The atomic number or proton number of a chemical element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. It is identical to the charge number of the nucleus. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element. In an uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons.

An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers.

An alloy is a combination of metals and of a metal or another element. Alloys are defined by a metallic bonding character. An alloy may be a solid solution of metal elements or a mixture of metallic phases. Intermetallic compounds are alloys with a defined stoichiometry and crystal structure. Zintl phases are also sometimes considered alloys depending on bond types.

The plum pudding model is one of several historical scientific models of the atom. First proposed by J. J. Thomson in 1904 soon after the discovery of the electron, but before the discovery of the atomic nucleus, the model tried to explain two properties of atoms then known: that electrons are negatively-charged particles and that atoms have no net electric charge.

In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.
Chemistry is the scientific discipline involved with elements and compounds composed of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances.

A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. The bond may result from the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.

A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full outer shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration.
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulas can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than are chemical names and structural formulas.
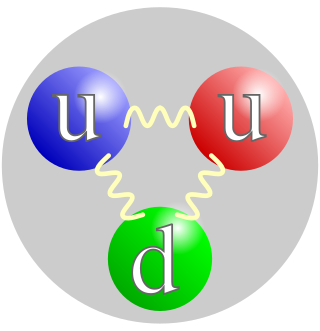
A proton is a subatomic particle, symbol
p
or
p+
, with a positive electric charge of +1e elementary charge and a mass slightly less than that of a neutron. Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are collectively referred to as "nucleons".

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:

Epicureanism is a system of philosophy based upon the teachings of the ancient Greek philosopher Epicurus, founded around 307 BC. Epicurus was an atomic materialist, following in the steps of Democritus. His materialism led him to a general attack on superstition and divine intervention. Following Aristippus—about whom very little is known—Epicurus believed that what he called "pleasure" (ἡδονή) was the greatest good, but that the way to attain such pleasure was to live modestly, to gain knowledge of the workings of the world, and to limit one's desires. This would lead one to attain a state of tranquility (ataraxia) and freedom from fear as well as an absence of bodily pain (aponia). The combination of these two states constitutes happiness in its highest form. Although Epicureanism is a form of hedonism insofar as it declares pleasure to be its sole intrinsic goal, the concept that the absence of pain and fear constitutes the greatest pleasure, and its advocacy of a simple life, make it very different from "hedonism" as colloquially understood.

RSS is a type of web feed which allows users and applications to access updates to online content in a standardized, computer-readable format. These feeds can, for example, allow a user to keep track of many different websites in a single news aggregator. The news aggregator will automatically check the RSS feed for new content, allowing the content to be automatically passed from website to website or from website to user. This passing of content is called web syndication. Websites usually use RSS feeds to publish frequently updated information, such as blog entries, news headlines, or episodes of audio and video series. RSS is also used to distribute podcasts. An RSS document includes full or summarized text, and metadata, like publishing date and author's name.

Captain Atom is a fictional superhero appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. Captain Atom has existed in three basic incarnations.

The name Atom applies to a pair of related Web standards. The Atom Syndication Format is an XML language used for web feeds, while the Atom Publishing Protocol is a simple HTTP-based protocol for creating and updating web resources.

The Rutherford model, also known as planetary model is a model which tried to describe an atom devised by Ernest Rutherford. Rutherford directed the famous Geiger–Marsden experiment in 1909 which suggested, upon Rutherford's 1911 analysis, that J. J. Thomson's plum pudding model of the atom was incorrect. Rutherford's new model for the atom, based on the experimental results, contained new features of a relatively high central charge concentrated into a very small volume in comparison to the rest of the atom and with this central volume also containing the bulk of the atomic mass of the atom. This region would be known as the "nucleus" of the atom.
Atomism is a natural philosophy that developed in several ancient traditions.

Atom Man vs. Superman is a 1950 Columbia Pictures film serial and the second Superman movie serial featuring Kirk Alyn as Superman. When Lex Luthor blackmails the city of Metropolis by threatening to destroy the entire community, Perry White, editor of the Daily Planet assigns Lois Lane, Jimmy Olsen and Clark Kent to cover the story.

A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules composed of atoms from more than one element held together by chemical bonds. A chemical element bonded to an identical chemical element is not a chemical compound since only one element, not two different elements, is involved.
Atom is a free and open-source text and source code editor for macOS, Linux, and Microsoft Windows with support for plug-ins written in Node.js, and embedded Git Control, developed by GitHub. Atom is a desktop application built using web technologies. Most of the extending packages have free software licenses and are community-built and maintained. Atom is based on Electron, a framework that enables cross-platform desktop applications using Chromium and Node.js. It is written in CoffeeScript and Less. It was able to be used as an integrated development environment (IDE), until that feature was 'retired' in December 2018. Atom was released from beta, as version 1.0, on 25 June 2015. Its developers call it a "hackable text editor for the 21st Century".