
The Book of Numbers is the fourth book of the Hebrew Bible, and the fourth of five books of the Jewish Torah. The book has a long and complex history, but its final form is probably due to a Priestly redaction of a Yahwistic source made some time in the early Persian period. The name of the book comes from the two censuses taken of the Israelites.

Agabus was an early follower of Christianity mentioned in the Acts of the Apostles as a prophet. He is traditionally remembered as one of the Seventy Disciples described in Luke 10:1-24.

Cape Baba, is the westernmost point of the Turkish mainland, making it the westernmost point of Asia. It is located at the village of Babakale, Ayvacık, Çanakkale, in the historical area of the Troad. There was a lighthouse at Cape Baba that was called Lekton in classical times, anglicised as Cape Lecture.

John 2 is the second chapter of the Gospel of John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It contains the famous stories of the miracle of Jesus turning water into wine and Jesus expelling the money changers from the Temple.

Matthew 19 is the nineteenth chapter in the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament section of the Christian Bible. The book containing this chapter is anonymous, but early Christian tradition uniformly affirmed that Matthew composed this Gospel. Jesus continues his final journey to Jerusalem, ministering through Perea.
Witness is the name of an altar referred to in Joshua 22:10–34. Its name appears as "Witness" in the New King James Version, the English Standard Version and the New Living Translation. The Geneva Bible and the King James Version transliterate the original Hebrew word Ed, while the New International Version regards all of the following words as the name of the altar: "A Witness Between Us that the LORD is God". The New Century Version recalls the altar's name as "Proof That We Believe the Lord Is God". The New American Standard Bible calls it "the Offensive Altar".

"Thou shalt not make unto thee any graven image" is an abbreviated form of one of the Ten Commandments which, according to the Book of Deuteronomy, were spoken by God to the Israelites and then written on stone tablets by the Finger of God.

Psalm 128 is the 128th psalm of the Book of Psalms in the Old Testament. It is one of fifteen psalms which begins with the words "A song of ascents". It contains only six verses, and discusses the blessed state of those who follow Yahweh. Its opening words in the King James Version are "Blessed is every one that feareth the LORD; that walketh in his ways". In the Greek Septuagint version of the bible, and in its Latin translation in the Vulgate, this psalm is Psalm 127 in a slightly different numbering system.
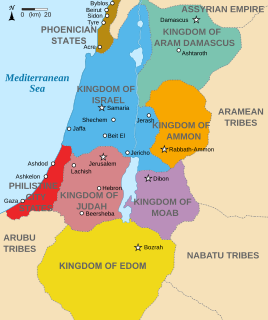
Transjordan is an area of land in the Southern Levant lying east of the Jordan River valley.
Transjordan, the East Bank, or the Transjordanian Highlands, is the part of the Southern Levant east of the Jordan River, mostly contained in present-day Jordan.

Amos 5 is the fifth chapter of the Book of Amos in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Amos, including a lamentation for Israel, Amos 5:1–3; an exhortation to repentance, Amos 5:4–20; God's rejection to their hypocritical service, Amos 5:21–27. It is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.
The Jamieson-Fausset-Brown Bible Commentary refers to a biblical commentary entitled a Commentary Critical and Explanatory on the Whole Bible, prepared by Robert Jamieson, Andrew Robert Fausset and David Brown and published in 1871; and derived works from this initial publication, in differing numbers of volumes and abridgements. The commentary uses the King James Version of the Bible as its text.
The Lord's Release is the title given by Deuteronomy 15:2 in the Hebrew Bible to the obligation and practice of releasing debtors from their debts every seventh year within the seven-year agricultural cycle mandated by the Torah:

Revelation 3 is the third chapter of the Book of Revelation or the Apocalypse of John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is traditionally attributed to John the Apostle, but the precise identity of the author remains a point of academic debate. This chapter contains messages to the churches of Sardis, Philadelphia and Laodicea, three of the seven churches of Asia located in modern-day Turkey, continuing from the messages for the other four churches which appear in chapter 2.

Micah 6 is the sixth chapter of the Book of Micah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Micah, and is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.

Amos 2 is the second chapter of the Book of Amos in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Amos, especially charges against Moab, Judah, and lastly Israel, the chief subject of Amos' prophecies. It is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.

Hosea 2 is the second chapter of the Book of Hosea in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Hosea son of Beeri, application of the symbols in the first chapter. It is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.

Hosea 3 is the third chapter of the Book of Hosea in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Hosea son of Beeri, about the symbol of Israel's condition in their present dispersion, subsequent to their return from Babylon. It is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.

Hosea 4 is the fourth chapter of the Book of Hosea in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This book contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Hosea son of Beeri. In this chapter he reproves the people and priests for their sins in the interregnum which followed Jeroboam's death; hence there is no mention of the king or his family; and in Hosea 4:2 bloodshed and other evils usual in a civil war are specified. It is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.

Hosea 12 is the twelfth chapter of the Book of Hosea in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. This chapter contains the prophecies spoken by the prophet Hosea son of Beeri, and was delivered about the time of Israel's seeking the aid of the Egyptian king So, in violation of their covenant with Assyria. He exhorts them to follow their father Jacob's persevering prayerfulness, which brought God's favor upon him. As God is unchangeable, He will show the same favor to Jacob's posterity as He did to Jacob, if, like him, they seek God. It is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.















