
The Achelous, also Acheloos, is a river in western Greece. It is 220 km (137 mi) long. It formed the boundary between Acarnania and Aetolia of antiquity. It empties into the Ionian Sea. In ancient times its spirit was venerated as the river god Achelous.

The Stratos Hydroelectric Dam is a dam on the river Acheloos in Aetolia-Acarnania, western Greece. It is situated just east of the village Stratos, and 9 km northwest of Agrinio. The dam created the Stratos artificial lake. There are four more dams upstream from the Stratos Dam: the Kastraki Dam, the Kremasta Dam, the Sykia Dam and the Mesochora Dam.

The Fryingpan-Arkansas Project, or "Fry-Ark," is a water diversion, storage and delivery project serving southeastern Colorado. The multi-purpose project was authorized in 1962 by President Kennedy to serve municipal, industrial, and hydroelectric power generation, and to enhance recreation, fish and wildlife interests. Construction began in 1964 and was completed in 1981. The project includes five dams and reservoirs, one federal hydroelectric power plant, and 22 tunnels and conduits totaling 87 miles (140 km) in length. The Bureau of Reclamation, under the Department of the Interior built and manages the project.

The Rio Grande Project is a United States Bureau of Reclamation irrigation, hydroelectricity, flood control, and interbasin water transfer project serving the upper Rio Grande basin in the southwestern United States. The project irrigates 193,000 acres (780 km2) along the river in the states of New Mexico and Texas. Approximately 60 percent of this land is in New Mexico. Some water is also allotted to Mexico to irrigate some 25,000 acres (100 km2) on the south side of the river. The project was authorized in 1905, but its final features were not implemented until the early 1950s.

Upper Gotvand Dam, or simply the Gotvand Dam, is an embankment dam on the Karun River about 12 km (7.5 mi) northeast of Gotvand in Khuzestan Province, Iran. It currently has an installed capacity of 1,000 MW with another 1,000 MW in the works for a second phase. Studies for the Karun River began in the 1960s and specific designs on the Upper Gotvand were presented in 1967, 1975 and 1982. After the design and location were chosen, a further study was carried out in 1997, the same year preliminary construction began. The river was diverted by April 2003 and excavation began soon thereafter. After completion of the dam, impounding of its reservoir began on 30 July 2011 during a ceremony attended by Iranian President Mahmood Ahmadinejad. The first generator of phase one was commissioned on 5 May 2012, two more by 18 September 2012 and the final in November 2012. Ahmadinejad was again present for the dam's inauguration on 22 April 2013. Phase 2 is estimated to be complete in 2015 and the dam is going to become one of Iran's largest power stations and is already its tallest earth-fill dam.

The La Grange Dam is a masonry-gravity diversion dam on the Tuolumne River near La Grange, California. The dam was completed in 1883 by the Turlock Irrigation District and Modesto Irrigation District in an effort to divert water into their canal systems for local farmers.

The Governor Ney Braga de Barros Hydroelectric Plant, formerly known as Segredo, is a dam and hydroelectric power plant on the Iguazu River near Segredo in Paraná, Brazil. It is the fourth dam upstream of the Iguazu Falls and was constructed between 1987 and 1991 while being inaugurated in 1992. The power station has a 1,260 megawatts (1,690,000 hp) capacity and is supplied with water by a concrete face rock-fill embankment dam.

The Machadinho Hydroelectric Power Plant is a dam and hydroelectric power plant on the Pelotas River near Machadinho on the border of Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The power station has a 1,140 MW (1,530,000 hp) capacity and is supplied with water by a concrete face rock-fill embankment dam. It is owned and operated by Machadinho Energetica and produces the equivalent of 37% of the energy consumed in Santa Catarina.

The Wanjiazhai Dam is a gravity dam on the Yellow River on the border of Pianguan County, Shaanxi Province and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. The main purpose of the dam is water supply for the Wanjiazhai Water Control Project along with peak hydroelectric power generation. Construction on the dam began in 1994, the first generator went online in 1998 and the last in 2000.

The Daguangba Dam is a multi-purpose dam on the Changhua River in Hainan Province, China. It is located 35 km (22 mi) east of Dongfang. As the primary component of the Daguangba Multipurpose Project, the dam was constructed between 1990 and 1995. It serves to provide water for both hydroelectric power generation and agriculture. It supports a 240 MW power station and supplies water for the irrigation of 12,700 ha. It is also the largest dam and hydroelectric power station in Hainan.

The Thisavros Dam is a rock-fill dam on the Nestos River in the regional unit of Drama in the northeastern portion of Greece. it is 21 kilometres (13 mi) north of Nikiforos and 21 kilometres (13 mi) northeast of the town of Drama. The 172-metre (564 ft) high dam is the tallest in Greece. It was constructed between 1986 and 1996. The purpose of the dam is irrigation and hydroelectric power production. Its reservoirs helps irrigate 80,937 hectares and its power station has an installed capacity of 384 megawatts (515,000 hp). The power station is a pumped-storage type which allows it to not only generate power but the turbines can reverse and pump water back into the reservoir. Power generation occurs during periods of high demand and pumping during those of low demand such as at night.

Jounama Dam is a major ungated rockfill embankment dam across the Tumut River in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is for the generation of hydro-power and is one of the sixteen major dams that comprise the Snowy Mountains Scheme, a vast hydroelectricity and irrigation complex constructed in south-east Australia between 1949 and 1974 and now run by Snowy Hydro.

Casecnan Irrigation and Hydroelectric Plant is a dam diverting water from the Casecnan and Taan Rivers to the Pantabangan Reservoir through a 25-kilometre (16 mi) long tunnel located near Pantabangan and Muñoz in Nueva Ecija province of the Philippines. The multi-purpose dam provides water for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation while its reservoir affords flood control. It was considered one of the most expensive hydroelectric plants built in the country, being next only to San Roque Dam.

The Sykia Dam is a mostly constructed but unused earth-filled embankment dam on the Acheloos River along the border of Karditsa and Arta, Greece. The 170 m (560 ft) tall dam is part of the Acheloos River Diversion which is intended to divert a portion of the Acheloos west to irrigate 240,000–380,000 ha in the Thessaly plains. The project includes the Sykia, Messochora, Mouzaki and Pyli Dams along with a 17.4 km (10.8 mi) long channel.

The Kastraki Dam is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Achelous River near the village of Kastraki in Aitoloakarnania, Greece. It was completed in 1969 for the purposes of hydroelectric power generator, flood control and irrigation. The dam's power station houses four 80 MW Francis turbine-generators for an installed capacity of 320 MW. In 2010 the dam's overflow chute spillway was upgraded with 20 fuse plugs which increased the maximum height of the reservoir by 1.93 m (6.3 ft) and its storage capacity by 44,000,000 m3 (36,000 acre⋅ft).

The Alpaslan-2 Dam is an embankment dam currently under construction on the Murat River in Muş Province, Turkey. The dam is located about 32 km (20 mi) north of the provincial capital, Muş. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and irrigation. Its power station will have an installed capacity of 280 MW and the reservoir will help irrigate 78,000 ha of land. Enerjisa Power Generation Inc. acquired the license for the power station from Özışık İnsaat & Enerji in April 2011 and Yenigün Construction started excavating the diversion tunnels May 2012. The diversion tunnels are expected to be complete by the end of 2012. In late May 2013 Pöyry was awarded the detailed design of the dam, power station, spillway and switch yard. Enerjisa expects the project to be complete in 2016.

The Yedigöze Dam, also known as Sani Bey Dam, is a concrete-face rock-fill dam on the Seyhan River bordering İmamoğlu and Aladağ districts in Adana Province, Turkey. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and irrigation. The dam's power station has an installed capacity of 320 MW and the reservoir will help irrigate 75,000 ha. Construction began in 2007 and the river was diverted by 2008. In the same year construction on the actual dam began and the reservoir began to fill on 15 June 2010. By November 2010 the remaining construction work was complete and the generators were commissioned in 2011. Construction on the irrigation works is ongoing.
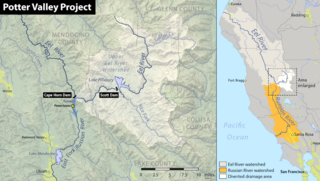
The Potter Valley Project is an interbasin water transfer project in Northern California in the United States, delivering water from the Eel River basin to the headwaters of the Russian River. The project is owned and operated by Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E). The main facilities are two dams on the Eel River, a diversion tunnel and hydroelectric plant. Average annual throughput is 159,000 acre⋅ft (196,000,000 m3), although this figure varies significantly with both the amount of precipitation in the Eel River basin and the demand on the Russian River.

The Yuba-Bear Hydroelectric Project is a complex hydroelectric scheme in the northern Sierra Nevada in California, tapping the upper Yuba River and Bear River drainage basins. The project area encompasses approximately 400 square miles (1,000 km2) in Nevada, Placer, and Sierra Counties. Owned by the Nevada Irrigation District, it consists of 16 storage dams plus numerous diversion and regulating dams, and four generating stations producing 425 million kilowatt hours of electricity each year. The Yuba-Bear Hydroelectric Project consists of the Bowman Development, Dutch Flat No. 2 Development, Chicago Park Development, and Rollins Development.

The Punta Negra Dam is a concrete-face rock-fill dam on the San Juan River about 28 kilometres (17 mi) west of San Juan in San Juan Province, Argentina. The purpose of the dam is to provide water for irrigation and the generation of hydroelectric power. The 101 metres (331 ft) tall dam supports a 62-megawatt (83,000 hp) power station and together with the Los Caracoles Dam upstream, it will provide for the irrigation of 15,000 hectares. Construction began in 2009 and the dam and was finished in August 29, 2015. It is being constructed immediately upstream of an diversion barrage.























