
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom (=N−). It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.

N,N-Dimethylaniline (DMA) is an organic chemical compound, a substituted derivative of aniline. It is a tertiary amine, featuring a dimethylamino group attached to a phenyl group. This oily liquid is colourless when pure, but commercial samples are often yellow. It is an important precursor to dyes such as crystal violet.
The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO−
2. Nitrite is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid.

Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.

In organic chemistry, nitration is a general class of chemical processes for the introduction of a nitro group into an organic compound. The term also is applied incorrectly to the different process of forming nitrate esters between alcohols and nitric acid. The difference between the resulting molecular structures of nitro compounds and nitrates is that the nitrogen atom in nitro compounds is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom, whereas in nitrate esters, the nitrogen is bonded to an oxygen atom that in turn usually is bonded to a carbon atom.

In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, C−H bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid.

Ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2[Ce(NO3)6]. This orange-red, water-soluble cerium salt is a specialised oxidizing agent in organic synthesis and a standard oxidant in quantitative analysis.

Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non-adjacent nitrogen atoms in meta-substitution.

Tollens' reagent is a chemical reagent used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones along with some alpha-hydroxy ketones which can tautomerize into aldehydes. The reagent consists of a solution of silver nitrate, ammonium hydroxide and some sodium hydroxide. It was named after its discoverer, the German chemist Bernhard Tollens. A positive test with Tollens' reagent is indicated by the precipitation of elemental silver, often producing a characteristic "silver mirror" on the inner surface of the reaction vessel.
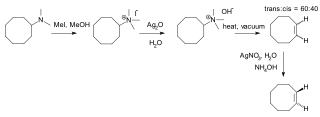
Hofmann elimination is an elimination reaction of an amine to form alkenes. The least stable alkene, called the Hofmann product, is formed. This tendency, known as the Hofmann alkene synthesis rule, is in contrast to usual elimination reactions, where Zaitsev's rule predicts the formation of the most stable alkene. It is named after its discoverer, August Wilhelm von Hofmann.

In organic chemistry, aromatic sulfonation is an organic reaction in which a hydrogen atom on an arene is replaced by a sulfonic acid functional group in an electrophilic aromatic substitution. Aryl sulfonic acids are used as detergents, dye, and drugs.
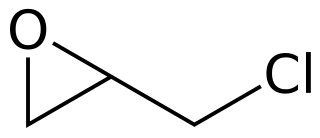
Epichlorohydrin is an organochlorine compound and an epoxide. Despite its name, it is not a halohydrin. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor, moderately soluble in water, but miscible with most polar organic solvents. It is a chiral molecule generally existing as a racemic mixture of right-handed and left-handed enantiomers. Epichlorohydrin is a highly reactive electrophilic compound and is used in the production of glycerol, plastics, epoxy glues and resins, epoxy diluents and elastomers.

Nickel nitrate is the inorganic compound Ni(NO3)2 or any hydrate thereof. In the hexahydrate, the nitrate anions are not bonded to nickel. Other hydrates have also been reported: Ni(NO3)2.9H2O, Ni(NO3)2.4H2O, and Ni(NO3)2.2H2O.

The Zincke nitration is a nitration reaction in which a bromine is replaced by a nitro group on an electron-rich aryl compound such as a phenol or cresol. Typical reagents are nitrous acid or sodium nitrite. The reaction is a manifestation of nucleophilic aromatic substitution and is named after Theodor Zincke, who first reported it in 1900.

The Wolffenstein–Böters reaction is an organic reaction converting benzene to picric acid by a mixture of aqueous nitric acid and mercury(II) nitrate.

Organosilver chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to silver chemical bond. The theme is less developed than organocopper chemistry.
Electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr) is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic system is replaced by an electrophile. Some of the most important electrophilic aromatic substitutions are aromatic nitration, aromatic halogenation, aromatic sulfonation, alkylation Friedel–Crafts reaction and acylation Friedel–Crafts reaction.

Titanium nitrate is the inorganic compound with formula Ti(NO3)4. It is a colorless, diamagnetic solid that sublimes readily. It is an unusual example of a volatile binary transition metal nitrate. Ill defined species called titanium nitrate are produced upon dissolution of titanium or its oxides in nitric acid.

Vanadyl nitrate, also called vanadium oxytrinitrate or vanadium oxynitrate is an inorganic compound of vanadium in the +5 oxidation state with nitrate ligands and oxygen. The formula is VO(NO3)3. It is a pale yellow viscous liquid.

Nitratoauric acid, hydrogen tetranitratoaurate, or simply called gold(III) nitrate is a crystalline gold compound that forms the trihydrate, HAu(NO3)4·3H2O or more correctly H5O2Au(NO3)4·H2O. This compound is an intermediate in the process of extracting gold. In older literature it is also known as aurinitric acid.


















