
Cis–trans isomerism, also known as geometric isomerism, describes certain arrangements of atoms within molecules. The prefixes "cis" and "trans" are from Latin: "this side of" and "the other side of", respectively. In the context of chemistry, cis indicates that the functional groups (substituents) are on the same side of some plane, while trans conveys that they are on opposing (transverse) sides. Cis–trans isomers are stereoisomers, that is, pairs of molecules which have the same formula but whose functional groups are in different orientations in three-dimensional space. Cis and trans isomers occur both in organic molecules and in inorganic coordination complexes. Cis and trans descriptors are not used for cases of conformational isomerism where the two geometric forms easily interconvert, such as most open-chain single-bonded structures; instead, the terms "syn" and "anti" are used.
In chemistry, a structural isomer of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept.

In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space. This contrasts with structural isomers, which share the same molecular formula, but the bond connections or their order differs. By definition, molecules that are stereoisomers of each other represent the same structural isomer.

A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state (higher energy) levels. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the 180m
73Ta
nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by 180m
73Ta
as well as 186m
75Re
, 192m2
77Ir
, 210m
83Bi
, 212m
84Po
, 242m
95Am
and multiple holmium isomers.

In organic chemistry, the cycloalkanes are the monocyclic saturated hydrocarbons. In other words, a cycloalkane consists only of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a structure containing a single ring, and all of the carbon-carbon bonds are single. The larger cycloalkanes, with more than 20 carbon atoms are typically called cycloparaffins. All cycloalkanes are isomers of alkenes.

Cyclohexanol is the organic compound with the formula HOCH(CH2)5. The molecule is related to cyclohexane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by a hydroxyl group. This compound exists as a deliquescent colorless solid with a camphor-like odor, which, when very pure, melts near room temperature. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.
Manganese(II) chloride is the dichloride salt of manganese, MnCl2. This inorganic chemical exists in the anhydrous form, as well as the dihydrate (MnCl2·2H2O) and tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), with the tetrahydrate being the most common form. Like many Mn(II) species, these salts are pink, with the paleness of the color being characteristic of transition metal complexes with high spin d5 configurations.

In organic chemistry, enolates are organic anions derived from the deprotonation of carbonyl compounds. Rarely isolated, they are widely used as reagents in the synthesis of organic compounds.
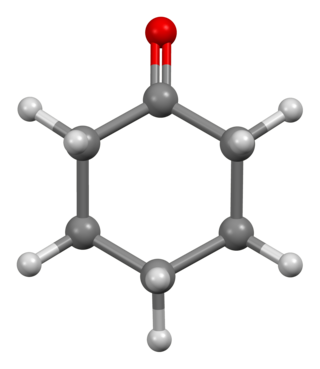
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.
In organic chemistry, the Knoevenagel condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction named after German chemist Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the aldol condensation.
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran (THF) by replacement of the methylene group (CH2) at the 2-position with an oxygen atom. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals.

Nucleophilic conjugate addition is a type of organic reaction. Ordinary nucleophilic additions or 1,2-nucleophilic additions deal mostly with additions to carbonyl compounds. Simple alkene compounds do not show 1,2 reactivity due to lack of polarity, unless the alkene is activated with special substituents. With α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds such as cyclohexenone it can be deduced from resonance structures that the β position is an electrophilic site which can react with a nucleophile. The negative charge in these structures is stored as an alkoxide anion. Such a nucleophilic addition is called a nucleophilic conjugate addition or 1,4-nucleophilic addition. The most important active alkenes are the aforementioned conjugated carbonyls and acrylonitriles.

The Doebner–Miller reaction is the organic reaction of an aniline with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds to form quinolines.
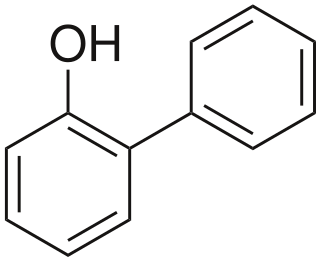
2-Phenylphenol, or o-phenylphenol, is an organic compound. In terms of structure, it is one of the monohydroxylated isomers of biphenyl. It is a white solid. It is a biocide used as a preservative with E number E231 and under the trade names Dowicide, Torsite, Fungal, Preventol, Nipacide and many others.

Ethinamate is a short-acting carbamate-derivative sedative-hypnotic medication used to treat insomnia. Regular use leads to drug tolerance, and it is usually not effective for more than 7 days. Prolonged use can lead to dependence.

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism refers to the existence or possibility of isomers.
Organomanganese chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to manganese chemical bond. In a 2009 review, Cahiez et al. argued that as manganese is cheap and benign, organomanganese compounds have potential as chemical reagents, although currently they are not widely used as such despite extensive research.

The Borsche–Drechsel cyclization is a chemical reaction used to synthesize tetrahydrocarbazoles by the acid-catalyzed cyclization of cyclohexanone arylhydrazones. The reaction was first described by Edmund Drechsel in 1888 and by Walter Borsche in 1908.
A cyclohexanetetrol is a chemical compound consisting of a cyclohexane molecule with four hydroxyl groups (–OH) replacing four of the twelve hydrogen atoms. It is therefore a cyclitol. Its generic formula is C
6H
12O
4 or C
6H
8(OH)
4.
3-Methylcyclohexene an organic compound consisting of cyclohexene with a methyl group substituent adjacent to the alkene group. Two other structural isomers are known: 1-methylcyclohexene and 4-methylcyclohexene. All are colorless volatile liquids classified as a cyclic olefins. They are specialized reagents.















