Mesopotamia is the historical region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, largely corresponding with the territory of modern Iraq.
Contents
Mesopotamia may also refer to:
Mesopotamia is the historical region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, largely corresponding with the territory of modern Iraq.
Mesopotamia may also refer to:

The Euphrates is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia. Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf.

The geography of Iraq is diverse and falls into five main regions: the desert, Upper Mesopotamia, the northern highlands of Iraq, Lower Mesopotamia, and the alluvial plain extending from around Tikrit to the Persian Gulf.
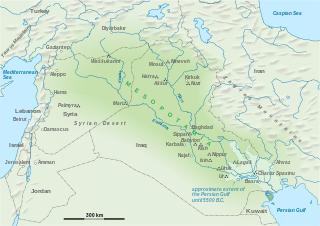
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region of Mesopotamia also includes parts of present-day Iran, Turkey, Syria and Kuwait.
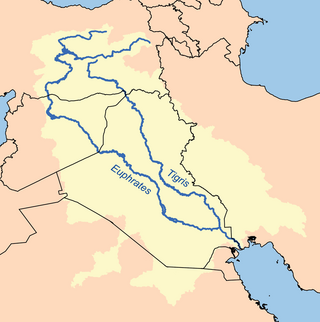
The Tigris is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, before merging with the Euphrates and reaching to the Persian Gulf.

The geography of Mesopotamia, encompassing its ethnology and history, centered on the two great rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates. While the southern is flat and marshy, the near approach of the two rivers to one another, at a spot where the undulating plateau of the north sinks suddenly into the Babylonian alluvium, tends to separate them still more completely. In the earliest recorded times, the northern portion was included in Mesopotamia; it was marked off as Assyria after the rise of the Assyrian monarchy. Apart from Assur, the original capital of Assyria, the chief cities of the country, Nineveh, Kalaḫ and Arbela, were all on the east bank of the Tigris. The reason was its abundant supply of water, whereas the great plain on the western side had to depend on streams flowing into the Euphrates.

The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in Western Asia that flows into the Persian Gulf. Its primary rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates, along with smaller tributaries.

Mesopotamian Arabic, also known as Iraqi Arabic, or just as Iraqi, is a group of varieties of Arabic spoken in the Mesopotamian basin of Iraq, as well as in Syria, southeastern Turkey, Iran, Kuwait and Iraqi diaspora communities.

Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the region has been known by the traditional Arabic name of al-Jazira and the Syriac variant Gāzartā or Gozarto (ܓܙܪܬܐ). The Euphrates and Tigris rivers transform Mesopotamia into almost an island, as they are joined together at the Shatt al-Arab in the Basra Governorate of Iraq, and their sources in eastern Turkey are in close proximity.

The Mesopotamian campaign or Mesopotamian front was a campaign in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I fought between the Allies represented by the British Empire, troops from Britain, Australia and the vast majority from British Raj, against the Central Powers, mostly the Ottoman Empire. It started after British amphibious landings in 1914 which sought to protect Anglo-Persian oil fields in Khuzestan and the Shatt al-Arab. However, the front later evolved into a larger campaign that sought to capture the key city of Baghdad and divert Ottoman forces from other fronts. It ended with the Armistice of Mudros in 1918, leading to the cession of Iraq and further partition of the Ottoman Empire.

Beth Nahrain ; lit. 'home of the (two) rivers' is the name for the region known as Mesopotamia in the Syriac language. Geographically, it refers to the areas between and surrounding the Euphrates and Tigris rivers. The Aramaic name also refers to the area around the rivers, not only literally between the rivers.

Assyria was a short-lived Roman province in Mesopotamia that was created by Trajan in 116 during his campaign against the Parthian Empire. After Trajan's death, the newly proclaimed emperor Hadrian ordered the evacuation of Assyria in 118.

The Civilization of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often called a cradle of civilization.

Mesopotamia was the name of a Roman province, initially a short-lived creation of the Roman emperor Trajan in 116–117 and then re-established by Emperor Septimius Severus in c. 198. Control of the province was subsequently fought over between the Roman and the Sassanian empires until the Muslim conquests of the 7th century.

The Battle of Qurna, was between British forces and Ottoman forces that had retreated from Basra, which they lost at the Battle of Basra (1914) during the Mesopotamian campaign of World War I.
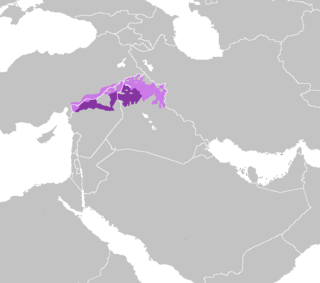
North Mesopotamian Arabic, also known as Moslawi, Mardelli, Mesopotamian Qeltu Arabic, or Syro-Mesopotamian Arabic, is one of the two main varieties of Mesopotamian Arabic, together with Gilit Mesopotamian Arabic.

The Mesopotamian Marshes, also known as the Iraqi Marshes, are a wetland area located in Southern Iraq and southwestern Iran. The marshes are primarily located on the floodplains of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers bound by the cities of Basra, Nasiriyah, Amarah and a portion of southwestern Iran. Historically the marshlands, mainly composed of the separate but adjacent Central, Hawizeh and Hammar Marshes, used to be the largest wetland ecosystem of Western Eurasia. The unique wetland landscape is home to the Marsh people, who have developed a unique culture tightly coupled to the landscape – harvesting reeds and rice, fishing, and herding water buffalo.
Al-Qurnah is a town in southern Iraq about 74 km northwest of Basra, that lies within the conglomeration of Nahairat. Qurna is located at the confluence point of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers to form the Shatt al-Arab waterway. Local folklore holds Qurnah to have been the original site of biblical paradise, the Garden of Eden, and location of the Tree of Knowledge.

The border between the Syrian Arab Republic and the Republic of Turkey is 909 kilometres (565 mi) long, and runs from the Mediterranean Sea in the west to the tripoint with Iraq in the east. It runs across Upper Mesopotamia for some 400 kilometres (250 mi), crossing the Euphrates and reaching as far as the Tigris. Much of the border follows the Southern Turkish stretch of the Baghdad Railway, roughly along the 37th parallel between the 37th and 42nd eastern meridians. In the west, it almost surrounds the Turkish Hatay Province, partly following the course of the Orontes River and reaching the Mediterranean coast at the foot of Jebel Aqra.

Lower Mesopotamia is a historical region of Mesopotamia. It is located in the alluvial plain of Iraq from the Hamrin Mountains to the Faw Peninsula near the Persian Gulf.

The Mesopotamian shrub desert is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in Western Asia. It extends across portions of Israel, Jordan, Syria, Iraq, and Iran.