Related Research Articles

A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating population information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices.
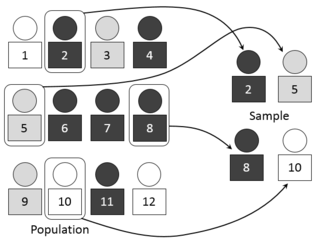
In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. Statisticians attempt to collect samples that are representative of the population. Sampling has lower costs and faster data collection compared to recording data from the entire population, and thus, it can provide insights in cases where it is infeasible to measure an entire population.
Statistics Canada, formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in Ottawa.

The American Community Survey (ACS) is an annual demographics survey program conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the decennial census, including ancestry, citizenship, educational attainment, income, language proficiency, migration, disability, employment, and housing characteristics. These data are used by many public-sector, private-sector, and not-for-profit stakeholders to allocate funding, track shifting demographics, plan for emergencies, and learn about local communities. Sent to approximately 295,000 addresses monthly, it is the largest household survey that the Census Bureau administers.
A statistical database is a database used for statistical analysis purposes. It is an OLAP, instead of OLTP system. Modern decision, and classical statistical databases are often closer to the relational model than the multidimensional model commonly used in OLAP systems today.
Integrated Public Use Microdata Series (IPUMS) is the world's largest individual-level population database. IPUMS consists of microdata samples from United States (IPUMS-USA) and international (IPUMS-International) census records, as well as data from U.S. and international surveys. The records are converted into a consistent format and made available to researchers through a web-based data dissemination and analysis system.
In medical research, social science, and biology, a cross-sectional study is a type of observational study that analyzes data from a population, or a representative subset, at a specific point in time—that is, cross-sectional data.
The 1860 United States census was the eighth census conducted in the United States starting June 1, 1860, and lasting five months. It determined the population of the United States to be 31,443,322 in 33 states and 10 organized territories. This was an increase of 35.4 percent over the 23,069,876 persons enumerated during the 1850 census. The total population included 3,953,762 slaves.

The 1880 United States census, conducted by the Census Office during June of 1880, was the tenth United States census. It was the first time that women were permitted to be enumerators. The Superintendent of the Census was Francis Amasa Walker. This was the first census in which a city—New York City—recorded a population of over one million, and the first census in which the 20 most populated cities all recorded over 100,000 residents.

Aggregate data is high-level data which is acquired by combining individual-level data. For instance, the output of an industry is an aggregate of the firms’ individual outputs within that industry. Aggregate data are applied in statistics, data warehouses, and in economics.

Data collection or data gathering is the process of gathering and measuring information on targeted variables in an established system, which then enables one to answer relevant questions and evaluate outcomes. Data collection is a research component in all study fields, including physical and social sciences, humanities, and business. While methods vary by discipline, the emphasis on ensuring accurate and honest collection remains the same. The goal for all data collection is to capture evidence that allows data analysis to lead to the formulation of credible answers to the questions that have been posed.
Barnardisation is a method of statistical disclosure control for tables of counts. It involves adding +1, 0 or -1 to some or all of the internal non-zero cells in a table in a pseudo-random fashion. The probability of adjustment for each internal cell is calculated as p/2, 1-p, p/2. The table totals are then calculated as the sum of the post-adjustment internal counts.
The North Atlantic Population Project (NAPP) is a collaboration of historical demographers in Britain, Canada, Denmark, Germany, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden to produce a massive census microdata collection for the North Atlantic Region in the late-nineteenth century. The database includes complete individual-level census enumerations for each country, and provides information on over 110 million people. This large scale allows detailed analysis of small geographic areas and population subgroups.
Differential privacy (DP) is an approach for providing privacy while sharing information about a group of individuals, by describing the patterns within the group while withholding information about specific individuals. This is done by making arbitrary small changes to individual data that do not change the statistics of interest. Thus the data cannot be used to infer much about any individual.
The Minnesota Population Center (MPC) is a university-wide interdisciplinary research center at the University of Minnesota. MPC was established in 2000, absorbing two earlier population research organizations. The primary goals of the center are to foster large-scale cross-disciplinary research collaborations and to provide shared infrastructure for demographic research. The center now has 100 faculty affiliates from 10 University of Minnesota Colleges, over 50 graduate student affiliates and 120 administrative and research staff.
Privacy for research participants is a concept in research ethics which states that a person in human subject research has a right to privacy when participating in research. Some typical scenarios this would apply to include, or example, a surveyor doing social research conducts an interview with a participant, or a medical researcher in a clinical trial asks for a blood sample from a participant to see if there is a relationship between something which can be measured in blood and a person's health. In both cases, the ideal outcome is that any participant can join the study and neither the researcher nor the study design nor the publication of the study results would ever identify any participant in the study. Thus, the privacy rights of these individuals can be preserved.
Statistics Botswana (StatsBots) is the National statistical bureau of Botswana. The organization was previously under the Ministry of Finance and development planning as a department and was called Central Statistics Office. The organisation was initially set up in 1967 through an Act of Parliament – the Statistics Act and thereafter transformed into a parastatal through the revised Statistics Act of 2009. This act gives the Statistics Botswana the mandate and authority to collect, process, compile, analyse, publish, disseminate and archive official national statistics. It is also responsible for "coordinating, monitoring and supervising the National Statistical System" in Botswana. The office has its main offices in Gaborone and three satellite offices in Maun, Francistown and Ghanzi. The different areas in statistics that should be collected are covered under this Act and are clearly specified. The other statistics that are not specified can be collected as long as they are required by the Government, stakeholders and the users.
Statistical disclosure control (SDC), also known as statistical disclosure limitation (SDL) or disclosure avoidance, is a technique used in data-driven research to ensure no person or organization is identifiable from the results of an analysis of survey or administrative data, or in the release of microdata. The purpose of SDC is to protect the confidentiality of the respondents and subjects of the research.
The National Pupil Database (NPD) is a database controlled by the Department for Education in England, based on multiple data collections from individuals age 2-21 in state funded education and higher education. Data are matched using pupil names, dates of birth and other personal and school characteristics, including special educational needs, disability, and indicators for free school meals, a child in care, and families in the armed forces. Personal details are linked to pupils' attainment and exam results over a lifetime school attendance.
The Fay–Herriot model is a statistical model which includes some distinct variation for each of several subgroups of observations. It is an area-level model, meaning some input data are associated with sub-aggregates such as regions, jurisdictions, or industries. The model produces estimates about the subgroups. The model is applied in the context of small area estimation in which there is a lot of data overall, but not much for each subgroup.
References
- 1 2 "IPUMS-l: FAQ". IPUMS International.
- ↑ "IPUMSl-Confidentiality". Minnesota Population Center, University of Minnesota. Archived from the original on 2007-08-23.