Related Research Articles
Artificial consciousness (AC), also known as machine consciousness (MC), synthetic consciousness or digital consciousness, is the consciousness hypothesized to be possible in artificial intelligence. It is also the corresponding field of study, which draws insights from philosophy of mind, philosophy of artificial intelligence, cognitive science and neuroscience. The same terminology can be used with the term "sentience" instead of "consciousness" when specifically designating phenomenal consciousness.
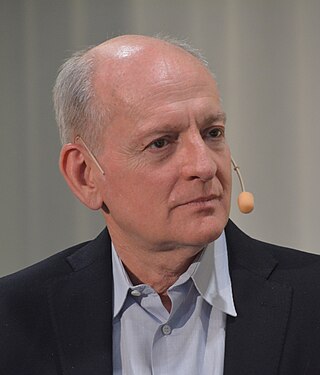
Stuart Jonathan Russell is a British computer scientist known for his contributions to artificial intelligence (AI). He is a professor of computer science at the University of California, Berkeley and was from 2008 to 2011 an adjunct professor of neurological surgery at the University of California, San Francisco. He holds the Smith-Zadeh Chair in Engineering at University of California, Berkeley. He founded and leads the Center for Human-Compatible Artificial Intelligence (CHAI) at UC Berkeley. Russell is the co-author with Peter Norvig of the authoritative textbook of the field of AI: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach used in more than 1,500 universities in 135 countries.

The School of Informatics is an academic unit of the University of Edinburgh, in Scotland, responsible for research, teaching, outreach and commercialisation in informatics. It was created in 1998 from the former department of artificial intelligence, the Centre for Cognitive Science and the department of computer science, along with the Artificial Intelligence Applications Institute (AIAI) and the Human Communication Research Centre.

Zoubin Ghahramani FRS is a British-Iranian researcher and Professor of Information Engineering at the University of Cambridge. He holds joint appointments at University College London and the Alan Turing Institute. and has been a Fellow of St John's College, Cambridge since 2009. He was Associate Research Professor at Carnegie Mellon University School of Computer Science from 2003–2012. He was also the Chief Scientist of Uber from 2016 until 2020. He joined Google Brain in 2020 as senior research director. He is also Deputy Director of the Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence.

Andrew Yan-Tak Ng is a British-American computer scientist and technology entrepreneur focusing on machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). Ng was a cofounder and head of Google Brain and was the former Chief Scientist at Baidu, building the company's Artificial Intelligence Group into a team of several thousand people.

Marta Zofia Kwiatkowska is a Polish theoretical computer scientist based in the United Kingdom.
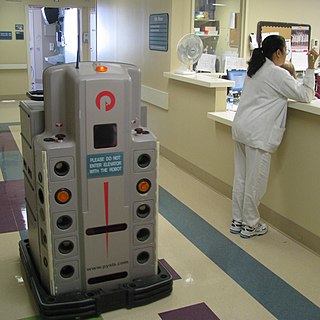
Technological unemployment is the loss of jobs caused by technological change. It is a key type of structural unemployment. Technological change typically includes the introduction of labour-saving "mechanical-muscle" machines or more efficient "mechanical-mind" processes (automation), and humans' role in these processes are minimized. Just as horses were gradually made obsolete as transport by the automobile and as labourer by the tractor, humans' jobs have also been affected throughout modern history. Historical examples include artisan weavers reduced to poverty after the introduction of mechanized looms. During World War II, Alan Turing's bombe machine compressed and decoded thousands of man-years worth of encrypted data in a matter of hours. A contemporary example of technological unemployment is the displacement of retail cashiers by self-service tills and cashierless stores.
Google Brain was a deep learning artificial intelligence research team under the umbrella of Google AI, a research division at Google dedicated to artificial intelligence. Formed in 2011, it combined open-ended machine learning research with information systems and large-scale computing resources. It created tools such as TensorFlow, which allow neural networks to be used by the public, and multiple internal AI research projects, and aimed to create research opportunities in machine learning and natural language processing. It was merged into former Google sister company DeepMind to form Google DeepMind in April 2023.
Brendan John Frey FRSC is a Canadian-born entrepreneur, engineer and scientist. He is Founder and CEO of Deep Genomics, Cofounder of the Vector Institute for Artificial Intelligence and Professor of Engineering and Medicine at the University of Toronto. Frey is a pioneer in the development of machine learning and artificial intelligence methods, their use in accurately determining the consequences of genetic mutations, and in designing medications that can slow, stop or reverse the progression of disease.
Murray Patrick Shanahan is a professor of Cognitive Robotics at Imperial College London, in the Department of Computing, and a senior scientist at DeepMind. He researches artificial intelligence, robotics, and cognitive science.

Carl Benedikt Frey is a Swedish-German economist and economic historian. He is the Dieter Schwarz Associate Professor of AI & Work at the Oxford Internet Institute and a Fellow of Mansfield College, University of Oxford. He is also Director of the Future of Work Programme and Oxford Martin Citi Fellow at the Oxford Martin School.
Paul Michael Newman is a British engineer and academic, the BP Professor of Information Engineering at the University of Oxford, and a Fellow of Keble College, Oxford. He is head of the Oxford Mobile Robotics Group (MRG) and CTO at Oxa.
Yee-Whye Teh is a professor of statistical machine learning in the Department of Statistics, University of Oxford. Prior to 2012 he was a reader at the Gatsby Charitable Foundation computational neuroscience unit at University College London. His work is primarily in machine learning, artificial intelligence, statistics and computer science.

Pieter Abbeel is a professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences, Director of the Berkeley Robot Learning Lab, and co-director of the Berkeley AI Research (BAIR) Lab at the University of California, Berkeley. He is also the co-founder of covariant.ai, a venture-funded start-up that aims to teach robots new, complex skills, and co-founder of Gradescope, an online grading system that has been implemented in over 500 universities nationwide. He is best known for his cutting-edge research in robotics and machine learning, particularly in deep reinforcement learning. In 2021, he joined AIX Ventures as an Investment Partner. AIX Ventures is a venture capital fund that invests in artificial intelligence startups.
In futurology, political science, and science fiction, a post-work society is a society in which the nature of work has been radically transformed and traditional employment has largely become obsolete due to technological progress.

Information engineering is the engineering discipline that deals with the generation, distribution, analysis, and use of information, data, and knowledge in systems. The field first became identifiable in the early 21st century.

Sandra Wachter is a professor and senior researcher in data ethics, artificial intelligence, robotics, algorithms and regulation at the Oxford Internet Institute. She is a former Fellow of The Alan Turing Institute.

Ai-Da is "the world's first ultra-realistic humanoid robot" artist. Completed in 2019, Ai-Da is an artificial intelligence robot that makes drawings, painting, and sculptures. It is named after Ada Lovelace The robot gained international attention when it was able to draw people from sight with a pencil using her bionic hand and cameras in her eyes.

Mind Foundry is an artificial intelligence company that is headquartered in Oxford, Oxfordshire. The company is a spin-out of the University of Oxford and was founded by two professors of machine learning at the university, Stephen Roberts. and Michael Osborne. The company specialises in “AI for high-stakes applications”. Mind Foundry primarily operates in three sectors: Insurance, Infrastructure, and Defence & National Security.
Stephen Roberts FREng is a British academic and scientist. He is a professor of machine learning at University of Oxford and leads the Machine Learning Research Group, a sub-group of the Department of Engineering Science.
References
- 1 2 @maosbot (October 19, 2021). "When I got #LongCovid in March 2020" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ↑ "home - Machine Learning Research Group". www.robots.ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-11-06.
- ↑ Foundry, Mind. "AI For High-Stakes Applications. Responsible, By Design". www.mindfoundry.ai. Retrieved 2023-11-06.
- ↑ "Oxford machine learning spinout unlocks big data insights | University of Oxford". www.ox.ac.uk. 2016-03-02. Retrieved 2023-10-19.
- ↑ @maosbot (December 2, 2023). "They say masks don't work, but" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- ↑ "About · Michael A Osborne". www.robots.ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-11-06.
- ↑ "Michael Osborne Academic CV" (PDF).
- ↑ "Michael A Osborne ResearchGate publications".
- ↑ "Michael A Osborne". scholar.google.co.uk. Retrieved 2023-11-06.
- ↑ "Michael Osborne". AI for Good. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "Professor Michael Osborne: Meeting the needs of society with AI". oxford.shorthandstories.com. Retrieved 2024-01-05.
- ↑ Hennig, P.; Osborne, M. A.; Kersting, H. P. (2022). Probabilistic Numerics (PDF). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1107163447.
- ↑ "The Future of Employment: How Susceptible are Jobs to Computerisation?". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "Carl Benedikt Frey". scholar.google.com. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "Carl Benedikt Frey and Michael Osborne on how AI benefits lower-skilled workers". The Economist. ISSN 0013-0613 . Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ Dunn, Will (2023-01-28). "Carl Benedikt Frey: in an automated future, trade unions will be more important than ever". New Statesman. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "25 January 2023 - Governance of artificial intelligence (AI) - Oral evidence".
- ↑ Correspondent, Rhys Blakely, Science (2023-11-08). "Rogue AI 'could kill everyone'". The Times . ISSN 0140-0460 . Retrieved 2023-11-08.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Rogue AI 'could kill everyone,' scientists warn". 2023-01-26. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "Professor Michael Osborne". Exeter College. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "Michael Osborne". www.ellis.ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "Michael Osborne". eng.ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "Professor Michael Osborne". Oxford Martin School. Retrieved 2023-11-06.
- ↑ "Academics". aims.robots.ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-11-06.