
An axon, or nerve fiber, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons, such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction has caused many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three types – group A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. These groups include both sensory fibers and motor fibers. Another classification groups only the sensory fibers as Type I, Type II, Type III, and Type IV.

A neuron or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. It is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells.

In physiology, an action potential (AP) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: this depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, endocrine cells and in some plant cells.

A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general anesthetic. When it is used on specific nerve pathways, paralysis also can be achieved.
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as medications to decrease blood pressure in patients with hypertension. CCBs are particularly effective against large vessel stiffness, one of the common causes of elevated systolic blood pressure in elderly patients. Calcium channel blockers are also frequently used to alter heart rate, to prevent peripheral and cerebral vasospasm, and to reduce chest pain caused by angina pectoris.

Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormal rhythms of the heart, such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.
The cardiac action potential is a brief change in voltage across the cell membrane of heart cells. This is caused by the movement of charged atoms between the inside and outside of the cell, through proteins called ion channels. The cardiac action potential differs from action potentials found in other types of electrically excitable cells, such as nerves. Action potentials also vary within the heart; this is due to the presence of different ion channels in different cells.
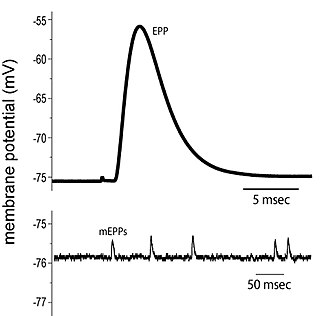
End plate potentials (EPPs) are the voltages which cause depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called "end plates" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.4mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.
Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject covers topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics and epigenetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.
The sucrose gap technique is used to create a conduction block in nerve or muscle fibers. A high concentration of sucrose is applied to the extracellular space, which prevents the correct opening and closing of sodium and potassium channels, increasing resistance between two groups of cells. It was originally developed by Robert Stämpfli for recording action potentials in nerve fibers, and is particularly useful for measuring irreversible or highly variable pharmacological modifications of channel properties since untreated regions of membrane can be pulled into the node between the sucrose regions.
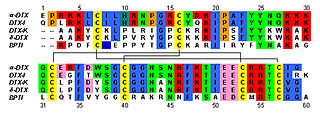
Dendrotoxins are a class of presynaptic neurotoxins produced by mamba snakes (Dendroaspis) that block particular subtypes of voltage-gated potassium channels in neurons, thereby enhancing the release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions. Because of their high potency and selectivity for potassium channels, dendrotoxins have proven to be extremely useful as pharmacological tools for studying the structure and function of these ion channel proteins.
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell's plasma membrane. They belong to the superfamily of cation channels and can be classified according to the trigger that opens the channel for such ions, i.e. either a voltage-change ("voltage-gated", "voltage-sensitive", or "voltage-dependent" sodium channel; also called "VGSCs" or "Nav channel") or a binding of a substance (a ligand) to the channel (ligand-gated sodium channels).

Acebutolol, sold under the brand names Sectral among others, is a beta blocker for the treatment of hypertension and arrhythmias. Acebutolol is a cardioselective beta-1 blocker and has intrinsic sympathetic activity. It is commonly used in the treatment of angina.
Guanethidine is an antihypertensive drug that reduces the release of catecholamines, such as norepinephrine. Guanethidine is transported across the sympathetic nerve membrane by the same mechanism that transports norepinephrine itself, and uptake is essential for the drug's action. Once guanethidine has entered the nerve, it is concentrated in transmitter vesicles, where it replaces norepinephrine. It may also inhibit the release of granules by decreasing norepinephrine.

Levobunolol is a non-selective beta blocker. It is used topically in the form of eye drops to manage ocular hypertension and open-angle glaucoma.

Prajmaline (Neo-gilurythmal) is a class Ia antiarrhythmic agent which has been available since the 1970s. Class Ia drugs increase the time one action potential lasts in the heart. Prajmaline is a semi-synthetic propyl derivative of ajmaline, with a higher bioavailability than its predecessor. It acts to stop arrhythmias of the heart through a frequency-dependent block of cardiac sodium channels.
Sodium channel blockers are drugs which impair the conduction of sodium ions (Na+) through sodium channels.

A channel blocker is the biological mechanism in which a particular molecule is used to prevent the opening of ion channels in order to produce a physiological response in a cell. Channel blocking is conducted by different types of molecules, such as cations, anions, amino acids, and other chemicals. These blockers act as ion channel antagonists, preventing the response that is normally provided by the opening of the channel.
Crotoxin (CTX) is the main toxic compound in the snake venom of the South American rattlesnake, Crotalus durissus terrificus. Crotoxin is a heterodimeric beta-neurotoxin, composed of an acidic, non-toxic and non-enzymatic subunit (CA), and a basic, weakly toxic, phospholipase A2 protein (CB). This neurotoxin causes paralysis by both pre- and postsynaptic blocking of acetylcholine signalling.










