
Gulf Islands National Park Reserve is a national park located on and around the Gulf Islands in British Columbia, Canada. In the National Parks System Plan, this park provides representation of the Strait of Georgia Lowlands natural region, the only place in Canada with a Mediterranean climate of dry, sunny summers and mild, wet winters, the result of a rain shadow effect from surrounding mountains between the region and the ocean. It has similar dominant vegetation as the Pacific Northwest, such as coastal Douglas-fir, western red cedar, shore pine, Pacific dogwood, bigleaf maple, and red alder, but also contains the northern extent of some of the more drought tolerant trees such as Garry oak and Arbutus. The park was created in 2003 as the fortieth national park. It covers 36 square kilometres (14 sq mi) of area on 16 islands and more than 30 islets, reefs and surrounding waters, making it the sixth smallest national park in Canada.

The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. As of 2021, it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.

Tallgrass Prairie National Preserve is a United States National Preserve located in the Flint Hills region of Kansas, north of Strong City. The preserve protects a nationally significant example of the once vast tallgrass prairie ecosystem. Of the 400,000 square miles (1,000,000 km2) of tallgrass prairie that once covered the North American continent, less than 5% remains, primarily in the Flint Hills. Since 2009, the preserve has been home to the Tallgrass Prairie bison herd.
Goose Island is one of the San Juan Islands in San Juan County, Washington, United States.

The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the Revolutionary War, the War of 1812, and the American Civil War, through the acquisition of battlefield land. The American Battlefield Trust was formerly known as the Civil War Trust. On May 8, 2018, the organization announced the creation of the American Battlefield Trust as the umbrella organization for two divisions, the Civil War Trust and the Revolutionary War Trust, which was formerly known as "Campaign 1776".

The National Wilderness Preservation System (NWPS) of the United States protects federally managed wilderness areas designated for preservation in their natural condition. Activity on formally designated wilderness areas is coordinated by the National Wilderness Preservation System. Wilderness areas are managed by four federal land management agencies: the National Park Service, the U.S. Forest Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and the Bureau of Land Management.

Malpai Borderlands is a land area along the U.S.-Mexico border. It encompasses the southeast corner of Arizona and the southwest corner of New Mexico. It is sometimes defined as including areas in the Mexican states of Chihuahua and Sonora. The Malpai is part of the Madrean Region which includes the arid and semi-arid borderlands of the United States and Mexico from California to Texas.

The Wilderness Society is an American non-profit land conservation organization that is dedicated to protecting natural areas and federal public lands in the United States. They advocate for the designation of federal wilderness areas and other protective designations, such as for national monuments. They support balanced uses of public lands, and advocate for federal politicians to enact various land conservation and balanced land use proposals. The Wilderness Society also engages in a number of ancillary activities, including education and outreach, and hosts one of the most valuable collections of Ansel Adams photographs at their headquarters in Washington, D.C.

Lummi Island lies at the southwest corner of Whatcom County, Washington, United States, between the mainland part of the county and offshore San Juan County. The Lummi Indian Reservation is situated on a peninsula east of the island, but it does not include Lummi Island. The island has a land area of 23.97 square kilometres and had a population of 822 as of the 2000 census. The population nearly doubles in summer when second-home owners from Canada and the U.S. arrive for the summer months.

Perryville Battlefield State Historic Site is a 745-acre (3.01 km2) park near Perryville, Kentucky. The park continues to expand with purchases of parcels by the Office of Kentucky Nature Preserves' Kentucky Heritage Land Conservation Fund and the American Battlefield Trust. An interpretive museum is located near the site where many Confederate soldiers killed in the Battle of Perryville were buried. Monuments, interpretive signage, and cannons also mark notable events during the battle. The site became part of the Kentucky State Park System in 1936.
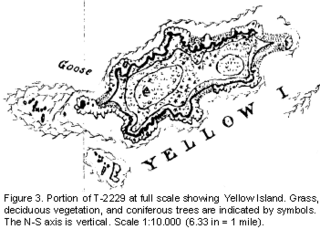
Yellow Island, one of the San Juan Islands, is an 11-acre (4.5 ha) island, located south-west of Orcas Island, and north of Shaw Island, near Jones Island State Park, in San Juan County, Washington, United States. The island is home to a wide array of flora and fauna, including over 50 species of wildflowers, bald eagles, harbor seals, black oystercatchers, and harlequin ducks. The island was purchased in 1979 by The Nature Conservancy, and is administered as a nature preserve.

Rancho San José y Sur Chiquito was a 8,876-acre (35.92 km2) Mexican land grant in present-day Big Sur, in Monterey County, California, given in 1835 to Teodoro Gonzalez and re-granted by Governor Juan Alvarado the same year to Marcelino Escobar. The grant, including Point Lobos, was located south of the Carmel River, extending inland along the coastal mountains, and south along the Pacific coast. It included San Jose Creek, Malpaso Creek, Soberanes Creek, Tres Pinos Creek, Garrapata Creek, and ended on the north side of Palo Colorado Canyon. A hand-drawn map created c. 1853 accompanying the grant indicated a road or trail was already present along the coast.
The San Juan Preservation Trust is a private, non-profit and membership-based land trust dedicated to helping people and communities conserve land on the San Juan Islands in Washington state. Noted for its $6.4 million purchase of Vendovi Island in 2010 and its $18.5 million acquisition of Turtleback Mountain on Orcas Island in 2006, the Preservation Trust has permanently protected 270 properties, 38 miles of shoreline and 16,000 acres on 20 islands, including land now managed as public parks, nature preserves, wildlife habitat, and working farms and forests. The organization was founded in 1979. The first transaction of the trust was made by Ernest K. Gann and Dodie Post Gann in 1980, when they donated 38 acres of their farm as a working agriculture preserve.
Beatriz Del Cueto López-Hidalgo is a Cuban-born architect specialising in conservation and architectural preservation. A resident of Puerto Rico since 1960, del Cueto is a Fellow of the American Academy in Rome, Fellow of the American Institute of Architects, and Henry Klumb Award winner in 2012.
The Wildlands Conservancy is a nonprofit organization with a mission to preserve land for public recreation. It manages 25 preserves, detailed in the list of its preserves, covering over 200,000 acres (81,000 ha) across the western United States. The preserve system encompasses diverse landscapes including mountains, valleys, deserts, rivers, and oceanfront lands. The Wildlands Conservancy buys and restores land, builds public visitor facilities, and provides outdoor education programs for children. All usage is free of charge, attracting over 1.5 million visitors annually.

Strawberry Island is an uninhabited island in the Niagara River located in Erie County, New York, southeast of Grand Island. The five-acre (2 ha) island is owned by the New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation and is managed as a fish and wildlife preserve.

The Big Sur Land Trust is a private 501(c)(3) non-profit located in Monterey, California, that has played an instrumental role in preserving land in California's Big Sur and Central Coast regions. The trust was the first to conceive of and use the "conservation buyer" method in 1989 by partnering with government and developers to offer tax benefits as an inducement to sell land at below-market rates. Since 1978, with the support of donors, funders and partners, it has conserved over 40,000 acres through conservation easements, acquisition and transfer of land to state, county and city agencies. It has placed conservation easements on 7,000 acres and has retained ownership of over 4,000 acres.

The Santa Lucia Preserve or The Preserve is a private, 20,000 acres (8,100 ha) gated development permitting 297 homesites. It is located in the foothills of the Santa Lucia Range between Palo Corona Regional Park and Carmel Valley, California. The Preserve consists of a 12,000 acres (4,900 ha) nature reserve, 8,000 acres (3,200 ha) of open land, and 2,000 acres (810 ha) for development. It contains most of the watershed of Las Garzas Creek, a tributary of the Carmel River.
The Maine Coast Heritage Trust is a nonprofit land conservation organization. Its conservation partner is the Maine Land Trust Network, which is one of its programs.

The Palo Corona Regional Park is a 4,500 acres (1,800 ha) park owned by the Monterey Peninsula Regional Park District on land east of Big Sur Coast Highway and Garrapata State Park in California. The 9,898 acres (4,006 ha) property stretches southeast about 11 miles (18 km) from the near the Carmel River State Beach to the Los Padres National Forest. The park is long from north to south, bordered on the northwest by Highway 1 and across from Carmel River State Beach. It wraps around Point Lobos Ranch and abuts Santa Lucia Preserve to the east. In the middle, it is sandwiched by Mitteldorf Preserve and Garrapata State Park. Its southern border abuts Joshua Creek Canyon Ecological Reserve. Environmental interests were concerned that it would be converted to an estate-type development like that done for Rancho San Carlos. In May 2002, the Big Sur Land trust and The Nature Conservancy joined to buy the Ranch. Overall, the park directly and indirectly connects nine conservation properties preserved for their biological, recreation and scenic values. The area includes the former Rancho Caňada Country Club and golf course in Carmel Valley.















