Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include sinus infections, poor growth, fatty stool, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms.

A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that has grouped together to form a sac ; however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, sometimes a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location.

An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. Often they cause no symptoms. Occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. The majority of cysts are harmless. If the cyst either breaks open or causes twisting of the ovary, it may cause severe pain. This may result in vomiting or feeling faint.
Postalveolar consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the back of the alveolar ridge, farther back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself but not as far back as the hard palate, the place of articulation for palatal consonants. Examples of postalveolar consonants are the English palato-alveolar consonants, as in the words "ship", "'chill", "vision", and "jump", respectively.

The labialized palatal approximant, also called the labial–palatal or labio-palatal approximant, is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. It has two constrictions in the vocal tract: with the tongue on the palate, and rounded at the lips. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɥ⟩, a rotated lowercase letter ⟨h⟩, or occasionally ⟨jʷ⟩, since it is a labialized.
The voiced palatal approximant is a type of consonant used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨j⟩. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is j, and in the Americanist phonetic notation it is ⟨y⟩. Because the English name of the letter J, jay, does not start with but with, this approximant is sometimes called yod instead, as in the phonological history terms yod-dropping and yod-coalescence.

In phonetics, alveolo-palatal consonants, sometimes synonymous with pre-palatal consonants, are intermediate in articulation between the coronal and dorsal consonants, or which have simultaneous alveolar and palatal articulation. In the official IPA chart, alveolo-palatals would appear between the retroflex and palatal consonants but for "lack of space". Ladefoged and Maddieson characterize the alveolo-palatals as palatalized postalveolars (palato-alveolars), articulated with the blade of the tongue behind the alveolar ridge and the body of the tongue raised toward the palate, whereas Esling describes them as advanced palatals (pre-palatals), the furthest front of the dorsal consonants, articulated with the body of the tongue approaching the alveolar ridge. These descriptions are essentially equivalent, since the contact includes both the blade and body of the tongue. They are front enough that the fricatives and affricates are sibilants, the only sibilants among the dorsal consonants.
The palatal lateral flap is a rare type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. There is no dedicated symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound. However, the symbol for a palatal lateral approximant with a breve denoting extra-short ⟨ʎ̆⟩ may be used.

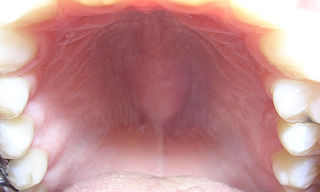
The nasopalatine duct cyst (NPDC) occurs in the median of the palate, usually anterior to first molars. It often appears between the roots of the maxillary central incisors. Radiographically, it may often appear as a heart-shaped radiolucency. It is usually asymptomatic, but may sometimes produce an elevation in the anterior portion of the palate. It was first described by Meyer in 1914.
Dental pertains to the teeth, including dentistry. Topics related to the dentistry, the human mouth and teeth include:
The voiceless palatal affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represent this sound are ⟨c͡ç⟩ and ⟨c͜ç⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is c_C. The tie bar may be omitted, yielding ⟨cç⟩ in the IPA and cC in X-SAMPA.
Cutaneous columnar cysts are a cutaneous condition, a group of different cysts lined by columnar epithelium. Types of cysts included in this group are:
Median raphe cysts are a cutaneous condition of the penis due to developmental defects near the glans.
Palatal consonants are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate. Consonants with the tip of the tongue curled back against the palate are called retroflex.
Gilmoremys is an extinct genus of softshell turtle which lived during the late Cretaceous of North Dakota, Montana and Wyoming, United States.
Odontogenic cyst are a group of jaw cysts that are formed from tissues involved in odontogenesis. Odontogenic cysts are closed sacs, and have a distinct membrane derived from rests of odontogenic epithelium. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. Intra-bony cysts are most common in the jaws, because the mandible and maxilla are the only bones with epithelial components. That odontogenic epithelium is critical in normal tooth development. However, epithelial rests may be the origin for the cyst lining later. Not all oral cysts are odontogenic cyst. For example, mucous cyst of the oral mucosa and nasolabial duct cyst are not of odontogenic origin.
In addition, there are several conditions with so-called (radiographic) 'pseudocystic appearance' in jaws; ranging from anatomic variants such as Stafne static bone cyst, to the aggressive aneurysmal bone cyst.
A cyst is a pathological epithelial lined cavity that fills with fluid or soft material and usually grows from internal pressure generated by fluid being drawn into the cavity from osmosis. The bones of the jaws, the mandible and maxilla, are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body. This is due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm, and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during odontogenesis. The bones of the jaws develop from embryologic processes which fuse together, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammation is thought to be a major factor. The high prevalence of tooth impactions and dental infections that occur in the bones of the jaws is also significant to explain why cysts are more common at these sites.
A median mandibular cyst is a type of cyst that occurs in the midline of the mandible, thought to be created by proliferation and cystic degeneration of resting epithelial tissue that is left trapped within the substance of the bone during embryologic fusion of the two halves of the mandible, along the plane of fusion later termed the symphysis menti. A true median mandibular cyst would therefore be classified as a non-odontogenic, fissural cyst. The existence of this lesion as a unique clinical entity is controversial, and some reported cases may have represented misdiagnosed odontogenic cysts, which are by far the most common type of intrabony cyst occurring in the jaws. It has also been suggested that the mandible develops as a bilobed proliferation of mesenchyme connected with a central isthmus. Therefore, it is unlikely that epithelial tissue would become trapped as there is no ectoderm separating the lobes in the first instance.

The human abdomen is divided into regions by anatomists and physicians for purposes of study, diagnosis, and therapy. In the four-region scheme, four quadrants allow localisation of pain and tenderness, scars, lumps, and other items of interest, narrowing in on which organs and tissues may be involved. The quadrants are referred to as the left lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, right upper quadrant and right lower quadrant, as follows below. These terms are not used in comparative anatomy, since most other animals do not stand erect.

Gingival cyst is a type of cysts of the jaws that originates from the dental lamina and is found in the mouth parts. It is a superficial cyst in the alveolar mucosa. It can be seen inside the mouth as small and whitish bulge. Depending on the ages in which they develop, the cysts are classified into gingival cyst of newborn and gingival cyst of adult. Structurally, the cyst is lined by thin epithelium and shows a lumen usually filled with desquamated keratin, occasionally containing inflammatory cells. The nodes are formed as a result of cystic degeneration of epithelial rests of the dental lamina.