Related Research Articles

Norfolk Island is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, 1,412 kilometres (877 mi) directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about 900 kilometres (560 mi) from Lord Howe Island. Together with the neighbouring Phillip Island and Nepean Island, the three islands collectively form the Territory of Norfolk Island. At the 2021 census, it had 2188 inhabitants living on a total area of about 35 km2 (14 sq mi). Its capital is Kingston.

The history of Norfolk Island dates back to the fourteenth or fifteenth century when it was settled by Polynesian seafarers.
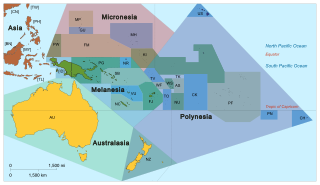
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania.

Lismore is a city in northeastern New South Wales, Australia and the main population centre in the City of Lismore local government area; it is also a regional centre in the Northern Rivers region of the State. It is situated on a low flood plain on the banks of the Wilsons River near the latter's junction with Leycester Creek, both tributaries of the Richmond River which enters the Pacific Ocean at Ballina, 30 km (19 mi) to the east. The original settlement initially developed as a grazing property in the 1840s, then became a timber and agricultural town and inland port based around substantial river traffic, which prior to the development of the road and rail networks was the principal means of transportation in the region. Use of the river for transport declined and then ceased around the mid-twentieth century, however by that time Lismore had become well established as the largest urban centre in the region, providing its surrounding area with a range of services. The city is also located on the Bruxner Highway which crosses the Wilsons River at Lismore, and was formerly a stop on the Casino-Murwillumbah railway line. It is the home of one of the three campuses of Southern Cross University.

The flag of Norfolk Island is a triband consisting of green, white, and green bands charged with a green Norfolk Island pine in the centre. Adopted in 1979 when the islands gained limited self-government, it has been the flag of the Territory of Norfolk Island since 6 June of that year. The pine is native to the territory and is its official tree.

Ernestine Hill was an Australian journalist, travel writer and novelist.

Burnt Pine is the largest town on Norfolk Island. It is the main commercial hub of the island, and travel from one side of the island to another generally involves passing through Burnt Pine as the island's sole thoroughfare runs through the town's centre.

Kingston is the administrative centre of the Australian external territory of Norfolk Island. The Norfolk Island Regional Council is based in Kingston. The settlement is the second-oldest in Australia, founded a little over a month after Sydney. It is part of the Kingston and Arthur's Vale Historic Area World Heritage site.

Burns Philp was once a major Australian shipping line and merchant that operated in the South Pacific. When the well-populated islands around New Guinea were targeted for blackbirding in the 1880s, a new rush for labour from these islands began. James Burns and Robert Philp purchased several well-known blackbirding ships to quickly exploit the human resource in this region, and Burns Philp entered the slave trade. The company ended its involvement in blackbirding in 1886. In later years the company was a major player in the food manufacturing business. Since its delisting from the Australian Securities Exchange in December 2006 and the subsequent sale of its assets, the company has mainly become a cashed up shell company. It is wholly owned by Graeme Hart's Rank Group.

Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of 7,617,930 square kilometres (2,941,300 sq mi), Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east, and mountain ranges in the south-east.

The first colonies of the British Empire on the continent of Australia were the penal colony of New South Wales, founded in 1788, and the Swan River Colony, founded in 1829. Over the next few decades, the colonies of New Zealand, Queensland, South Australia, Van Diemen's Land, and Victoria were created from New South Wales, as well as an aborted Colony of North Australia. On 1 January 1901, these colonies, excepting New Zealand, became states in the Commonwealth of Australia. Since federation, the internal borders have remained mostly stable, except for the creation of some territories with limited self-government: the Northern Territory from South Australia, to govern the vast, sparsely populated centre of the country; the split of the Northern Territory into Central Australia and North Australia, and then the quick merger of those back into the Northern Territory; and the Australian Capital Territory, a federal district ceded from New South Wales.
Diane Robin (Di) Bell is an Australian feminist anthropologist, author and activist. She is Professor Emerita of Anthropology at the George Washington University in Washington, D.C, USA and Distinguished Honorary Professor of Anthropology at the Australian National University, Canberra. Her work focuses on the Aboriginal people of Australia, Indigenous land rights, human rights, Indigenous religions, violence against women, and on environmental issues.

The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul, Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, Meganesia, or Papualand to distinguish it from the country of Australia, is located within the Southern and Eastern hemispheres. The name "Sahul" takes its name from the Sahul Shelf, which is a part of the continental shelf of the Australian continent. The continent includes mainland Australia, Tasmania, the island of New Guinea, the Aru Islands, the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, most of the Coral Sea Islands, and some other nearby islands. Situated in the geographical region of Oceania, Australia is the smallest of the seven traditional continents.
Sir Jonathan Atkins was Governor of Guernsey and Governor of Barbados.

The second voyage of James Cook, from 1772 to 1775, commissioned by the British government with advice from the Royal Society, was designed to circumnavigate the globe as far south as possible to finally determine whether there was any great southern landmass, or Terra Australis. On his first voyage, Cook had demonstrated by circumnavigating New Zealand that it was not attached to a larger landmass to the south, and he charted almost the entire eastern coastline of Australia, yet Terra Australis was believed to lie further south. Alexander Dalrymple and others of the Royal Society still believed that this massive southern continent should exist. After a delay brought about by the botanist Joseph Banks' unreasonable demands, the ships Resolution and Adventure were fitted for the voyage and set sail for the Antarctic in July 1772.
Luise Anna Hercus, née Schwarzschild, was a German-born linguist who lived in Australia from 1954. After significant early work on Middle Indo-Aryan dialects (Prakrits) she had specialised in Australian Aboriginal languages since 1963, when she took it up as a hobby. Works authored or co-authored by her are influential, and often among the primary resource materials on many languages of Australia.

Kathy Jetn̄il-Kijiner is a poet and climate change activist from the Marshall Islands.
Jeni Thornley is an Australian feminist documentary filmmaker, writer, film valuer and research associate at University of Technology, Sydney. Since leaving her job as Manager of the Women's Film Fund at the Australian Film Commission in 1986, Thornley has worked as an independent writer, director and producer at Anandi Films. She has fulfilled teaching roles at UTS and the Australian School for Film and Television. Thornley is currently an Honorary Research Associate in the Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences at UTS. She is also a consultant film valuer for the Cultural Gifts Program, Dept of Communications and the Arts.
The Arches is a heritage-listed ruin at Rocky Point Road in the former settlement of Longridge in the Australian territory of Norfolk Island. It was added to the Australian Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004.

Ellen Maev O'Collins, MBE was an Australian social worker by training, who became Emeritus Professor in the Department of Anthropology and Sociology at the University of Papua New Guinea.
References
- 1 2 "Merval Hoare". AustLit: Discover Australian Stories. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ↑ O'Collins, Maev (2010). An Uneasy Relationship: Norfolk Island and the Commonwealth of Australia. ANU E Press. p. 157. ISBN 9781921666995 . Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ↑ Hoare, Michael E. (2016). The Resolution Journal of Johann Reinhold Forster, 1772–1775. Routledge. ISBN 9781351882972 . Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ↑ O'Collins, Maev (2010). An Uneasy Relationship: Norfolk Island and the Commonwealth of Australia. ANU E Press. p. ix. ISBN 9781921666995.
- 1 2 3 Hoare, Merval (2015). Nelson Bear and the Yellow Umbrella. Captain Honey. p. About the author. ISBN 9780992474676 . Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ↑ "Norfolk Island: A Revised and Enlarged History 1774-1998 - Hoare, Merval". rareaussiebooks.com.au. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ↑ King, Russell; Connell, John (1999). Small Worlds, Global Lives. A&C Black. p. 220. ISBN 9781855675483 . Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ↑ "Shop". norfolkislandmuseum.com.au. Norfolk Island Museum. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ↑ Pacific Islands Monthly: PIM. Pacific Publications. 1984. p. 47. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- ↑ "Predator in paradise". Ben Hills. 2 January 2014. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
- 1 2 3 "Amazon.com: Merval Hoare: Books, Biography, Blog, Audiobooks, Kindle". amazon.com. Amazon. Retrieved 27 November 2017.