Diagnosis
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (March 2019) |
| Microcephaly lymphoedema chorioretinal dysplasia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MLCRD syndrome |
Microcephaly lymphoedema chorioretinal dysplasia also known as lymphedema microcephaly chorioretinopathy syndrome [1] is a rare genetic condition associated with:
In 1992, Feingold and Bartoshesky described two unrelated children with microcephaly, lymphoedema and chorioretinal dysplasia (MIM 152950) as a distinct entity. Since then there have been further reports of children with these three features (Angle et al. 1994, Fryns et al. 1995, Limwongse et al. 1999, Casteels et al. 2001)
Children have also been seen with two of the above features:
The distinct facial feature include upslanting palpebral fissures, a broad nose with rounded tip, long philtrum with a thin upper lip, pointed chin and prominent ears (Vasudevan 2005)
The former (microcephaly and lymphoedema) has been described as an autosomal dominant (MIM 156590) or X-linked trait, while the latter (microcephaly and chorioretinal dysplasia) has been described as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive (MIM 251270 or Mirhosseini-Holmes-Walton syndrome) or X-linked trait.
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (March 2019) |

Macrocephaly is a condition in which circumference of the human head is abnormally large. It may be pathological or harmless, and can be a familial genetic characteristic. People diagnosed with macrocephaly will receive further medical tests to determine whether the syndrome is accompanied by particular disorders. Those with benign or familial macrocephaly are considered to have megalencephaly.

Sabinas brittle hair syndrome, also called Sabinas syndrome or brittle hair-mental deficit syndrome, is an autosomal recessive congenital disorder affecting the integumentary system.

Ectodermal dysplasia (ED) is a group of genetic syndromes all deriving from abnormalities of the ectodermal structures. More than 150 different syndromes have been identified.

Popliteal pterygium syndrome (PPS) is an inherited condition affecting the face, limbs, and genitalia. The syndrome goes by a number of names including the popliteal web syndrome and, more inclusively, the facio-genito-popliteal syndrome. The term PPS was coined by Gorlin et al. in 1968 on the basis of the most unusual anomaly, the popliteal pterygium.

Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder, characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis), which affects the shape of the head and face. The syndrome includes abnormalities of the hands and feet, such as wide and deviated thumbs and big toes.
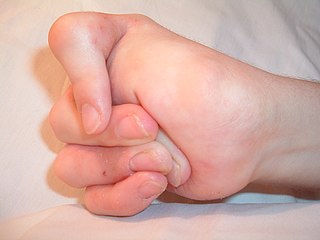
Freeman–Sheldon syndrome (FSS) is a very rare form of multiple congenital contracture (MCC) syndromes (arthrogryposes) and is the most severe form of distal arthrogryposis (DA). It was originally described by Ernest Arthur Freeman and Joseph Harold Sheldon in 1938.

Raine syndrome (RNS), also called osteosclerotic bone dysplasia, is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder characterized by craniofacial anomalies including microcephaly, noticeably low set ears, osteosclerosis, a cleft palate, gum hyperplasia, a hypoplastic nose, and eye proptosis. It is considered to be a lethal disease, and usually leads to death within a few hours of birth. However, a recent report describes two studies in which children with Raine syndrome have lived to 8 and 11 years old, so it is currently proposed that there is a milder expression that the phenotype can take.

Feingold syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant hereditary disorder. It is named after Murray Feingold, an American physician who first described the syndrome in 1975. Until 2003, at least 79 patients have been reported worldwide.

Progressive ankylosis protein homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANKH gene.

Oral-facial-digital syndrome 1 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OFD1 gene.

Dymeclin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYM gene.
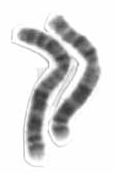
2p15-16.1 microdeletion is an extremely rare genetic disorder caused by a small deletion in the short arm of human chromosome 2. First described in two patients in 2007, by 2013 only 21 people have been reported as having the disorder in the medical literature.
Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome was formerly thought to be a unique autosomal dominant disorder due to a P63 gene mutation. However, it was recently shown to the same disease as Hay–Wells syndrome.

Hennekam syndrome also known as intestinal lymphagiectasia–lymphedema–mental retardation syndrome, is an autosomal recessive disorder consisting of intestinal lymphangiectasia, facial anomalies, peripheral lymphedema, and mild to moderate levels of growth and intellectual disability.

Fryns syndrome is an autosomal recessive multiple congenital anomaly syndrome that is usually lethal in the neonatal period. Fryns (1987) reviewed the syndrome.

Floating–Harbor syndrome, also known as Pelletier–Leisti syndrome, is a rare disease with fewer than 50 cases described in the literature. It is usually diagnosed in early childhood and is characterized by the triad of proportionate short stature with delayed bone age, characteristic facial appearance, and delayed speech development. Although its cause is unknown, it is thought to result from genetic mutation, and diagnosis is established by the presence of a heterozygous SRCAP mutation in those with clinical findings of FHS.
Focal facial dermal dysplasia is a rare genetically heterogeneous group of disorders that are characterized by congenital bilateral scar like facial lesions, with or without associated facial anomalies. It is characterized by hairless lesions with fingerprint like puckering of the skin, especially at the temples, due to alternating bands of dermal and epidermal atrophy.
Acro–dermato–ungual–lacrimal–tooth syndrome is a rare genetic disease. It is an autosomal dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia, a group of disorders that affects the hair, teeth, nails, sweat glands, and extremities. The syndrome arises from a mutation in the TP63 gene. This disease was previously thought to be a form of ectrodactyly–ectodermal dysplasia–cleft syndrome (EEC), but was classified as a different disease in 1993 by Propping and Zerres.

Ischiopatellar dysplasia is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by a hypoplasia of the patellae as well as other bone anomalies, especially concerning the pelvis and feet. It is also known as small patella syndrome, with earlier synonyms being Scott-Taor syndrome, Coxo-podo-patellar syndrome, Patella aplasia, coxa vara, tarsal synostosis, Congenital coxa vara, patella aplasia and tarsal synostosis ischiocoxopodopatellar syndrome.