
The Mid-Atlantic Bight is a coastal region running from Massachusetts to North Carolina. [1] It contains the New York Bight. It is separated from the South Atlantic Bight by Cape Hatteras to the south and the Gulf of Maine to the north by Cape Cod.

The Mid-Atlantic Bight is a coastal region running from Massachusetts to North Carolina. [1] It contains the New York Bight. It is separated from the South Atlantic Bight by Cape Hatteras to the south and the Gulf of Maine to the north by Cape Cod.

The bluefish is the only extant species of the family Pomatomidae. It is a marine pelagic fish found around the world in temperate and subtropical waters, except for the northern Pacific Ocean. Bluefish are known as tailor in Australia and New Zealand, elf and shad in South Africa. It is a popular gamefish and food fish.

The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the region encompassing the coastline where the Eastern United States meets the Atlantic Ocean. The Thirteen Colonies, which formed the United States in 1776 were located on this coast, and it has played an important role in the development of the United States.

Ross Island is an island in Antarctica lying on the east side of McMurdo Sound and extending 43 nautical miles from Cape Bird in the north to Cape Armitage in the south, and a similar distance from Cape Royds in the west to Cape Crozier in the east. The island is entirely volcanic. Mount Erebus, 3,795 metres (12,451 ft), near the center, is an active volcano. Mount Terror, 3,230 metres (10,600 ft) about 20 nautical miles eastward, is an extinct volcano. Mount Bird rises to 1,765 metres (5,791 ft) just south of Cape Bird. Ross Island lies within the boundary of Ross Dependency, an area of Antarctica claimed by New Zealand.

The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern coastline of mainland Australia.

The Bight of Benin, or Bay of Benin, is a bight in the Gulf of Guinea area on the western African coast that derives its name from the historical Kingdom of Benin.

The Bight of Biafra, also known as the Bight of Bonny, is a bight off the west-central African coast, in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Guinea.

South Jersey comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of New Jersey. It is located between Pennsylvania and the lower Delaware River to its west, the Atlantic Ocean to its east, Delaware to its south, and Central Jersey or North Jersey to its north, depending on the definition of North Jersey.
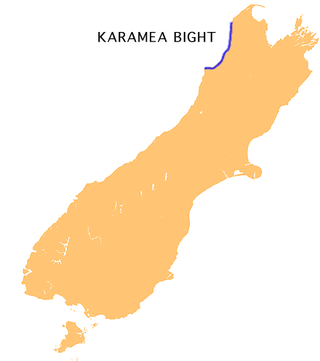
The Karamea Bight is the name given to a large bay in the Tasman Sea formed by a curved stretch of the West Coast of New Zealand's South Island. It stretches for 100 kilometres north from Cape Foulwind to just north of the mouth of the Heaphy River.

Cape Egmont, splitting Northern and Southern Taranaki Bights, is the westernmost point of Taranaki, on the west coast of New Zealand's North Island. It is located close to the volcanic cone of Mount Taranaki or Mount Egmont.

The South Taranaki Bight is a large bay on the west coast of New Zealand, south of Taranaki, west of the Manawatu, north and west of the western entrance of Cook Strait and north of the South Island. The name is sometimes used for a much smaller bay in South Taranaki, between the mouth of the Kaupokonui Stream directly south of Mount Taranaki and the mouth of the Pātea River.
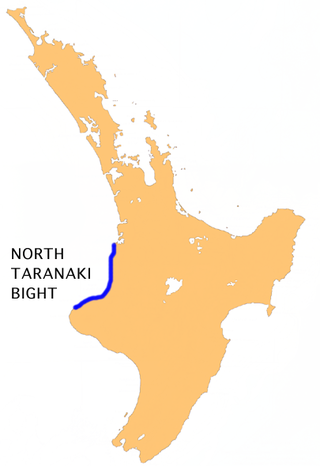
The North Taranaki Bight is a large bay that extends north and east from the north coast of Taranaki in New Zealand's North Island. The name is echoed by the South Taranaki Bight to the south of Cape Egmont.

In geography, a bight is a concave bend or curvature in a coastline, river or other geographical feature, or it may refer to a very open bay formed by such a feature. Such bays are typically broad, open, shallow and only slightly recessed.

The New York/New Jersey Bight is the geological identification applied to a roughly triangular indentation, regarded as a bight, along the Atlantic coast of the United States that extends northeasterly from Cape May Inlet in New Jersey to Montauk Point on the eastern tip of Long Island. As the result of direct contact with the Gulf Stream along the coast of North America, the coastal climate of the bight area is temperate.
The Burin Peninsula is a peninsula located on the south coast of the island of Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. Marystown is the largest population centre on the peninsula.

Southern Bight, also known as the Flanders Bight, and the Hoofden, is the southern bight of the North Sea bounded by the coasts of the Netherlands, Belgium, France and Great Britain. The Southern Bight is south west of the German Bight and the Wadden Sea. The Southern Bight is roughly delimited in the north by a roughly straight line between The Wash and the West Frisian Islands going south of the Dogger Bank, a large shallow part in the North Sea, and the Outer Silver Pit, a deep water channel south of the Dogger Bank. It corresponds to sea area Thames and the northern part of sea area Dover.

South Coast Tasmania runs from the South East Cape to the South West Cape of Tasmania. South Coast Tasmania is sometimes conflated with the South West Tasmania wilderness region.

The Igbo of Igboland became one of the principal ethnic groups to be enslaved during the Atlantic slave trade. An estimated 14.6% of all enslaved people were taken from the Bight of Biafra, a bay of the Atlantic Ocean that extends from the Nun outlet of the Niger River (Nigeria) to Limbe (Cameroon) to Cape Lopez (Gabon) between 1650 and 1900. The Bight’s major slave trading ports were located in Bonny and Calabar.

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.
The Northeastern United States Continental Shelf (NEUS) is the large marine ecosystem designated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration that occupies the portion of the continental shelf of the Atlantic Ocean. The NEUS is defined as extending roughly from the Canadian province of Nova Scotia to Cape Hatteras in the US state of North Carolina. This large marine ecosystem is notable for its proximity to the Gulf Stream current, meridional variation of climate, and commercial fisheries.

The South Atlantic Bight is a bight in the United States coastline extending from Cape Hatteras, North Carolina to the Upper Florida Keys. The Bight forms the western boundary of the Sargasso Sea and the Gulf Stream ocean current forms the eastern boundary of the ecosystem of the bight. Major cities along the bight include from north to south: Wilmington, Myrtle Beach, Charleston, Savannah, Jacksonville, St. Augustine, West Palm Beach, Fort Lauderdale, and Miami.