Related Research Articles

Orthopaedic surgery or orthopaedics, is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopaedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders.

Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant, that is, a hip prosthesis. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total replacement or a hemi (half) replacement. Such joint replacement orthopaedic surgery is generally conducted to relieve arthritis pain or in some hip fractures. A total hip replacement consists of replacing both the acetabulum and the femoral head while hemiarthroplasty generally only replaces the femoral head. Hip replacement is currently one of the most common orthopaedic operations, though patient satisfaction short- and long-term varies widely. Approximately 58% of total hip replacements are estimated to last 25 years. The average cost of a total hip replacement in 2012 was $40,364 in the United States, and about $7,700 to $12,000 in most European countries.
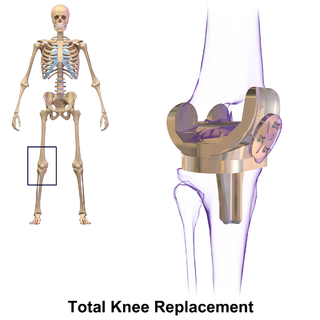
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the weight-bearing surfaces of the knee joint to relieve pain and disability. It is most commonly performed for osteoarthritis, and also for other knee diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. In patients with severe deformity from advanced rheumatoid arthritis, trauma, or long-standing osteoarthritis, the surgery may be more complicated and carry higher risk. Osteoporosis does not typically cause knee pain, deformity, or inflammation and is not a reason to perform knee replacement.

Computer-assisted orthopedic surgery or computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery is a discipline where computer technology is applied pre-, intra- and/or post-operatively to improve the outcome of orthopedic surgical procedures. Although records show that it has been implemented since the 1990s, CAOS is still an active research discipline which brings together orthopedic practitioners with traditionally technical disciplines, such as engineering, computer science and robotics.

Replacement arthroplasty, or joint replacement surgery, is a procedure of orthopedic surgery in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis. Joint replacement is considered as a treatment when severe joint pain or dysfunction is not alleviated by less-invasive therapies. It is a form of arthroplasty, and is often indicated from various joint diseases, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.

Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) is a surgical procedure used to relieve arthritis in one of the knee compartments in which the damaged parts of the knee are replaced. UKA surgery may reduce post-operative pain and have a shorter recovery period than a total knee replacement procedure, particularly in people over 75 years of age. Moreover, UKAs may require a smaller incision, less tissue damage, and faster recovery times.
Ankle replacement, or ankle arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the human ankle joint with prosthetic components. This procedure is becoming the treatment of choice for patients requiring arthroplasty, replacing the conventional use of arthrodesis, i.e. fusion of the bones. The restoration of range of motion is the key feature in favor of ankle replacement with respect to arthrodesis. However, clinical evidence of the superiority of the former has only been demonstrated for particular isolated implant designs.
John Nevil Insall (1930–2000) was a pioneering English orthopaedic surgeon who contributed extensively to the advancement of total knee replacement surgery. He designed four models of widely used systems.
Evan Flatow, M.D. is President of Mount Sinai West, part of the Mount Sinai Health System, and an American orthopaedic surgeon. Prior to Dr. Flatow's appointment as President of Mount Sinai West, he served as the Bernard J. Lasker Professor and Chair of the Leni and Peter W. May Department of Orthopaedic Surgery at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and as Director of the Orthopaedic Surgery Service at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City.
Professor Derek McMinn is a British orthopaedic surgeon and inventor who practises in Birmingham, United Kingdom at the BMI Edgbaston Hospital. Prof. McMinn developed the first successful modern metal-on-metal hip resurfacing and the instrumentation and surgical technique to implant it. Hip resurfacing is a bone-conserving, less invasive alternative to total hip replacement (THR) for young patients, markedly improves the health-related quality of life measures and currently makes up around a tenth of all hip arthroplasty procedures performed in the United Kingdom. McMinn is also the inventor of several other prostheses for the hip and knee.
Sean E. McCance, M.D., is an American orthopedic surgeon and Co-Director of Spine Surgery in the Leni and Peter W. May Department of Orthopaedics at the Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York City. Additionally, he is Associate Clinical Professor of Orthopaedics at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine and Attending Spine Physician at Lenox Hill Hospital.
Andrew C. Hecht, M.D., is an American orthopaedic surgeon and a nationally recognized leader in surgery on the spine.

David Giorgio Mendes Nassi is an Israeli orthopedic surgeon who has developed advanced methodologies and systems in the area of Hip and Knee artificial joint replacement. .

William H. Harris, is an American orthopaedic surgeon, Founder and Director Emeritus of the Massachusetts General Hospital Harris Orthopaedics Laboratory, and creator of the Advances in Arthroplasty course held annually since 1970.
Ashok Rajgopal is an Indian orthopaedic surgeon, credited with close to 20,000 Arthroscopic and over 35,000 Total Knee Arthroplasty surgeries and reported to be one of the most experienced in his field in India. He was honoured by the Government of India in 2014, by bestowing on him the Padmashri, the fourth highest civilian award, for his services to the fields of orthopaedic surgery. He has also been awarded the Dr. BC Roy award by the Medical Council of India to "Recognize the Best Talents in Encouraging the Development of Specialties in Different Branches in Medicine" for 2014.
Armin M. Tehrany, M.D., is an American orthopaedic surgeon, assistant clinical professor of orthopedic surgery at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, and film producer.

Raju Vaishya is an Indian researcher with contributions in the field of orthopaedics. He is former President and founder member of Indian Cartilage Society (2018–19) and Founder President of Arthritis Care Foundation. He has established a center for Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) at Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi, India. Instrumental (PSI) in starting the first cartilage club in Delhi, to enhance the awareness about the cartilage science and regenerative treatments used in Orthopaedics. He has the credit of doing the first preplan patient specific instruments (PSI) total knee arthroplasty, in Northern India in May 2013.
Dr. Javad Parvizi is an American Board Certified Orthopaedic Surgeon and the director of clinical research at the Rothman Orthopaedic Institute, Philadelphia. He holds the James Edwards Professor Chair of Orthopaedics at Thomas Jefferson University. He is the co-founder of the International Consensus Meeting and President of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society (MSIS).

Mount Sinai West, opened in 1871 as Roosevelt Hospital, is affiliated with the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Mount Sinai Health System.
References
- ↑ "Sunday House Call with Dr. Barry Dworkin". 3 September 2006. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ "Women Fitness - April News" . Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ "Biomet". Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ Michael O'Keeffe (December 11, 2007). "Local hospitals aid NFL retirees". New York Daily News.
- 1 2 3 4 "Mount Sinai Medical Center – Doctor profile" . Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ "healthgrades.com" . Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ "Lenox Hill Hospital" . Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ "New York County Medical Society". Archived from the original on June 27, 2002. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ "Independent Doctors of New York". Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved December 1, 2010.
- ↑ "Michael Bronson :: Doctor - New York, New York (NY) :: Doctor Profile :: Super Doctors".