Related Research Articles

A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (C
5H−
5, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula (C5H5)2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride or vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to [Cp2ZrCH3]+ catalyze olefin polymerization.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.
A salt metathesis reaction, sometimes called a double displacement reaction, is a chemical process involving the exchange of bonds between two reacting chemical species which results in the creation of products with similar or identical bonding affiliations. This reaction is represented by the general scheme:

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel tetracarbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometallic complexes.
Iron shows the characteristic chemical properties of the transition metals, namely the ability to form variable oxidation states differing by steps of one and a very large coordination and organometallic chemistry: indeed, it was the discovery of an iron compound, ferrocene, that revolutionalized the latter field in the 1950s. Iron is sometimes considered as a prototype for the entire block of transition metals, due to its abundance and the immense role it has played in the technological progress of humanity. Its 26 electrons are arranged in the configuration [Ar]3d64s2, of which the 3d and 4s electrons are relatively close in energy, and thus it can lose a variable number of electrons and there is no clear point where further ionization becomes unprofitable.
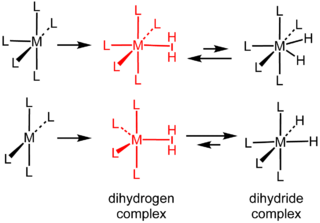
Dihydrogen complexes are coordination complexes containing intact H2 as a ligand. They are a subset of sigma complexes. The prototypical complex is W(CO)3(PCy3)2(H2). This class of compounds represent intermediates in metal-catalyzed reactions involving hydrogen. Hundreds of dihydrogen complexes have been reported. Most examples are cationic transition metals complexes with octahedral geometry.

Sodium cyclopentadienide is an organosodium compound with the formula C5H5Na. The compound is often abbreviated as NaCp, where Cp− is the cyclopentadienide anion. Sodium cyclopentadienide is a colorless solid, although samples often are pink owing to traces of oxidized impurities.

Cyclopentadienylcobalt dicarbonyl is an organocobalt compound with formula (C5H5)Co(CO)2, abbreviated CpCo(CO)2. It is an example of a half-sandwich complex. It is a dark red air sensitive liquid. This compound features one cyclopentadienyl ring that is bound in an η5-manner and two carbonyl ligands. The compound is soluble in common organic solvents.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. While iron adopts oxidation states from Fe(−II) through to Fe(VII), Fe(IV) is the highest established oxidation state for organoiron species. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.

Iron tetracarbonyl dihydride is the organometallic compound with the formula H2Fe(CO)4. This compound was the first transition metal hydride discovered. The complex is stable at low temperatures but decomposes rapidly at temperatures above –20 °C.
In chemistry, decarbonylation is a type of organic reaction that involves the loss of carbon monoxide (CO). It is often an undesirable reaction, since it represents a degradation. In the chemistry of metal carbonyls, decarbonylation describes a substitution process, whereby a CO ligand is replaced by another ligand.
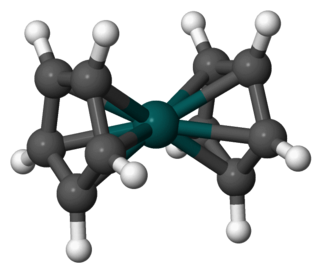
Rhodocene is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh(C5H5)2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar aromatic systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has (haptic) covalent rhodium–carbon bonds. The [Rh(C5H5)2] radical is found above 150 °C (302 °F) or when trapped by cooling to liquid nitrogen temperatures (−196 °C [−321 °F]). At room temperature, pairs of these radicals join via their cyclopentadienyl rings to form a dimer, a yellow solid.
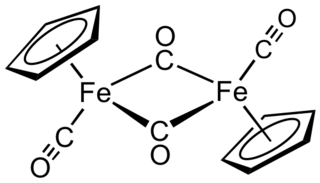
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(η5-C5H5)Fe(CO)2]2, often abbreviated to Cp2Fe2(CO)4, [CpFe(CO)2]2 or even Fp2, with the colloquial name "fip dimer". It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is reasonably stable to storage under air and serves as a convenient starting material for accessing other Fp (CpFe(CO)2) derivatives (described below).

Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl iodide is an organoiron compound with the formula (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I. It is a dark brown solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I, or FpI as it is often known, is an intermediate for the preparation of other organoiron compounds such as in ferraboranes.

Metal carbonyl hydrides are complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide and hydride as ligands. These complexes are useful in organic synthesis as catalysts in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation.
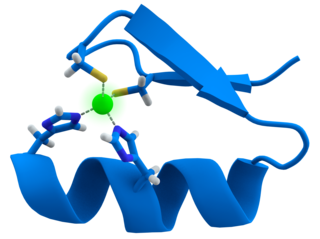
Transition metal thiolate complexes are metal complexes containing thiolate ligands. Thiolates are ligands that can be classified as soft Lewis bases. Therefore, thiolate ligands coordinate most strongly to metals that behave as soft Lewis acids as opposed to those that behave as hard Lewis acids. Most complexes contain other ligands in addition to thiolate, but many homoleptic complexes are known with only thiolate ligands. The amino acid cysteine has a thiol functional group, consequently many cofactors in proteins and enzymes feature cysteinate-metal cofactors.

A lanthanocene is a type of metallocene compound that contains an element from the lanthanide series. The most common lanthanocene complexes contain two cyclopentadienyl anions and an X type ligand, usually hydride or alkyl ligand.

Transition metal acyl complexes describes organometallic complexes containing one or more acyl (RCO) ligands. Such compounds occur as transient intermediates in many industrially useful reactions, especially carbonylations.
Germyl, trihydridogermanate(1-), trihydrogermanide, trihydridogermyl or according to IUPAC Red Book: germanide is an anion containing germanium bounded with three hydrogens, with formula GeH−3. Germyl is the IUPAC term for the –GeH3 group. For less electropositive elements the bond can be considered covalent rather than ionic as "germanide" indicates. Germanide is the base for germane when it loses a proton.
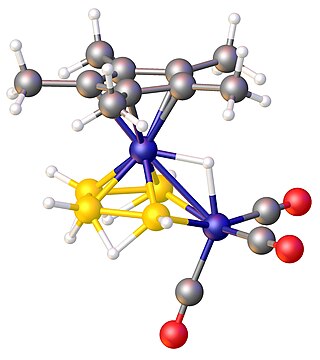
In chemistry, a metallaborane is a compound that contains one or more metal atoms and one or more boron hydride. These compounds are related conceptually and often synthetically to the boron-hydride clusters by replacement of BHn units with metal-containing fragments. Often these metal fragments are derived from metal carbonyls or cyclopentadienyl complexes. Their structures can often be rationalized by polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory. The inventory of these compounds is large, and their structures can be quite complex.
References
- ↑ James R. Sweet; William A. G. Graham (1982). "Hydrido and Hydroxycarbonyl Compounds of the Carbonyl(η-cyclopentadienyl)nitrosylrhenium Group". Organometallics. 1 (7): 982–986. doi:10.1021/om00067a016.
- ↑ Kolomnikov, T. V.; Lysyak, Yu (1988). "Metal-carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives". Russ. Chem. Rev. 57 (5): 406. Bibcode:1988RuCRv..57..406K. doi:10.1070/rc1988v057n05abeh003359. S2CID 250838386.
- ↑ Brunet, J. J. (1990). "Tetracarbonylhydridoferrates, MHFe(CO),: Versatile Tools in Organic Synthesis and Catalysis". Chem. Rev. 90 (6): 1041–1059. doi:10.1021/cr00104a006.
- ↑ Dombek, R. Duane; Angelici, Robert J. (1977). "Dicarbonyl(η5-Cyclopentadienylxthio-Carbonyl)Iron(1 +) Hexafluorophosphate(1 -) and Dicarbonyl(η 5-Cyclopentadienyl)-[(Methylthio)Thiocarbonyl]Iron". Inorganic Syntheses. 17: 100ff. doi:10.1002/9780470132487.ch29. ISBN 978-0-470-13248-7.