Membrane corticosteroid receptor include:
Membrane corticosteroid receptor include:

Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis and phagocytosis. It is a form of active transport.
Receptor may refer to:

Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular response. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand binding in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a signaling pathway.
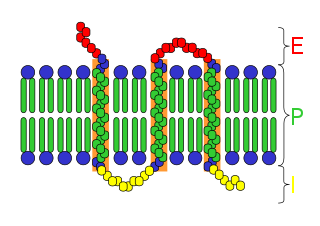
An integral membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All transmembrane proteins are IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comprise a significant fraction of the proteins encoded in an organism's genome. Proteins that cross the membrane are surrounded by annular lipids, which are defined as lipids that are in direct contact with a membrane protein. Such proteins can only be separated from the membranes by using detergents, nonpolar solvents, or sometimes denaturing agents.

A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids and sex steroids. Within those two classes are five types according to the receptors to which they bind: glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids and androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Vitamin D derivatives are a sixth closely related hormone system with homologous receptors. They have some of the characteristics of true steroids as receptor ligands.
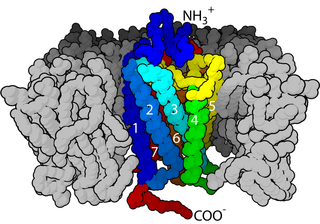
A neurotransmitter receptor is a membrane receptor protein that is activated by a neurotransmitter. Chemicals on the outside of the cell, such as a neurotransmitter, can bump into the cell's membrane, in which there are receptors. If a neurotransmitter bumps into its corresponding receptor, they will bind and can trigger other events to occur inside the cell. Therefore, a membrane receptor is part of the molecular machinery that allows cells to communicate with one another. A neurotransmitter receptor is a class of receptors that specifically binds with neurotransmitters as opposed to other molecules.

Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can follow this pathway all the way to lysosomes for degradation or can be recycled back to the cell membrane in the endocytic cycle. Molecules are also transported to endosomes from the trans Golgi network and either continue to lysosomes or recycle back to the Golgi apparatus.
A hormone receptor is a receptor molecule that binds to a specific hormone. Hormone receptors are a wide family of proteins made up of receptors for thyroid and steroid hormones, retinoids and Vitamin D, and a variety of other receptors for various ligands, such as fatty acids and prostaglandins. There are two main classes of hormone receptors. Receptors for peptide hormones tend to be cell surface receptors built into the plasma membrane of cells and are thus referred to as trans membrane receptors. An example of this is insulin. Receptors for steroid hormones are usually found within the cytoplasm and are referred to as intracellular or nuclear receptors, such as testosterone. Upon hormone binding, the receptor can initiate multiple signaling pathways, which ultimately leads to changes in the behavior of the target cells.

In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway.
Tim or TIM may refer to:
Steroid hormone receptors are found in the nucleus, cytosol, and also on the plasma membrane of target cells. They are generally intracellular receptors and initiate signal transduction for steroid hormones which lead to changes in gene expression over a time period of hours to days. The best studied steroid hormone receptors are members of the nuclear receptor subfamily 3 (NR3) that include receptors for estrogen and 3-ketosteroids. In addition to nuclear receptors, several G protein-coupled receptors and ion channels act as cell surface receptors for certain steroid hormones.

Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (i.e. a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter.
Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject covers topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics and epigenetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.
In biology, cell signaling or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals. Chemical signals can be hydrophobic or hydrophilic. Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage.
The formyl peptide receptors (FPR) belong to a class of G protein-coupled receptors involved in chemotaxis. In humans, there are three formyl peptide receptor isoforms, each encoded by a separate gene that are named FPR1, FPR2, and FPR3. These receptors were originally identified by their ability to bind N-formyl peptides such as N-formylmethionine produced by the degradation of either bacterial or host cells. Hence formyl peptide receptors are involved in mediating immune cell response to infection. These receptors may also act to suppress the immune system under certain conditions. The close phylogenetic relation of signaling in chemotaxis and olfaction was recently proved by detection formyl peptide receptor like proteins as a distinct family of vomeronasal organ chemosensors in mice.

Cytokine receptors are receptors that bind to cytokines.
Adrenergic means "working on adrenaline (epinephrine) or noradrenaline (norepinephrine)". When not further qualified, it is usually used in the sense of enhancing or mimicking the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine in the body.

Cell surface receptors are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral membrane proteins that allow communication between the cell and the extracellular space. The extracellular molecules may be hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, growth factors, cell adhesion molecules, or nutrients; they react with the receptor to induce changes in the metabolism and activity of a cell. In the process of signal transduction, ligand binding affects a cascading chemical change through the cell membrane.
Membrane sex steroid receptor may refer to:
The hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor (abbreviated HCA receptor and HCAR) family includes the following human proteins: