Calas or Callas was an ancient Greek, son of Harpalus of Elimiotis and first cousin to Antigonus, king of Asia.
Oxyathres was a brother of the Persian king Darius III Codomannus. He was distinguished for his bravery, and in the battle of Issus, 333 BC, took a prominent part in the combat in defence of the king, when attacked by the Macedonian cavalry under Alexander himself, as shown in the celebrated Alexander Mosaic found in Pompeii. He afterwards accompanied Darius on his flight into Bactria, and fell into the hands of Alexander during the pursuit, but was treated with the utmost distinction by the conqueror, who even assigned him an honourable post about his own person; and subsequently devolved upon him the task of punishing Bessus for the murder of Darius. He was the father of Amastris queen of Heraclea.
Philotas was a Macedonian soldier, father of Parmenion, the general of Alexander the Great. It appears that he had two other sons, Asander and Agathon.

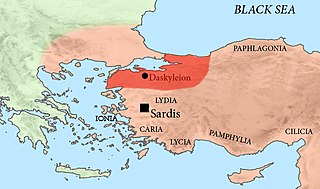
Spithridates was a Persian satrap of Lydia and Ionia under the high king Darius III Codomannus. He was one of the Persian commanders at the Battle of the Granicus, in 334 BC. In this engagement, while he was aiming a blow from behind at Alexander the Great, his arm was cut off by Cleitus the Black and he subsequently died.
Amyntas was a Macedonian officer in Alexander the Great's army, son of Andromenes from Tymphaia. After the battle of the Granicus, 334 BC, when the garrison of Sardis was quietly surrendered to Alexander, Amyntas was the officer sent forward to receive it from the commander, Mithrenes. Two years after, 332, we again hear of him as being sent into Macedonia to collect levies, while Alexander after the siege of Gaza advanced to Egypt; and he returned with them in the ensuing year, when the king was in possession of Susa.
For other persons with the same name, see Simmias
Erigyius, a Mytilenaean, son of Larichus, was an officer in Alexander the Great's army. He had been driven into banishment by Philip II, king of Macedon, because of his faithful attachment to Alexander, and returned when the latter came to the throne in 336 BC. At the battle of Gaugamela, 331 BC, he commanded the cavalry of the allies, as he did also when Alexander set out in 330 BC from Ecbatana in pursuit of Darius III. In the same year Erigyius was entrusted with the command of one of the three divisions with which Alexander invaded Hyrcania. He was also among the generals sent against Satibarzanes, whom he slew in battle with his own hand. In 329 BC, together with Craterus and Hephaestion, and with the assistance of Aristander, a soothsayer, he endeavoured to dissuade Alexander from crossing the Jaxartes river against the Scythians. In 328 BC he fell in a battle against the Bactrian fugitives.

Satibarzanes, a Persian, was satrap of Aria under Darius III, king of Persia.
Caranus, a Macedonian member of the elite cavalry body known as the hetairoi (Greek:ἑταῖροι), was one of the generals sent by Alexander the Great against Satibarzanes when, for a second time, he had encouraged Aria to revolt. Caranus and his colleagues were successful in achieving their objective by defeating and slaying Satibarzanes in the winter of 330 BC.
Pharnuches was a Lycian appointed by Alexander the Great to command the force sent into Sogdiana against Spitamenes in 329 BC. The result of the expedition was disastrous, with the destruction of the whole army. Pharnuches had been entrusted with its superintendence, because he was acquainted with the language of the inhabitants of the region, and had shown much dexterity in his intercourse with them. According to Aristobulus he was conscious of his deficiency in military skill, and wished to cede the command to the three Macedonian officers who were acting under him, but they refused to accept it.
Menander was an officer in the service of Alexander the Great. He was one of those called etairoi, but he held the command of a body of mercenaries. He was appointed by Alexander to the government of Lydia, during the settlement of the affairs of Asia made by Alexander when at Tyre. Menander appears to have remained at that post until the year 323 BC, when he was commissioned to lead a reinforcement of troops to Alexander at Babylon — he arrived there just before the king's last illness. In the division of the provinces, after the death of Alexander, Menander received his former government of Lydia, of which he was quick to take possession.
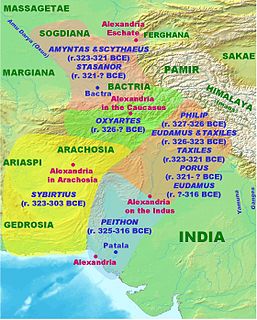
Sibyrtius was a Greek officer from Crete in the service of Alexander the Great, who was the satrap of Arachosia and Gedrosia shortly after the death of Alexander until about 303 BC.
For other persons with the same name, see Tlepolemus (disambiguation)

Philip, son of Machatas and brother of Harpalus, was an officer in the service of Alexander the Great, who in 327 BC was appointed by Alexander as satrap of India, including the provinces westward of the Hydaspes, as far south as the junction of the Indus with the Acesines. After the conquest of the Malli and Oxydracae, these tribes also were added to his government.
Nicanor, son of Parmenion, was a distinguished officer in the service of Alexander the Great. He is first mentioned at the passage of the Danube river, in the expedition of Alexander against the Getae, 335, when he led the phalanx. But during the expedition into Asia he appears to have uniformly held the chief command of the body of troops called the Hypaspists (υπασπισται) or foot-guards, numbering three units of 1,000 men. As his brother Philotas did that of the εταιρoι, or horse-guards. We find him mentioned, as holding this post, in the three great battles of the Granicus, of Issus, and of Gaugamela. He afterwards accompanied Alexander with a part of the troops under his command, during the rapid march of the king in pursuit of the king Darius III Codomannus in 330; which was probably his last service, as he died of disease shortly afterwards, during the advance of Alexander into Bactria. His death at this juncture was considered a fortunate event, as it prevented him from participating either in the designs or the fate of his brother Philotas.
Philoxenus was a Macedonian officer appointed to superintend the collection of the tribute in the provinces north of the Taurus Mountains after Alexander the Great's return from Egypt in 331 BC. However, he did not immediately assume this command because he was sent forward by Alexander from the field of Gaugamela to take possession of Susa and the treasures there deposited, which he effected without opposition. After this he seems to have remained quietly in the discharge of his functions in Asia Minor, until the commencement of the year 323, when he brought troops from Caria to Babylon, where he arrived just before the last illness of Alexander. In the distribution of the provinces which followed the death of that monarch, there is no mention of Philoxenus, but in 321 he was appointed by Perdiccas to succeed Philotas in the government of Cilicia. By what means he afterwards conciliated the favour of Antipater is unknown, but in the partition at Triparadisus after the fall of Perdiccas the same year he was still allowed to retain his satrapy of Cilicia. No information exists beyond then.

Orontobates was a Persian, who married the daughter of Pixodarus, the usurping satrap of Caria, and was sent by the king of Persia to succeed him. On the approach of Alexander the Great of Macedon Orontobates and Memnon of Rhodes entrenched themselves in Halicarnassus. But at last, despairing of defending it, they set fire to the town, and under cover of the conflagration crossed over to Cos, whither they had previously removed their treasures. In addition to the island of Cos, Orontobates, retained control of the citadel at Salmacis, and the towns Myndus, Caunus, Thera and Callipolis together with Triopium.
Ptolemy ; died 333 BC) son of Seleucus from Orestis or Tymphaia, was one of the select officers called Somatophylaces, or guards of the king's person; he combined with that distinguished post the command of one of the divisions of the phalanx. Ptolemy was from an upper noble family. He was lately married when he accompanied Alexander on his expedition to Asia, 334 BC, on which account he was selected by the king to command the body of Macedonians, who were allowed to return home for the winter at the end of the first campaign. In the following spring he rejoined Alexander at Gordium, with the troops under his command, accompanied by fresh reinforcements. At the Battle of Issus his division of the phalanx was one of those opposed to the Greek mercenaries under Darius III, and upon which the real brunt of the action consequently devolved; and he himself fell in the conflict, after displaying the utmost valour.
Aeschylus of Rhodes was appointed by Alexander the Great one of the inspectors of the governors of that country after its conquest in 332 BC. He is not spoken of again until 319, when he is mentioned as conveying in four ships six hundred talents of silver from Cilicia to Macedonia, which were detained at Ephesus by Antigonus, in order to pay his foreign mercenaries.
Ptolemy, son of Philip was an officer who commanded the leading squadron of Macedonian cavalry at the Battle of the Granicus. Both Gronovius and Droysen, suppose that he is the same man that Alexander left with a force of 3,000 infantry and 200 cavalry to defend the province of Caria, and who subsequently, together with Asander the governor of Lydia, defeated the Persian general Orontobates, 332 BC.










