlaxcallans, or Tlaxcaltecs, are an indigenous Nahua people who originate from Tlaxcala, Mexico. The Confederacy of Tlaxcala was instrumental in overthrowing the Aztec Empire in 1521, alongside conquistadors from the Kingdom of Spain. The Tlaxcallans remained allies of the Spanish for 300 years until the Independence of Mexico in 1821.

Aztec society was a highly complex and stratified society that developed among the Aztecs of central Mexico in the centuries prior to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and which was built on the cultural foundations of the larger region of Mesoamerica. Politically, the society was organized into independent city-states, called altepetls, composed of smaller divisions (calpulli), which were again usually composed of one or more extended kinship groups. Socially, the society depended on a rather strict division between nobles and free commoners, both of which were themselves divided into elaborate hierarchies of social status, responsibilities, and power. Economically the society was dependent on agriculture, and also to a large extent on warfare. Other economically important factors were commerce, long-distance and local, and a high degree of trade specialization.

The Ramírez Codex, not to be confused with the Tovar Codex, is a post-conquest codex from the late 16th century entitled Relación del origen de los indios que hábitan esta Nueva España según sus Historias. The manuscript is named after the Mexican scholar José Fernando Ramírez, who discovered it in 1856 in the convent of San Francisco in Mexico City.

The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was a pivotal event in the history of the Americas, marked by the collision of the Aztec Triple Alliance and the Spanish Empire, ultimately reshaping the course of human history. Taking place between 1519 and 1521, this event saw the Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés, and his small army of European soldiers and numerous indigenous allies, overthrowing one of the most powerful empires in Mesoamerica.

Tlaxcala was a pre-Columbian city and state in central Mexico.

Alonso de Molina was a Franciscan priest and grammarian, who wrote a well-known dictionary of the Nahuatl language published in 1571 and still used by scholars working on Nahuatl texts in the tradition of the New Philology. He also wrote a bilingual confessional manual for priests who served in Nahuatl-speaking communities.

Fray Ángel María Garibay Kintana was a Mexican Roman Catholic priest, philologist, linguist, historian, and scholar of pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, specifically of the Nahua peoples of the central Mexican highlands. He is particularly noted for his studies and translations of conquest-era primary source documents written in Classical Nahuatl, the lingua franca of Postclassic central Mexico and the then-dominant Aztec empire. Alongside his former student Miguel León-Portilla, Garibay ranks as one of the pre-eminent Mexican authorities on the Nahuatl language and its literary heritage, and as one who has made a significant contribution towards the promotion and preservation of the indigenous cultures and languages of Mexico.

Xicotencatl I or Xicotencatl the Elder was a long-lived teuctli of Tizatlan, a Nahua altepetl (city-state) within the Confederacy of Tlaxcala, in what is now Mexico. According to one source, Xicotencatl was instrumental in allying the Tlaxcaltecs with the Spanish to overthrow the Aztec Empire.

The Mexica were a Nahuatl-speaking people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of the Triple Alliance, more commonly referred to as the Aztec Empire. The Mexica established Tenochtitlan, a settlement on an island in Lake Texcoco, in 1325. A dissident group in Tenochtitlan separated and founded the settlement of Tlatelolco with its own dynastic lineage. In 1521, their empire was overthrown by an alliance of Spanish conquistadors and rival indigenous nations, most prominently the Tlaxcaltecs. The Mexica were subjugated under the Spanish Empire for 300 years, until the Mexican War of Independence overthrew Spanish dominion in 1821. In the 21st century, the government of Mexico broadly classifies all Nahuatl-speaking peoples as Nahuas. While the Mexica no longer exist as a distinct group, aspects of Mexica language and culture still remain.
Xicotencatl II Axayacatl, also known as Xicotencatl the Younger, was a prince and warleader, probably with the title of Tlacochcalcatl, of the pre-Columbian state of Tlaxcala at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire.

Tizatlan, in pre-Columbian Mexico, was one of the four independent altepemeh that constituted the confederation of Tlaxcallan. Today Tizatlan is a part of the modern city of Tlaxcala, and the Pre-Columbian city is visible as a small archaeological site in the San Esteban Tizatlán district of the city. The site is in the state of Tlaxcala in central Mexico.

Ocotelolco, in pre-Columbian Mexico, was one of the four independent altepetl (polities) that constituted the confederation of Tlaxcallan. The site is in the present day state of Tlaxcala in central Mexico.

Tlatelolco was a pre-Columbian altepetl, or city-state, in the Valley of Mexico. Its inhabitants, known as the Tlatelolca, were part of the Mexica, a Nahuatl-speaking people who arrived in what is now central Mexico in the 13th century. The Mexica settled on an island in Lake Texcoco and founded the altepetl of Mexico-Tenochtitlan on the southern portion of the island. In 1337, a group of dissident Mexica broke away from the Tenochca leadership in Tenochtitlan and founded Mexico-Tlatelolco on the northern portion of the island. Tenochtitlan was closely tied with its sister city, which was largely dependent on the market of Tlatelolco, the most important site of commerce in the area.

Nahuatl, Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about 1.7 million Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller populations in the United States.
Chichimecatecuthli was a Tlaxcaltec nobleman and military man. He was a general of the armies of Tlaxcala during the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, in which he first warred against Hernán Cortés before allying with him along with his people. He belonged possibly to the faction of Ocotelolco.

















