
Irrigation is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been developed by many cultures around the world. Irrigation helps to grow crops, maintain landscapes, and revegetate disturbed soils in dry areas and during times of below-average rainfall. In addition to these uses, irrigation is also employed to protect crops from frost, suppress weed growth in grain fields, and prevent soil consolidation. It is also used to cool livestock, reduce dust, dispose of sewage, and support mining operations. Drainage, which involves the removal of surface and sub-surface water from a given location, is often studied in conjunction with irrigation.
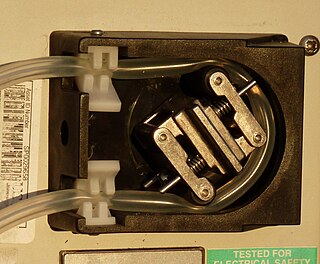
A peristaltic pump, also commonly known as a roller pump, is a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained in a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump casing. Most peristaltic pumps work through rotary motion, though linear peristaltic pumps have also been made. The rotor has a number of "wipers" or "rollers" attached to its external circumference, which compress the flexible tube as they rotate by. The part of the tube under compression is closed, forcing the fluid to move through the tube. Additionally, as the tube opens to its natural state after the rollers pass, more fluid is drawn into the tube. This process is called peristalsis and is used in many biological systems such as the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, there will be two or more rollers compressing the tube, trapping a body of fluid between them. The body of fluid is transported through the tube, toward the pump outlet. Peristaltic pumps may run continuously, or they may be indexed through partial revolutions to deliver smaller amounts of fluid.
Season extension in agriculture is any method that allows a crop to be grown beyond its normal outdoor growing season and harvesting time frame, or the extra time thus achieved. To extend the growing season into the colder months, one can use unheated techniques such as floating row covers, low tunnels, caterpillar tunnels, or hoophouses. However, even if colder temperatures are mitigated, most crops will stop growing when the days become shorter than 10 hours, and resume after winter as the daylight increases above 10 hours. A hothouse — a greenhouse which is heated and illuminated — creates an environment where plants are fooled into thinking it is their normal growing season. Though this is a form of season extension for the grower, it is not the usual meaning of the term.

Plastic mulch is a product used in plasticulture in a similar fashion to mulch, to suppress weeds and conserve water in crop production and landscaping. Certain plastic mulches also act as a barrier to keep methyl bromide, both a powerful fumigant and ozone depleter, in the soil. Crops grow through slits or holes in thin plastic sheeting. Plastic mulch is often used in conjunction with drip irrigation. Some research has been done using different colors of mulch to affect crop growth. Use of plastic mulch is predominant in large-scale vegetable growing, with millions of acres cultivated under plastic mulch worldwide each year.
Drip irrigation or trickle irrigation is a type of micro-irrigation system that has the potential to save water and nutrients by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of plants, either from above the soil surface or buried below the surface. The goal is to place water directly into the root zone and minimize evaporation. Drip irrigation systems distribute water through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. Depending on how well designed, installed, maintained, and operated it is, a drip irrigation system can be more efficient than other types of irrigation systems, such as surface irrigation or sprinkler irrigation.
Glass tubes are mainly cylindrical hollow-wares. Their special shape combined with the huge variety of glass types, allows the use of glass tubing in many applications. For example, laboratory glassware, lighting applications, solar thermal systems and pharmaceutical packaging to name the largest.
An irrigation controller is a device to operate automatic irrigation systems such as lawn sprinklers and drip irrigation systems. Most controllers have a means of setting the frequency of irrigation, the start time, and the duration of watering. Some controllers have additional features such as multiple programs to allow different watering frequencies for different types of plants, rain delay settings, input terminals for sensors such as rain and freeze sensors, soil moisture sensors, weather data, remote operation, etc.

An irrigation sprinkler is a device used to irrigate (water) agricultural crops, lawns, landscapes, golf courses, and other areas. They are also used for cooling and for the control of airborne dust. Sprinkler irrigation is the method of applying water in a controlled manner in way similar to rainfall. The water is distributed through a network that may consist of pumps, valves, pipes, and sprinklers.

A garden hose, hosepipe, or simply hose is a flexible tube used to convey water. There are a number of common attachments available for the end of the hose, such as sprayers and sprinklers. Hoses are usually attached to a hose spigot or tap.

A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.
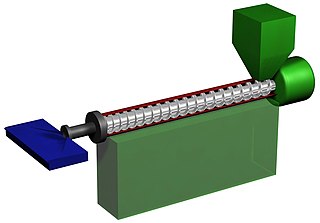
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation.

The term plasticulture refers to the practice of using plastic materials in agricultural applications. The plastic materials themselves are often and broadly referred to as "ag plastics". Plasticulture ag plastics include soil fumigation film, irrigation drip tape/tubing, plastic plant packaging cord, nursery pots and bales, but the term is most often used to describe all kinds of plastic plant/soil coverings. Such coverings range from plastic mulch film, row coverings, high and low tunnels (polytunnels), to plastic greenhouses.

Taprogge GmbH is a medium-sized company based in Wetter, Germany. The company is named after founding brothers Ludwig and Josef Taprogge. Founded in 1953, the company is known for its tube cleaning systems for steam turbine condensers, heat exchangers and debris filters for water-cooled shell and tube heat exchangers and condensers.
Rivulis is a global manufacturer and provider of complete micro and drip irrigation systems and solutions for seasonal horticulture, orchards, vineyards, row crops, SDI and greenhouse, soilless, hydroponic applications. Founded in 1966 as Plastro Irrigation Systems Ltd, Rivulis is headquartered in Kibbutz Gvat, Jezreel Valley, Israel. The company represents an integration of four industry pioneers and veterans: Plastro, T-Systems, Roberts Irrigation, and Eurodrip. It has 3,300 business partners worldwide, and a wholesale retail and vast dealer network in over 120 countries. The company operates 16 factories worldwide and has 2,000 employees. Rivulis has multiple global design centers and 3 R&D centers in agricultural hotspots of Israel, California, and Greece.

Copper tubing is most often used for heating systems and as a refrigerant line in HVAC systems. Copper tubing is slowly being replaced by PEX tubing in hot and cold water applications. There are two basic types of copper tubing, soft copper and rigid copper. Copper tubing is joined using flare connection, compression connection, pressed connection, or solder. Copper offers a high level of corrosion resistance but is becoming very costly.
Driptech Inc. is a company engaged in making of irrigation-equipment, a type of drip irrigation method. The company won awards for its innovative, low cost drip irrigation system, eliminating expensive and complex emitters used by traditional drip irrigation systems. The company is based out of Mountain View, California. In 2016 Jain Irrigation system Ltd owned Driptech India.

Micro-irrigation, also called Micro-spray,localized, low-volume, low-flow, or trickle irrigation, is an irrigation method with lower water pressure and flow than a traditional sprinkler system. Low-volume irrigation is used in agriculture for row crops, orchards, and vineyards. It is also used in horticulture in wholesale nurseries, in landscaping for civic, commercial, and private landscapes and gardens, and in the science and practice of restoration ecology and environmental remediation. The lower volume allows the water to be absorbed into slow-percolation soils such as clay, minimizing runoff.

Subsurface Textile Irrigation (SSTI) is a technology designed specifically for subsurface irrigation in all soil textures from desert sands to heavy clays. The use of SSTI will significantly reduce the usage of water, fertilizer and herbicide. It will lower on-going operational costs and, if maintained properly, will last for decades. By delivering water and nutrients directly to the root zone, plants are healthier and have a far greater yield.

An electrical conduit is a tube used to protect and route electrical wiring in a building or structure. Electrical conduit may be made of metal, plastic, fiber, or fired clay. Most conduit is rigid, but flexible conduit is used for some purposes.

Selenisa sueroides, the pale-edged selenisa or legume caterpillar, is an owlet moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found in North America.













