In reliability theory and reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings:
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a mechanical or electronic system, during normal system operation. MTBF can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (average) time between failures of a system. The term is used for repairable systems, while mean time to failure (MTTF) denotes the expected time to failure for a non-repairable system.

The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure, and supporting utilities in industrial, business, governmental, and residential installations. Over time, this has come to include multiple wordings that describe various cost-effective practices to keep equipment operational; these activities take place either before or after a failure.
Customer support is a range of customer services to assist customers in making cost effective and correct use of a product. It includes assistance in planning, installation, training, troubleshooting, maintenance, upgrading, and disposal of a product.
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes dependability in the lifecycle management of a product. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time.
Integrated logistic support (ILS) is an integrated and iterative process for developing materiel and a support strategy that optimizes functional support, leverages existing resources, and guides the system engineering process to quantify and lower life cycle cost and decrease the logistics footprint, making the system easier to support. Although originally developed for military purposes, it is also widely used in commercial product support or customer service organisations.
Mean time to repair (MTTR) is a basic measure of the maintainability of repairable items. It represents the average time required to repair a failed component or device. Expressed mathematically, it is the total corrective maintenance time for failures divided by the total number of corrective maintenance actions for failures during a given period of time. It generally does not include lead time for parts not readily available or other Administrative or Logistic Downtime (ALDT).

Aircraft maintenance checks are periodic inspections that have to be done on all commercial and civil aircraft after a certain amount of time or usage. Military aircraft normally follow specific maintenance programmes which may, or may not, be similar to those of commercial and civil operators.
High availability (HA) is a characteristic of a system, which aims to ensure an agreed level of operational performance, usually uptime, for a higher than normal period.
The term downtime is used to refer to periods when a system is unavailable. Downtime or outage duration refers to a period of time that a system fails to provide or perform its primary function. Reliability, availability, recovery, and unavailability are related concepts. The unavailability is the proportion of a time-span that a system is unavailable or offline. This is usually a result of the system failing to function because of an unplanned event, or because of routine maintenance.

Portable appliance testing is the name of a process in the United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland, New Zealand and Australia by which electrical appliances are routinely checked for safety. The formal term for the process is "in-service inspection & testing of electrical equipment". Testing involves a visual inspection of the equipment and any flexible cables for good condition, and also where required, verification of earthing (grounding) continuity, and a test of the soundness of insulation between the current carrying parts, and any exposed metal that may be touched. The formal limits for pass/fail of these electrical tests vary somewhat depending on the category of equipment being tested.
In the strictest legal sense a warranty of any kind within the United States must adhere to guidelines set at the states' and federal government's levels. A home warranty is a contract that agrees to provide you with discounted repair and replacement services. However, the words "home warranty" are not always used explicitly to mean a legal warranty is being conveyed. In many cases, at least in the United States, a home warranty is not a warranty at all, but rather a home service contract that covers the repair and/or replacement costs of home appliances, major systems such as heating and cooling, and possibly other components of a home, structural or otherwise. The home service contract generally covers home systems such as the home’s plumbing or electrical, and appliances like dishwashers that fail from old age/normal wear and tear. Coverage varies significantly across home warranty companies.
Healthcare Technology Management is a term for the professionals who manage operations, analyze and improve utilization and safety, and support servicing healthcare technology. These healthcare technology managers are, much like other healthcare professionals referred to by various specialty or organizational hierarchy names.
A prediction of reliability is an important element in the process of selecting equipment for use by telecommunications service providers and other buyers of electronic equipment, and it is essential during the design stage of engineering systems life cycle. Reliability is a measure of the frequency of equipment failures as a function of time. Reliability has a major impact on maintenance and repair costs and on the continuity of service.
Availability is the probability that a system will work as required when required during the period of a mission. The mission could be the 18-hour span of an aircraft flight. The mission period could also be the 3 to 15-month span of a military deployment. Availability includes non-operational periods associated with reliability, maintenance, and logistics.
Maintenance Philosophy is the mix of strategies that ensure an item works as expected when needed.
RAMP Simulation Software for Modelling Reliability, Availability and Maintainability (RAM) is a computer software application developed by WS Atkins specifically for the assessment of the reliability, availability, maintainability and productivity characteristics of complex systems that would otherwise prove too difficult, cost too much or take too long to study analytically. The name RAMP is an acronym standing for Reliability, Availability and Maintainability of Process systems.
Design for Availability is the design process for a system targeting availability of the system for guarantying readiness as the major part of goal specification. This design is generally used toward availability based contracts. Design for availability means that design process should start by given parameters of requirement space and maps them to design parameter space. However, the conventional trial and error of parameters set followed by sensitivity analysis might end to the same result area in the design plane.
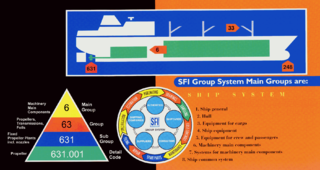
The SFI Group System is the most widely used classification system for the maritime and offshore industry worldwide. It is an international standard, which provides a functional subdivision of technical and financial ship or rig information.
Eight dimensions of product quality management can be used at a strategic level to analyze quality characteristics. The concept was defined by David A. Garvin, formerly C. Roland Christensen Professor of Business Administration at Harvard Business School. Some of the dimensions are mutually reinforcing, whereas others are not—improvement in one may be at the expense of others. Understanding the trade-offs desired by customers among these dimensions can help build a competitive advantage.



