
A metacestode is the larval stage of a tapeworm, found in an intermediate host. [1] [2] It can take various forms, for example, the hydatid cyst, strobilocercus, cysticercus or cysticercoid. [3]

A metacestode is the larval stage of a tapeworm, found in an intermediate host. [1] [2] It can take various forms, for example, the hydatid cyst, strobilocercus, cysticercus or cysticercoid. [3]
Echinococcosis is a parasitic disease of tapeworms of the Echinococcus type. The two main types of the disease are cystic echinococcosis and alveolar echinococcosis. Less common forms include polycystic echinococcosis and unicystic echinococcosis.
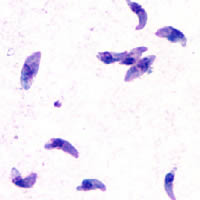
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or months of mild, flu-like illness such as muscle aches and tender lymph nodes. In a small number of people, eye problems may develop. In those with a weak immune system, severe symptoms such as seizures and poor coordination may occur. If a person becomes infected during pregnancy, a condition known as congenital toxoplasmosis may affect the child.

Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, T. gondii is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids, such as domestic cats, are the only known definitive hosts in which the parasite may undergo sexual reproduction.
Silva is a surname in Portuguese-speaking countries, such as Portugal and Brazil. It is derived from the Latin word silva, meaning "forest" or "woodland". It is the family name of the House of Silva.

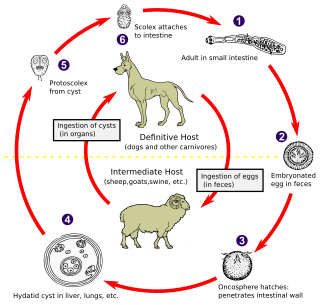
Echinococcus is a genus within cestoda, a parasitic class of the platyhelminthes phylum. Human echinococcosis is an infectious disease caused by the following species: E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, or E. vogeli.

Echinococcus granulosus, also called the hydatid worm, hyper tape-worm or dog tapeworm, is a cyclophyllid cestode that dwells in the small intestine of canids as an adult, but which has important intermediate hosts such as livestock and humans, where it causes cystic echinococcosis, also known as hydatid disease. The adult tapeworm ranges in length from 3 mm to 6 mm and has three proglottids ("segments") when intact—an immature proglottid, mature proglottid and a gravid proglottid. The average number of eggs per gravid proglottid is 823. Like all cyclophyllideans, E. granulosus has four suckers on its scolex ("head"), and E. granulosus also has a rostellum with hooks. Several strains of E. granulosus have been identified, and all but two are noted to be infective in humans.

Echinococcus multilocularis is a small cyclophyllid tapeworm found extensively in the northern hemisphere. E. multilocularis, along with other members of the Echinococcus genus, produce diseases known as echinococcosis. Unlike E. granulosus,E. multilocularis produces many small cysts that spread throughout the internal organs of the infected animal. The resultant disease is called Alveolar echinococcosis, and is caused by ingesting the eggs of E. multilocularis.

Schistosoma mansoni is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes (Schistosoma). The adult lives in the blood vessels near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis. Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease. As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 236.6 million people have schistosomiasis and most of it is due to S. mansoni. It is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Caribbean, Brazil, Venezuela and Suriname.
Echinococcus shiquicus is a parasitic worm first identified in 2005. It was found in Tibetan foxes in the Qinghai–Tibet plateau region. Two types of adult worms were recovered and the variant which had a short strobila consisting of single immature and single gravid segments constituted the majority of the specimens. The strobila, rostellar hooks, location of the genital pore and the number of eggs in gravid uterus helped in differentiating Echinococcus shiquicus from the other species. The metacestode of E. shiquicus was detected exclusively from plateau pikas. The larvae are unique and they develop into unilocular minicysts approximately 1 cm in diameter within the liver or lungs.

The Rio Mayo titi is a species of titi, a type of New World monkey, endemic to Peru. The Rio Mayo titi, was thought previously to have a small range of origin in the Alto Mayo valley, but research has proven that the range extends southward and reaches the Huayamba River, as well as Bajo Mayo. It had been classified as vulnerable but due to major habitat loss and restricted living space, it is now classified as Critically Endangered. In October 2012, it was included in The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates list. An increase in deforestation is leading to the decrease in available living space for this titi monkey, forcing it to live in sympatry with another species of Callicebus. Yet in some areas, such drastic deforestation has resulted in extremely high population density. The Rio Mayo titi is better adapted to moderately populated areas, thus overpopulation negatively impacts the species. The forests the Rio Mayo titi lives in are being destroyed for agricultural purposes, leaving little forest for the monkeys. They were only seen a few times and featured in museums until 2003 when more research was done on them. In order for this species to survive, their forests need to be protected to avoid overpopulation. Different conservation groups are working to help P. oenanthe survive. Neotropical Primate Conservation, Proyecto Mono Tocón and Amazónicos para la Amazonia are working in the more southern areas to protect the monkey. The Rio Mayo titi is a fairly inconspicuous creature, making observation and research difficult to obtain. Therefore, the traditional use of transect observation to monitor the monkey's population, is less effective. Instead, other methods of calculating the titi monkey's density in certain areas have been taken, such as research into the species-specific calls endemic to a certain area.

The cat flea is an extremely common parasitic insect whose principal host is the domestic cat, although a high proportion of the fleas found on dogs also belong to this species. This is despite the widespread existence of a separate and well-established "dog" flea, Ctenocephalides canis. Cat fleas originated in Africa but can now be found globally. As humans began domesticating cats, the prevalence of the cat flea increased and spread throughout the world.
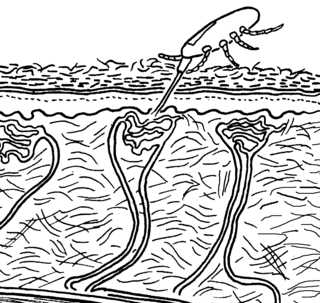
Gamasoidosis, or dermanyssosis, is a frequently unrecognized ectoparasitosis and source of growing concern in human medicine, occurring after contact with avian mites which infest canaries, sparrows, starlings, pigeons and poultry and caused by two genera of mites, Ornithonyssus and Dermanyssus. Avian mite species implicated include the red mite, tropical fowl mite and northern fowl mite . Mite dermatitis is also associated with rodents infested with the tropical rat mite, spiny rat mite and house-mouse mite, where the condition is known as rodent mite dermatitis. Urban gamasoidosis is associated with window-sills, ventilation and air-conditioning intakes, roofs and eaves, which serve as shelters for nesting birds. Humans bitten by these mites experience a non-specific dermatitis with intense itching.

Biomphalaria glabrata is a species of air-breathing freshwater snail, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails.
Taenia asiatica, commonly known as Asian taenia or Asian tapeworm, is a parasitic tapeworm of humans and pigs. It is one of the three species of Taenia infecting humans and causes taeniasis. Discovered only in 1980s from Taiwan and other East Asian countries as an unusual species, it is so notoriously similar to Taenia saginata, the beef tapeworm, that it was for a time regarded as a slightly different strain. But anomaly arose as the tapeworm is not of cattle origin, but of pigs. Morphological details also showed significant variations, such as presence of rostellar hooks, shorter body, and fewer body segments. The scientific name designated was then Asian T. saginata. But the taxonomic consensus turns out to be that it is a unique species. It was in 1993 that two Korean parasitologists, Keeseon S. Eom and Han Jong Rim, provided the biological bases for classifying it into a separate species. The use of mitochondrial genome sequence and molecular phylogeny in the late 2000s established the taxonomic status.

An oncosphere is the larval form of a tapeworm once it has been ingested by an intermediate host animal. The intermediate host must ingest the tapeworm's eggs either in food or water-- once this has happened, the eggs hatch and develop into oncospheres which will then burrow through the gut wall of the intermediate host in order to access the organs or tissues of that host where they will continue the next stage of their development as cysticerci or bladderworms. The bladderworm is a cyst created by the oncosphere. In order to become an adult tapeworm, a cysticercus must then be consumed by its definitive host and establish itself by anchoring in that host's digestive tract. From there, the worm will grow in length and eventually produce proglottids which will exit the intestinal tract with other waste material and then burst, releasing the worm's eggs and completing the cycle.