
Aten also Aton, Atonu, or Itn was the focus of Atenism, the religious system formally established in ancient Egypt by the late Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Akhenaten. Exact dating for the 18th dynasty is contested, though a general date range places the dynasty in the years 1550 to 1292 B.C.E. The worship of Aten and the coinciding rule of Akhenaten are major identifying characteristics of a period within the 18th dynasty referred to as the Amarna Period.

Thebes, known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile about 800 kilometers (500 mi) south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Thebes was the main city of the fourth Upper Egyptian nome and was the capital of Egypt for long periods during the Middle Kingdom and New Kingdom eras. It was close to Nubia and the Eastern Desert, with its valuable mineral resources and trade routes. It was a cult center and the most venerated city during many periods of ancient Egyptian history. The site of Thebes includes areas on both the eastern bank of the Nile, where the temples of Karnak and Luxor stand and where the city was situated; and the western bank, where a necropolis of large private and royal cemeteries and funerary complexes can be found. In 1979, the ruins of ancient Thebes were classified by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site.
Amenhotep is an ancient Egyptian name. Its Greek version is Amenophis (Ἀμένωφις). Its notable bearers were:

The necropolis of Draʻ Abu el-Naga' is located on the West Bank of the Nile at Thebes, Egypt, just by the entrance of the dry bay that leads up to Deir el-Bahari and north of the necropolis of el-Assasif. The necropolis is located near the Valley of the Kings.

The necropolis of Sheikh Abd el-Qurna is located on the West Bank at Thebes in Upper Egypt. It is part of the archaeological area of Deir el-Bahari, and named after the domed tomb of the local saint. This is the most frequently visited cemetery on the Theban west bank, with the largest concentration of private tombs.
Amenemḥat or Amenemhēt, hellenized as Ammenémēs or as Ammanémēs, is an Ancient Egyptian name meaning "Amun is in front". Amenemhat was the name of a number of kings, princes and administration officials throughout ancient Egyptian history.
Amun was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. With the 11th Dynasty, Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu.

Mery was a High Priest of Amun from the time of Amenhotep II.

The ancient Egyptian noble Prehotep II was Vizier in the latter part of the reign of Ramesses II, during the 19th Dynasty.
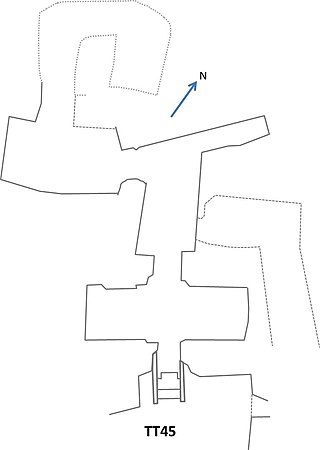
The Theban Tomb TT45 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite modern Luxor. It was originally the burial place of the ancient Egyptian named Djehuty (Thoth), who was a scribe of the offering-table of Mery, high-priest of Amun, head of all the weavers of Amun, and steward of Mery, high priest of Amun. Djehuty lived during the reign of Amenhotep II. He was the son of a lady also named Djehuty.

The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmosid Dynasty for the four pharaohs named Thutmose.
Mery or Méry may refer to:

Women in ancient Egypt had some special rights other women did not have in other comparable societies. They could own property and were, at court, legally equal to men. However, Ancient Egypt was a patriarchal society dominated by men. Only a few women are known to have important positions in administration, though there were female rulers and even female pharaohs. Women at the royal court gained their positions by relationship to male kings.
Menkheperre was an ancient Egyptian theophoric name. Its most famous use is as the throne name of three Egyptian monarchs:

Wenennefer was an ancient Egyptian High Priest of Osiris at Abydos, during the reign of pharaoh Ramesses II of the 19th Dynasty.
The Second Prophet of Amun, also called the Second Priest of Amun, was a high ranking priestly official in the cult of the ancient Egyptian god Amun. The Second Prophet of Amun office was created in the New Kingdom, at the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty.
Mery was an ancient Egyptian High Priest of Osiris at Abydos, during the reign of pharaoh Sety I and Ramesses II of the 19th Dynasty.
Hat was an ancient Egyptian High Priest of Osiris at Abydos, during the reign of pharaoh Sety I of the 19th Dynasty.
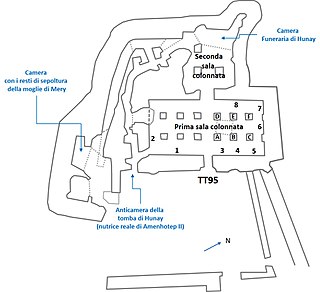
The Theban Tomb TT95 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. The tomb belongs to an ancient Egyptian named Mery, who was a High Priest of Amun at Karnak, during the reign of pharaoh Amenhotep II of the 18th Dynasty. Mery was the son of the First Prophet of Min of Koptos (Qift) named Nebpehtire and the Lady Hunayt. Mery's wife was named Dey.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.










