Related Research Articles
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology.

Southern blot is a method used for detection and quantification of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples. This method is used in molecular biology. Briefly, purified DNA from a biological sample is digested with restriction enzymes, and the resulting DNA fragments are separated by using an electric current to move them through a sieve-like gel or matrix, which allows smaller fragments to move faster than larger fragments. The DNA fragments are transferred out of the gel or matrix onto a solid membrane, which is then exposed to a DNA probe labeled with a radioactive, fluorescent, or chemical tag. The tag allows any DNA fragments containing complementary sequences with the DNA probe sequence to be visualized within the Southern blot.
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.

The western blot, or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination.

Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is primarily used to measure the amount of a specific RNA. This is achieved by monitoring the amplification reaction using fluorescence, a technique called real-time PCR or quantitative PCR (qPCR). Combined RT-PCR and qPCR are routinely used for analysis of gene expression and quantification of viral RNA in research and clinical settings.

A DNA microarray is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles of a specific DNA sequence, known as probes. These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridize a cDNA or cRNA sample under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of fluorophore-, silver-, or chemiluminescence-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was invented by Patrick O. Brown. An example of its application is in SNPs arrays for polymorphisms in cardiovascular diseases, cancer, pathogens and GWAS analysis. It is also used for the identification of structural variations and the measurement of gene expression.

Electron ionization is an ionization method in which energetic electrons interact with solid or gas phase atoms or molecules to produce ions. EI was one of the first ionization techniques developed for mass spectrometry. However, this method is still a popular ionization technique. This technique is considered a hard ionization method, since it uses highly energetic electrons to produce ions. This leads to extensive fragmentation, which can be helpful for structure determination of unknown compounds. EI is the most useful for organic compounds which have a molecular weight below 600. Also, several other thermally stable and volatile compounds in solid, liquid and gas states can be detected with the use of this technique when coupled with various separation methods.

Elemental analysis is a process where a sample of some material is analyzed for its elemental and sometimes isotopic composition. Elemental analysis can be qualitative, and it can be quantitative. Elemental analysis falls within the ambit of analytical chemistry, the instruments involved in deciphering the chemical nature of our world.
In molecular biology, a hybridization probe(HP) is a fragment of DNA or RNA of usually 15–10000 nucleotide long which can be radioactively or fluorescently labeled. HP can be used to detect the presence of nucleotide sequences in analyzed RNA or DNA that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. The labeled probe is first denatured (by heating or under alkaline conditions such as exposure to sodium hydroxide) into single stranded DNA (ssDNA) and then hybridized to the target ssDNA (Southern blotting) or RNA (northern blotting) immobilized on a membrane or in situ.
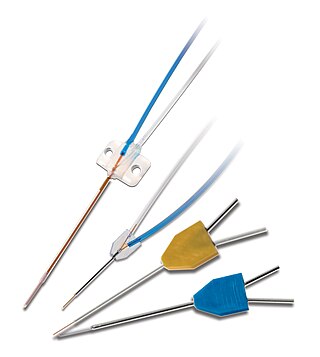
Microdialysis is a minimally-invasive sampling technique that is used for continuous measurement of free, unbound analyte concentrations in the extracellular fluid of virtually any tissue. Analytes may include endogenous molecules to assess their biochemical functions in the body, or exogenous compounds to determine their distribution within the body. The microdialysis technique requires the insertion of a small microdialysis catheter into the tissue of interest. The microdialysis probe is designed to mimic a blood capillary and consists of a shaft with a semipermeable hollow fiber membrane at its tip, which is connected to inlet and outlet tubing. The probe is continuously perfused with an aqueous solution (perfusate) that closely resembles the (ionic) composition of the surrounding tissue fluid at a low flow rate of approximately 0.1-5μL/min. Once inserted into the tissue or (body)fluid of interest, small solutes can cross the semipermeable membrane by passive diffusion. The direction of the analyte flow is determined by the respective concentration gradient and allows the usage of microdialysis probes as sampling as well as delivery tools. The solution leaving the probe (dialysate) is collected at certain time intervals for analysis.
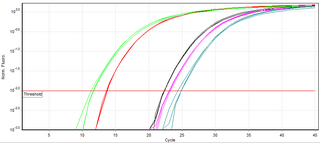
A real-time polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR, not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively and semi-quantitatively.

A molecular-weight size marker, also referred to as a protein ladder, DNA ladder, or RNA ladder, is a set of standards that are used to identify the approximate size of a molecule run on a gel during electrophoresis, using the principle that molecular weight is inversely proportional to migration rate through a gel matrix. Therefore, when used in gel electrophoresis, markers effectively provide a logarithmic scale by which to estimate the size of the other fragments.
SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles. SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase of interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.

A nucleic acid test (NAT) is a technique used to detect a particular nucleic acid sequence and thus usually to detect and identify a particular species or subspecies of organism, often a virus or bacterium that acts as a pathogen in blood, tissue, urine, etc. NATs differ from other tests in that they detect genetic materials rather than antigens or antibodies. Detection of genetic materials allows an early diagnosis of a disease because the detection of antigens and/or antibodies requires time for them to start appearing in the bloodstream. Since the amount of a certain genetic material is usually very small, many NATs include a step that amplifies the genetic material—that is, makes many copies of it. Such NATs are called nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs). There are several ways of amplification, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR), strand displacement assay (SDA), or transcription mediated assay (TMA).
OLIGO Primer Analysis Software was the first publicly available software for DNA primer design. The first papers describing this software were published in 1989 and 1990, and consecutive upgrades in the 1990s and 2000s, all have been cited together over 600 times in scientific journals and over 500 times in patents. The program is a comprehensive real time PCR primer and probe search and analysis tool, and also does other tasks such as siRNA and molecular beacon searches, open reading frame, restriction enzyme analysis, etc. It has been created and maintained by Wojciech Rychlik and Piotr Rychlik. The OLIGO has been reviewed several times in scientific journals, for the first time in 1991 in a review in Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and for its next upgrades.
The reverse northern blot is a method by which gene expression patterns may be analyzed by comparing isolated RNA molecules from a tester sample to samples in a control cDNA library. It is a variant of the northern blot in which the nucleic acid immobilized on a membrane is a collection of isolated DNA fragments rather than RNA, and the probe is RNA extracted from a tissue and radioactively labelled. A reverse northern blot can be used to profile expression levels of particular sets of RNA sequences in a tissue or to determine presence of a particular RNA sequence in a sample. Although DNA Microarrays and newer next-generation techniques have generally supplanted reverse northern blotting, it is still utilized today and provides a relatively cheap and easy means of defining expression of large sets of genes.
Molecular Inversion Probe (MIP) belongs to the class of Capture by Circularization molecular techniques for performing genomic partitioning, a process through which one captures and enriches specific regions of the genome. Probes used in this technique are single stranded DNA molecules and, similar to other genomic partitioning techniques, contain sequences that are complementary to the target in the genome; these probes hybridize to and capture the genomic target. MIP stands unique from other genomic partitioning strategies in that MIP probes share the common design of two genomic target complementary segments separated by a linker region. With this design, when the probe hybridizes to the target, it undergoes an inversion in configuration and circularizes. Specifically, the two target complementary regions at the 5’ and 3’ ends of the probe become adjacent to one another while the internal linker region forms a free hanging loop. The technology has been used extensively in the HapMap project for large-scale SNP genotyping as well as for studying gene copy alterations and characteristics of specific genomic loci to identify biomarkers for different diseases such as cancer. Key strengths of the MIP technology include its high specificity to the target and its scalability for high-throughput, multiplexed analyses where tens of thousands of genomic loci are assayed simultaneously.
COLD-PCR is a modified polymerase chain reaction (PCR) protocol that enriches variant alleles from a mixture of wildtype and mutation-containing DNA. The ability to preferentially amplify and identify minority alleles and low-level somatic DNA mutations in the presence of excess wildtype alleles is useful for the detection of mutations. Detection of mutations is important in the case of early cancer detection from tissue biopsies and body fluids such as blood plasma or serum, assessment of residual disease after surgery or chemotherapy, disease staging and molecular profiling for prognosis or tailoring therapy to individual patients, and monitoring of therapy outcome and cancer remission or relapse. Common PCR will amplify both the major (wildtype) and minor (mutant) alleles with the same efficiency, occluding the ability to easily detect the presence of low-level mutations. The capacity to detect a mutation in a mixture of variant/wildtype DNA is valuable because this mixture of variant DNAs can occur when provided with a heterogeneous sample – as is often the case with cancer biopsies. Currently, traditional PCR is used in tandem with a number of different downstream assays for genotyping or the detection of somatic mutations. These can include the use of amplified DNA for RFLP analysis, MALDI-TOF genotyping, or direct sequencing for detection of mutations by Sanger sequencing or pyrosequencing. Replacing traditional PCR with COLD-PCR for these downstream assays will increase the reliability in detecting mutations from mixed samples, including tumors and body fluids.

Viral metagenomics is the metagenomic study of viral genetic material obtained from environmental DNA samples or clinical DNA samples obtained from a host or natural reservoir. Metagenomic methods can be applied to study viruses in any system and has been used to describe various viruses associated with cancerous tumors, extreme environments, terrestrial ecosystems, and the blood and feces of humans. The term virome is also used to refer to viruses investigated by metagenomic sequencing of viral nucleic acids and is frequently used to describe environmental shotgun metagenomes. Viral metagenomics is a culture independent methodology that provides insights on viral diversity, abundance, and functional potential of viruses within the environment. Viruses lack a universal phylogenetic marker making metagenomics the only way to assess the genetic diversity of viruses in an environmental sample. With the advancements of techniques that can exploit next-generation sequencing, viruses can now be studied outside of culturable virus-host pairs. This approach has created improvements in molecular epidemiology and accelerated the discovery of novel viruses.
Chemoproteomics entails a broad array of techniques used to identify and interrogate protein-small molecule interactions. Chemoproteomics complements phenotypic drug discovery, a paradigm that aims to discover lead compounds on the basis of alleviating a disease phenotype, as opposed to target-based drug discovery, in which lead compounds are designed to interact with predetermined disease-driving biological targets. As phenotypic drug discovery assays do not provide confirmation of a compound's mechanism of action, chemoproteomics provides valuable follow-up strategies to narrow down potential targets and eventually validate a molecule's mechanism of action. Chemoproteomics also attempts to address the inherent challenge of drug promiscuity in small molecule drug discovery by analyzing protein-small molecule interactions on a proteome-wide scale. A major goal of chemoproteomics is to characterize the interactome of drug candidates to gain insight into mechanisms of off-target toxicity and polypharmacology.
References
- ↑ Kaukinen KH, Supernault KJ, Miller KM (2004). "Enrichment of tetranucleotide microsatellite loci from invertebrate species". Journal of Shellfish Research. 23 (2): 621.
- ↑ Jennings, TN; Knaus, BJ; Mullins, TD; Haig, SM; Cronn, RC (2011-06-16). "Multiplexed microsatellite recovery using massively parallel sequencing". Molecular Ecology Resources. 11 (6): 1060–7. doi:10.1111/j.1755-0998.2011.03033.x. PMID 21676207. S2CID 42109222.