Related Research Articles

The coconut tree is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus Cocos. The term "coconut" can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which botanically is a drupe, not a nut. The name comes from the old Portuguese word coco, meaning "head" or "skull", after the three indentations on the coconut shell that resemble facial features. They are ubiquitous in coastal tropical regions and are a cultural icon of the tropics.

Sweet corn, also called sugar corn and pole corn, is a variety of maize grown for human consumption with a high sugar content. Sweet corn is the result of a naturally occurring recessive mutation in the genes which control conversion of sugar to starch inside the endosperm of the corn kernel. Unlike field corn varieties grown for animal fodder, which are harvested when the kernels are dry and mature, sweet corn is picked when immature and prepared and eaten as a vegetable, rather than a grain. Since the process of maturation involves converting sugar to starch, sweet corn stores poorly and must be eaten fresh, canned, or frozen, before the kernels become tough and starchy.

Lodoicea, commonly known as the sea coconut, coco de mer, or double coconut, is a monotypic genus in the palm family. The sole species, Lodoicea maldivica, is endemic to the islands of Praslin and Curieuse in the Seychelles. It has the biggest seed in a plant. It formerly also was found on the small islets of St Pierre, Chauve-Souris, and Ile Ronde, all located near Praslin, but had become extinct there for a time until recently reintroduced. The name of the genus, Lodoicea, may be derived from Lodoicus, one Latinised form of Louis, in honour of King Louis XV of France. Other sources say that Lodoicea is from Laodice, the daughter of Priam and Hecuba.

Fusarium wilt is a common vascular wilt fungal disease, exhibiting symptoms similar to Verticillium wilt. This disease has been investigated extensively since the early years of this century. The pathogen that causes Fusarium wilt is Fusarium oxysporum. The species is further divided into formae speciales based on host plant.

Panama disease is a plant disease that infects banana plants. It is a wilting disease caused by the fungus Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc). The pathogen is resistant to fungicides and its control is limited to phytosanitary measures.
An F1 hybrid (also known as filial 1 hybrid) is the first filial generation of offspring of distinctly different parental types. F1 hybrids are used in genetics, and in selective breeding, where the term F1 crossbreed may be used. The term is sometimes written with a subscript, as F1 hybrid. Subsequent generations are called F2, F3, etc.

"Open pollination" and "open pollinated" refer to a variety of concepts in the context of the sexual reproduction of plants. Generally speaking, the term refers to plants pollinated naturally by birds, insects, wind, or human hands.
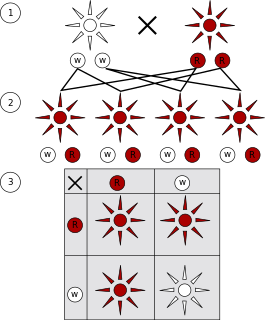
A monohybrid cross is a cross between two organisms with different variations at one genetic locus of interest. The character(s) being studied in a monohybrid cross are governed by two or multiple variations for a single location of a gene. To carry out such a cross, each parent is chosen to be homozygous or true breeding for a given trait (locus). When a cross satisfies the conditions for a monohybrid cross, it is usually detected by a characteristic distribution of second-generation (F2) offspring that is sometimes called the monohybrid ratio.

The Key lime is a citrus hybrid native to tropical Southeast Asia. It has a spherical fruit, 25–50 mm (1–2 in) in diameter. The Key lime is usually picked while it is still green, but it becomes yellow when ripe.

Chamaerops is a genus of flowering plants in the family Arecaceae. The only currently fully accepted species is Chamaerops humilis, variously called European fan palm or the Mediterranean dwarf palm. It is one of the most cold-hardy palms and is used in landscaping in temperate climates.

Lethal yellowing (LY) is a phytoplasma disease that attacks many species of palms, including some commercially important species such as the coconut and date palm. In the Caribbean it is spread by the planthopper Haplaxius crudus which is native to Florida, parts of the Caribbean, parts of Australia and Central America. The only effective cure is prevention, i.e. planting resistant varieties of coconut palm and preventing a park-like or golf-course-like environment which attracts the planthopper. Some cultivars, such as the Jamaica Tall coconut cultivar, nearly died out because of lethal yellowing. Heavy turf grasses and similar green ground cover attracts the planthopper to lay its eggs there, and the nymphs develop at the roots of these grasses. The planthoppers' eggs and nymphs can pose a great threat to coconut-growing countries' economies, especially ones into which grass seeds for golf courses and lawns are imported from the Americas.
Hybrid rice is a type of Asian rice that has been crossbred from two very different parent varieties. As with other types of hybrids, hybrid rice typically displays heterosis or "hybrid vigor", so when grown under the same conditions as comparable purebred rice varieties, it can produce up to 30% more yield. To produce hybrid seeds in large quantity, a purebred sterile rice variety is fertilized with fertile pollen from a different variety. High-yield crops, including hybrid rice, are one of the most important tools for combatting worldwide food crises.

Phytelephas seemannii, commonly called Panama ivory palm, is a species of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. It is one of the plants used for vegetable ivory.
Dwarf coconut is a range of varieties of coconut palm. The use of the word “dwarf” here does not refer to the tree's size, as it can reach heights of 50–100 feet which is certainly not a dwarf. Instead, the dwarf designation refers to the size in which it will begin to produce the coveted or harvestable coconut.

Roystonea regia, commonly known as the Cuban royal palm or Florida royal palm, is a species of palm that is native to Mexico, parts of Central America and the Caribbean, and southern Florida. A large and attractive palm, it has been planted throughout the tropics and subtropics as an ornamental tree. Although it is sometimes called R. elata, the conserved name R. regia is now the correct name for the species. The royal palm reaches heights from 50 to over 80 feet tall. Populations in Cuba and Florida were long seen as separate species, but are now considered a single species.

Ulmus 'Morfeo' is a hybrid elm cultivar raised by the Istituto per la Protezione delle Piante (IPP), Florence, in 2000. 'Morfeo' arose from a crossing of the Dutch hybrid clone '405' and the Chenmou Elm, the latter a small tree from the provinces of Anhui and Jiangsu in eastern China, The '405' clone is a full sister of 'Groeneveld', a crossing of an English U. × hollandica and a French U. minor from the Barbier Nursery, Orléans.
Cadang-cadang is a disease caused by Coconut cadang-cadang viroid (CCCVd), a lethal viroid of coconut, African oil palm, anahaw, and buri palms. The name cadang-cadang comes from the word gadang-gadang that means dying in Bicol. It was originally reported on San Miguel Island in the Philippines in 1927/1928. "By 1962, all but 100 of 250,000 palms on this island had died from the disease," indicating an epidemic. Every year one million coconut palms are killed by CCCVd and over 30 million coconut palms have been killed since Cadang-cadang was discovered. CCCVd directly affects the production of copra, a raw material for coconut oil and animal feed. Total losses of about 30 million palms and annual yield losses of about 22,000 tons of copra have been attributed to Cadang-cadang disease in the Philippines.

Elaeis guineensis is a species of palm commonly just called oil palm but also sometimes African oil palm or macaw-fat. It is the principal source of palm oil. It is native to west and southwest Africa, specifically the area between Angola and the Gambia; the species name, guineensis, refers to the name for the area, Guinea, and not the modern country now bearing that name. The species is also now naturalised in Madagascar, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Indonesia, Central America, Cambodia, the West Indies, and several islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. The closely related American oil palm Elaeis oleifera and a more distantly related palm, Attalea maripa, are also used to produce palm oil.
Haplaxius crudus is a planthopper species in the genus Haplaxius.
Starmaya is an F1 hybrid coffee tree that can be propagated by seed rather than through somatic embryogenesis (SE). It was propagated from a parent plant that is male-sterile. This facilitates controlled pollination because breeders do not have to manually castrate each individual flower of the autogamous coffee tree.
References
- ↑ Centre for Information on Coconut Lethal Yellowing (CICLY) Archived 2009-06-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Harries, H.C. & Romney, D.H. (1974) Maypan: an F1 hybrid coconut variety for commercial production in Jamaica. World Crops 26, 110-111. (Reprinted: The Farmer 79(3) 57-60, 1974).
- ↑ P.K. Thampan. 1981. Handbook on Coconut Palm. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co.