| Medirigiriya Vatadage | |
|---|---|
මැදිරිගිරිය වටදාගෙය | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Geographic coordinates | 8°9′22″N80°59′45″E / 8.15611°N 80.99583°E |
Medirigiriya Vatadageya is a Buddhist structure (Vatadage) in Medirigiriya, Sri Lanka.
| Medirigiriya Vatadage | |
|---|---|
මැදිරිගිරිය වටදාගෙය | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Geographic coordinates | 8°9′22″N80°59′45″E / 8.15611°N 80.99583°E |
Medirigiriya Vatadageya is a Buddhist structure (Vatadage) in Medirigiriya, Sri Lanka.
Constructed during the Anuradhapura era. [1] , this is believed to be the ancient Mandalagiraka Vihara to which King Kanittha Tissa added an Uposathaghara (a chapter house). [2] [3]
The site was documented in 3D in 2019 by the Zamani Project. [4]

Poḷonnaruwa, also referred as Pulathisipura and Vijayarajapura in ancient times, is the main town of Polonnaruwa District in North Central Province, Sri Lanka. The modern town of Polonnaruwa is also known as New Town, and the other part of Polonnaruwa remains as the royal ancient city of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa.

Tourism in Sri Lanka faces many challenges, including the ongoing economic and political crisis. In 2018, tourist arrivals peaked at 2.5 million, who spent a total of US$ 5.6 billion in the country. However, the COVID-19 pandemic caused tourist numbers to decrease by 92% in 2020. As of 2022, tourist numbers have not rebounded from the pre-crisis high. The government is attempting to attract foreign investment in the country's tourism industry, which began in earnest after the end of the Sri Lankan Civil War in 2009.

Buddhist religious architecture developed in the Indian subcontinent. Three types of structures are associated with the religious architecture of early Buddhism: monasteries (viharas), places to venerate relics (stupas), and shrines or prayer halls, which later came to be called temples in some places.

Thuparamaya is the earliest documented Buddhist temple in Sri Lanka. Its building dates to the arrival of Mahinda Thera (Mahindagamanaya) and the introduction of Buddhism to the island.
Atamasthana or Eight sacred places are a series of locations in Sri Lanka where the Buddha had visited during his three visits to the country. The sacred places are known as Jaya Sri Maha Bodhiya, Ruwanwelisaya, Thuparamaya, Lovamahapaya, Abhayagiri Dagaba, Jetavanarama, Mirisaveti Stupa and Lankarama. They are situated in Anuradhapura, the capital of the ancient Anuradhapura Kingdom.

The architecture of ancient Sri Lanka displays a rich diversity, varying in form and architectural style from the Anuradhapura Kingdom through the Kingdom of Kandy (1469–1815). Sinhalese architecture also displays many ancient North Indian influences. Buddhism had a significant influence on Sri Lankan architecture after it was introduced to the island in the 3rd century BC, and ancient Sri Lankan architecture was mainly religious, with more than 25 styles of Buddhist monasteries. Significant buildings include the stupas of Jetavanaramaya and Ruwanvelisaya in the Anuradhapura kingdom and further in the Polonnaruwa Kingdom. The palace of Sigiriya is considered a masterpiece of ancient architecture and ingenuity, and the fortress in Yapahuwa and the Temple of the tooth in Kandy are also notable for their architectural qualities. Ancient Sri Lankan architecture is also significant to sustainability, notably Sigiriya which was designed as an environmentally friendly structure.

Stupas, also called dagebas and cetiyas, are considered an outstanding type of architectural creation of ancient Sri Lanka. Under the influence of Buddhism, there were several changes in the field of architecture in Sri Lanka. The stupa commands a prominent place among these changes. The Stupa is also known by synonymous names such as Chaithya, Dagaba, Thupa, Seya and Vehera. Stupas designed and constructed in Sri Lanka are the largest brick structures known to the pre-modern world.
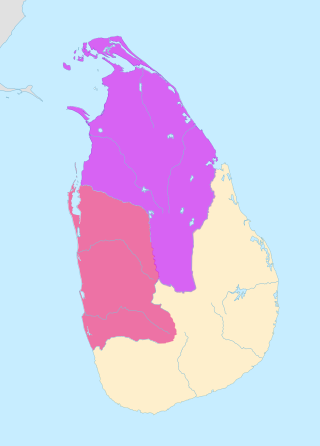
The Kingdom of Polonnaruwa was the Sinhalese kingdom that expanded across the island of Sri Lanka and several overseas territories, from 1070 until 1232. The kingdom started expanding its overseas authority during the reign of Parakramabahu the Great.

Polonnaruwa District is one of the 25 districts of Sri Lanka, the second level administrative division of the country. It is also one of the two districts of North Central Province and has an area of 3,293 km2.

Bogambara Prison was a maximum security prison and the second largest prison in the country after Welikada Prison in Colombo, Sri Lanka. After operating for 138 years, the prison was closed on 1 January 2014, and the inmates were transferred to the new Dumbara prison complex in Pallekele. In 2019, the government declared the prison site would become a cultural tourism centre, the Bogambara Cultural Park.
Belilena Cave is a cave in Sri Lanka, located 8 km (5.0 mi) from the town of Kitulgala. Evidence of prehistoric human presence as early as 32,000 years ago was recorded at the site. The skeletal remains of ten individuals were discovered by Paul E. P. Deraniyagala, who attributed them to Balangoda Man. Balangoda Man is assumed to have lived as early as 32,000 years ago and occupied high altitude territories of up to 2,000 ft (609.6 m) above sea level.

The Polonnaruwa Vatadage is an ancient structure dating back to the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa of Sri Lanka. It is believed to have been built during the reign of Parakramabahu I to hold the Relic of the tooth of the Buddha or during the reign of Nissanka Malla of Polonnaruwa to hold the alms bowl used by the Buddha. Both these venerated relics would have given the structure a great significance and importance at the time. Located within the ancient city of Polonnaruwa, it is the best preserved example of a vatadage in the country, and has been described as the "ultimate development" of this type of architecture. Abandoned for several centuries, excavation work at the Polonnaruwa Vatadage began in 1903.

A vaṭadāge is a type of Buddhist structure found in Sri Lanka. It also known as a dage, thupagara and a cetiyagara. Although it may have had some Indian influence, it is a structure that is more or less unique to the architecture of ancient Sri Lanka. Vatadages were built around small stupas for their protection, which often enshrined a relic or were built on hallowed ground. Circular in shape, they were commonly built of stone and brick and adorned with elaborate stone carvings. Vatadages may have also had a wooden roof, supported by a number of stone columns arranged in several concentric rows.

Hatadage is an ancient relic shrine in the city of Polonnaruwa, Sri Lanka. It was built by King Nissanka Malla, and had been used to keep the Relic of the tooth of the Buddha. The Hatadage had been built using stone, brick and wood, although only parts of the brick and stone walls now remain. It appears to have been a two-storey structure, but the upper storey has now been destroyed. Three Buddha statues carved out of granite rock are located within a chamber of the shrine.
The Port of Jambukolapattinam or Dambakola Patuna is an ancient port to the north of Jaffna, in the Northern Province, Sri Lanka.
Medirigiriya Divisional Secretariat is a Divisional Secretariat of Polonnaruwa District, of North Central Province, Sri Lanka.
Medirigiriya electoral district was an electoral district of Sri Lanka between July 1977 and February 1989. The district was named after the town of Medirigiriya in Polonnaruwa District, North Central Province. The 1978 Constitution of Sri Lanka introduced the proportional representation electoral system for electing members of Parliament. The existing 160 mainly single-member electoral districts were replaced with 22 multi-member electoral districts. Medirigiriya electoral district was replaced by the multi-member electoral district at the 1989 general elections, the first under the proportional representation system.

Medirigiriya is a town located in Polonnaruwa District in North Central Province, Sri Lanka. The elevation of the town is 61 m (200 ft). The famous archaeological site of Medirigiriya Vatadage is located about 1 km (0.62 mi) from the town centre.

Pilikuththuwa Raja Maha Vihara is an ancient Cave temple situated in Pilikuththuwa, Sri Lanka. It is located on the Gampaha - Wathurugama road approximately 3.8 km (2.4 mi) away from the Miriswatta junction and 1.6 km (0.99 mi) from the ancient Buddhist temple, Maligatenna Raja Maha Vihara. The temple has been formally recognised by the Government as an archaeological site in Sri Lanka.

Gonagolla Vihara is an ancient cave temple situated in Ampara District, Sri Lanka. The vihara is also known as Punchi Seegiriya by the locals since the temple contains ancient frescoes similar to those in Sigiriya. The site is in Kotmale Canal Settlement in Wewagampattuwa Division and lies about 4.8 km (3.0 mi) east of Kohombana Junction on Ampara – Gonagolla Road. The temple has been formally recognised by the government as an archaeological site in Sri Lanka. The designation was declared on 10 October 2014 under the government Gazette number 1884.