Related Research Articles
Center for Democracy & Technology (CDT) is a Washington, D.C.–based 501(c)(3) nonprofit organisation that advocates for digital rights and freedom of expression. CDT seeks to promote legislation that enables individuals to use the internet for purposes of well-intent, while at the same time reducing its potential for harm. It advocates for transparency, accountability, and limiting the collection of personal information.
Computer Professionals' Union is a mass organization of information and communications technology (ICT) professionals, practitioners, and workers in the Philippines. It is registered in the Philippines as a non-stock, non-profit, non-government organization that promotes activist ICT principles and organize ICT professionals to provide ICT services to Filipino people. Their office is located at Quezon City and their current National Coordinator is Rick Bahague.

European Digital Rights (EDRi) is an international advocacy group headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. EDRi is a network collective of non-profit organizations (NGO), experts, advocates and academics working to defend and advance digital rights across the continent. As of October 2022, EDRi is made of more than 40 NGOs, as well as experts, advocates and academics from all across Europe.

Free Press is a United States advocacy group that is part of the media reform or media democracy movement. Their mission includes, "saving Net Neutrality, achieving affordable internet access for all, uplifting the voices of people of color in the media, challenging old and new media gatekeepers to serve the public interest, ending unwarranted surveillance, defending press freedom and reimagining local journalism." The group is a major supporter of net neutrality.
In the United States, internet censorship is the suppression of information published or viewed on the Internet in the United States. The First Amendment of the United States Constitution protects freedom of speech and expression against federal, state, and local government censorship.

Michael Wayne Godwin is an American attorney and author. He was the first staff counsel of the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), and he created the Internet adage Godwin's law and the notion of an Internet meme. From July 2007 to October 2010, he was general counsel for the Wikimedia Foundation. In March 2011, he was elected to the Open Source Initiative board. Godwin has served as a contributing editor of Reason magazine since 1994. In April 2019, he was elected to the Internet Society board. From 2015 to 2020, he was general counsel and director of innovation policy at the R Street Institute. In August 2020, he and the Blackstone Law Group filed a lawsuit against the Trump administration on behalf of the employees of TikTok, and worked there between June 2021 and June 2022. Since October 2022, he has worked as the policy and privacy lead at Anonym.
Public Knowledge is a non-profit Washington, D.C.–based public interest group. Founded in 2001 by David Bollier, Gigi Sohn, and Laurie Racine, Public Knowledge is primarily involved in the fields of intellectual property law, competition and choice in the digital marketplace, and an open standards/end-to-end internet.

Access Now is a non-profit organization founded in 2009 with a mission to defend and extend the digital civil rights of people around the world. Access Now supports programs including an annual conference on Human Rights (RightsCon), an index of internet shutdowns (#KeepItOn), and providing exit nodes for Tor network.
Fandom Forward is a nonprofit organization that was initially run by Harry Potter fans but that has since expanded to include members of various fandoms. It was founded by Andrew Slack in 2005 to draw attention to human rights violations in Sudan. Since then, the organization's campaigns have focused on topics such as literacy, United States immigration reform, economic justice, LGBT rights, sexism, labor rights, mental health, body image, and climate change. They have received recognition from many popular figures in the Harry Potter community and have been the subject of multiple academic studies on fan activism and civic engagement among youth.

Sascha Meinrath is an American policy activist and educator. He is currently the Palmer Chair in Telecommunications at Penn State University.

The Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) was a proposed United States congressional bill to expand the ability of U.S. law enforcement to combat online copyright infringement and online trafficking in counterfeit goods. Introduced on October 26, 2011, by Representative Lamar Smith (R-TX), provisions included the requesting of court orders to bar advertising networks and payment facilities from conducting business with infringing websites, and search engines from linking to the websites, and court orders requiring Internet service providers to block access to the websites. The proposed law would have expanded existing criminal laws to include unauthorized streaming of copyrighted content, imposing a maximum penalty of five years in prison.

The Online Protection and Enforcement of Digital Trade Act is a bill introduced in the United States Congress proposed as an alternative to the Stop Online Piracy Act and PROTECT IP Act, by Senator Ron Wyden of Oregon, a Democrat, and Representative Darrell Issa of California, a Republican. The text of the bill is available for public comment at keepthewebopen.com.
There were different but similar copyright bills in the 112th United States Congress: The Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) in the House of Representatives and the PROTECT IP Act (PIPA) in the Senate. A typical route for legislation like this is to pass some version in both houses, then refer the two bills to a conference committee, which would produce a single bill likely to pass both houses.
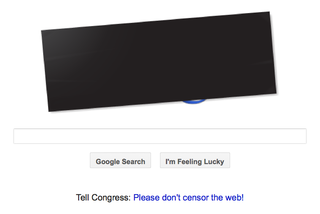
On January 18, 2012, a series of coordinated protests occurred against two proposed laws in the United States Congress—the Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) and the PROTECT IP Act (PIPA). These followed smaller protests in late 2011. Protests were based on concerns that the bills, intended to provide more robust responses to copyright infringement arising outside the United States, contained measures that could possibly infringe online freedom of speech, websites, and Internet communities. Protesters also argued that there were insufficient safeguards in place to protect sites based upon user-generated content.

The Internet Defense League is an organization and network launched in March 2012 with the aim of organizing protests and other responses to perceived threats to Internet freedom and the open Internet. It was formed following the protests against SOPA and PIPA. It had 30,000 members as of 2013, consisting of organizations, websites, and individuals.

Move Your Domain Day was an annual observance encouraging owners of domain names to transfer their domain registration away from registrars that supported the Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA). It was first held on 29 December 2011, the idea coming from a post on Reddit as a protest against prominent registrar GoDaddy's support for SOPA. In 2012, rival registrar Namecheap began an initiative to make Move Your Domain Day an annual event. Subsequent events were held on 22 January 2013, 5 February 2014, 27 January 2015, 2 February 2016, and 6 March 2018. The Electronic Frontier Foundation, Reddit, and domain registrars Name.com and Hover have also participated. Namecheap has defined the initiative as "an annual protest and a commemoration of sorts that will continue to shine a light on the issue of a free and open internet". There have been no major Move Your Domain Day events since 2018.
Fight for the Future is a nonprofit advocacy group in the area of digital rights founded in 2011. The group aims to promote causes related to copyright legislation, as well as online privacy and censorship through the use of the Internet.
Demand Progress is an internet activist-related entity encompassing a 501(c)4 arm sponsored by the Sixteen Thirty Fund and a 501(c)(3) arm sponsored by the New Venture Fund. It specializes in online-intensive and other grassroots activism to support Internet freedom, civil liberties, transparency, and human rights, and in opposition to censorship and corporate control of government. The organization was founded through a petition in opposition to the Combating Online Infringement and Counterfeits Act, sparking the movement that eventually defeated COICA's successor bills, the Stop Online Piracy Act and the PROTECT IP Act, two highly controversial pieces of United States legislation.

Internet Slowdown Day, part of the "Battle for the Net" initiative, was a series of protests against the repeal of net neutrality laws coordinated by websites and advocacy groups in the United States occurring on September 10, 2014. The official site explains: "On September 10th, sites across the web will display an alert with a symbolic 'loading' symbol and promote a call to action for users to push comments to the FCC, Congress, and the White House."
References
- 1 2 "Advocacy in the New World of Policy Influence". Arabella Advisors. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ "Media Democracy Fund-2006 Grants | Grantmakers in Film and Electronic Media". Old.gfem.org. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ Laura Vitto (2014-11-11). "Tumblr taps artists to design shirts for net neutrality". Mashable.com. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ "Worcester's Fight for the Future helped ignite an Internet revolt against antipiracy bills - Metro". The Boston Globe. 2012-01-27. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ "How We Won Net Neutrality | Craig Aaron". Huffingtonpost.com. 2015-02-26. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ Jessica Meyers (2015-02-19). "Outsider group from Massachusetts helped shift the net neutrality fight - Nation". The Boston Globe. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ Carl Franzen (2012-01-20). "How The Web Killed SOPA and PIPA". Talkingpointsmemo.com. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ "MAG-NetAbout". MAG-Net. 2014-06-20. Retrieved 2015-03-09.
- ↑ "Sub Funds". Mediademocracyfund.org. Retrieved 2015-03-09.