
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern and Western Europe. It consists of a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land border, as well as nearly 800 islands, notably Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares its borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia, and two enclaves: Vatican City and San Marino. It is the tenth-largest country in Europe by area, covering 301,340 km2 (116,350 sq mi), and third-most populous member state of the European Union, with a population of nearly 60 million. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome; other major urban areas include Milan, Naples, Turin, Palermo, Bologna, Florence, Genoa, and Venice.

A think tank, or public policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, military, technology, and culture. Most think tanks are non-governmental organizations, but some are semi-autonomous agencies within government, and some are associated with particular political parties, businesses or the military. Think tanks are often funded by individual donations, with many also accepting government grants.

The unification of Italy, also known as the Risorgimento, was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 resulted in the consolidation of various states of the Italian Peninsula and its outlying isles into a single state, the Kingdom of Italy. Inspired by the rebellions in the 1820s and 1830s against the outcome of the Congress of Vienna, the unification process was precipitated by the Revolutions of 1848, and reached completion in 1871 after the capture of Rome and its designation as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy.
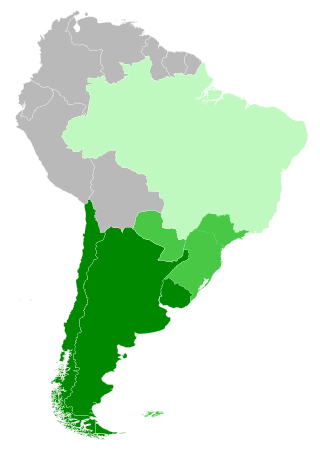
The Southern Cone is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the east by the Atlantic Ocean. In terms of social, economic and political geography, the Southern Cone comprises Argentina, Chile, Uruguay and Paraguay, and sometimes includes Brazil's four southernmost states.

Italians are an ethnic group native to the Italian geographical region. Italians share a common culture, history, ancestry and language. Their predecessors differ regionally, but generally include native populations such as the Etruscans, the Rhaetians, the Ligurians, the Adriatic Veneti, and the Italic peoples, including the Latins, from which the Romans emerged and helped create and evolve the modern Italian identity. Foreign influences include the ancient Greeks in Magna Graecia, and the Phoenicians, who had a presence in Sicily and Sardinia, the Celts, who settled in parts of the north, the Germanics and the Slavs. Legally, Italian nationals are citizens of Italy, regardless of ancestry or nation of residence and may be distinguished from ethnic Italians in general or from people of Italian descent without Italian citizenship and ethnic Italians living in territories adjacent to the Italian peninsula without Italian citizenship. The Latin equivalent of the term Italian had been in use for natives of the geographical region since antiquity.

Forza Italia was a centre-right liberal-conservative political party in Italy, with Christian democratic, liberal, social democratic and populist tendencies. It was founded by Silvio Berlusconi, who served as Prime Minister of Italy four times.
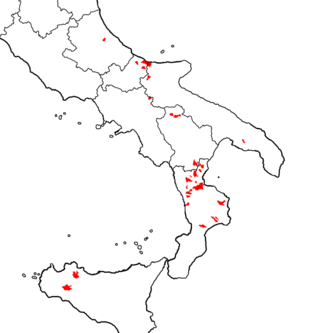
The Arbëreshë, also known as Albanians of Italy or Italo-Albanians, are an Albanian ethnolinguistic group minority historically settled in Southern and Insular Italy.

Southern Italy, also known as Meridione or Mezzogiorno, is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern regions.

The Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa is a public university institution in Pisa and Florence, Tuscany, Italy, currently attended by about 600 undergraduate and postgraduate (PhD) students. Together with the University of Pisa and Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies, it is part of the Pisa University System.

Egyptians speak a continuum of dialects. The predominant dialect in Egypt is Egyptian Colloquial Arabic or Masri/Masry, which is the vernacular language. Literary Arabic is the official language and the most widely written. The Coptic language is used primarily by Egyptian Copts and it is the liturgical language of Coptic Christianity.

Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore is an Italian private research university founded in 1921. Its main campus is located in Milan, Italy, with satellite campuses in Brescia, Piacenza, Cremona and Rome.
Five nationwide popular referendums were held in Italy on 8 November 1987, with three questions about nuclear energy after the Chernobyl disaster, and two questions about justice. Voting day had been postponed by six months, according to the Italian Constitution, because of the snap election of spring.

Sabino Cassese is an Italian jurist, former minister for the public function in the Ciampi government (1993–1994), and judge of the Constitutional Court of Italy (2005–2014).

This is a history of the economy of Italy. For more information on historical, cultural, demographic and sociological developments in Italy, see the chronological era articles in the template to the right. For more information on specific political and governmental regimes in Italy, see the Kingdom and Fascist regime articles. The economic history of pre-unitarian Italy traces the economic and social changes of the Italian territory from Roman times to the unification of Italy (1860).

Racism in Italy deals with the relationship between Italians and other populations of different ethnicities and/or nationalities which has existed throughout the country's history.
The Right group, later called Historical Right by historians to distinguish it from the right-wing groups of the 20th century, was an Italian conservative parliamentary group during the second half of the 19th century. After 1876, the Historical Right constituted the Constitutional opposition toward the left governments. It originated in the convergence of the most liberal faction of the moderate right and the moderate wing of the democratic left. The party included men from heterogeneous cultural, class, and ideological backgrounds, ranging from British-American individualist liberalism to Neo-Hegelian liberalism as well as liberal-conservatives, from strict secularists to more religiously-oriented reformists. Few prime ministers after 1852 were party men; instead they accepted support where they could find it, and even the governments of the Historical Right during the 1860s included leftists in some capacity.

Mario Alicata was an Italian Partisan, literary critic and politician.

Fashizmi ('Fascism') was a daily Albanian-Italian bilingual newspaper published from Tirana, Albanian Kingdom 1939-1940. It functioned as the official organ of the Albanian Fascist Party. Fejzi Alizoti was the editor of Fashizmi. Vangjel Koça served as the managing director of the newspaper.
Tommaso Fiore was an Italian meridionalist writer and a socialist intellectual and politician. He is known for his attention and his descriptions and studies on the inhumane conditions of Southern Italian and often specifically Apulian peasants at that time. He is also known for his Viareggio Prize-winning book Un popolo di formiche. In the 1920s, he was appointed as mayor of his hometown Altamura. During the twenty-year period of the Italian Fascist era, he strenuously opposed the regime before being sent into internal exile in 1942 and then being jailed in 1943.

Giuseppe Luciano Calogero "Peppe" Provenzano is an Italian politician and member of the Democratic Party. On 5 September 2019, he was appointed Minister for the South in the government of Giuseppe Conte. Provenzano is a meridionalist.

















