
The Norwegian Sea is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between Iceland and the Faroe Islands. To the north, the Jan Mayen Ridge separates it from the Greenland Sea.

Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus Gadus, belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus Gadus is commonly not called cod.

The Atlantic cod is a fish of the family Gadidae, widely consumed by humans. It is also commercially known as cod or codling.

Boreogadus saida, known as the polar cod or as the Arctic cod, is a fish of the cod family Gadidae, related to the true cod. Another fish species for which both the common names Arctic cod and polar cod are used is Arctogadus glacialis.

Litopenaeus setiferus is a species of prawn found along the Atlantic coast of North America and in the Gulf of Mexico. It was the subject of the earliest shrimp fishery in the United States.

The Kuroshio Current, also known as the Black Current or Japan Current is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean basin. It was named for the deep blue appearance of its waters. Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Kuroshio is a powerful western boundary current that transports warm equatorial water poleward and forms the western limb of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Off the East Coast of Japan, it merges with the Oyashio Current to form the North Pacific Current.

Pandalus borealis is a species of caridean shrimp found in cold parts of the northern Atlantic and northern Pacific Oceans, although the latter population now often is regarded as a separate species, P. eous. The Food and Agriculture Organization refers to them as the northern prawn. Other common names include pink shrimp, deepwater prawn, deep-sea prawn, Nordic shrimp, great northern prawn, northern shrimp, coldwater prawn and Maine shrimp.

The winter flounder, also known as the black back, is a right-eyed ("dextral") flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is native to coastal waters of the western north Atlantic coast, from Labrador, Canada to Georgia, United States, although it is less common south of Delaware Bay. It is the most common near-shore (shallow-water) flounder in the waters from Newfoundland down through Massachusetts Bay, reaching a maximum size around 61 cm in length and 2.25 kg in weight. The species grows larger on Georges Bank, where they can reach a length of 70 cm and weight of 3.6 kg. Although winter flounder historically supported large commercial and recreational fisheries, biomass and landings have decreased since the 1980s.

The Lessepsian migration is the migration of marine species along the Suez Canal, usually from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, and more rarely in the opposite direction. When the canal was completed in 1869, fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other marine animals and plants were exposed to an artificial passage between the two naturally separate bodies of water, and cross-contamination was made possible between formerly isolated ecosystems. The phenomenon is still occurring today. It is named after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French diplomat in charge of the canal's construction. The term was coined by Francis Dov Por in his 1978 book.

A harmful algal bloom (HAB), or excessive algae growth, is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, water deoxygenation, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are sometimes defined as only those algal blooms that produce toxins, and sometimes as any algal bloom that can result in severely lower oxygen levels in natural waters, killing organisms in marine or fresh waters. Blooms can last from a few days to many months. After the bloom dies, the microbes that decompose the dead algae use up more of the oxygen, generating a "dead zone" which can cause fish die-offs. When these zones cover a large area for an extended period of time, neither fish nor plants are able to survive. Harmful algal blooms in marine environments are often called "red tides".
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.

Cod fisheries are fisheries for cod. Cod is the common name for fish of the genus Gadus, belonging to the family Gadidae, and this article is confined to three species that belong to this genus: the Atlantic cod, the Pacific cod and the Greenland cod. Although there is a fourth species of the cod genus Gadus, Alaska pollock, it is commonly not called cod and therefore currently not covered here.
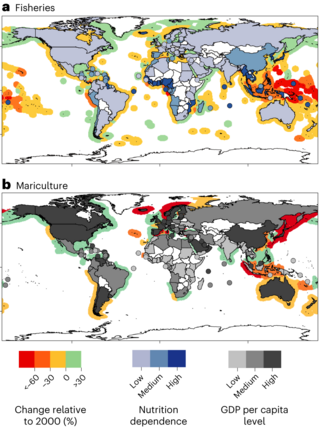
Fisheries are affected by climate change in many ways: marine aquatic ecosystems are being affected by rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification and ocean deoxygenation, while freshwater ecosystems are being impacted by changes in water temperature, water flow, and fish habitat loss. These effects vary in the context of each fishery. Climate change is modifying fish distributions and the productivity of marine and freshwater species. Climate change is expected to lead to significant changes in the availability and trade of fish products. The geopolitical and economic consequences will be significant, especially for the countries most dependent on the sector. The biggest decreases in maximum catch potential can be expected in the tropics, mostly in the South Pacific regions.

Fishing in Israel is a branch of the Israeli economy with historical significance. The three main natural fishing zones are the Mediterranean Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Kinneret. A fourth area that was once historically significant, Lake Hula, no longer exists, as it was drained in the 1950s. In addition, aquaculture the growth of fish in ponds or in cages, is rising in prominence.

The Gulf flounder is a species of saltwater flounder.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to fisheries:

A planktivore is an aquatic organism that feeds on planktonic food, including zooplankton and phytoplankton. Planktivorous organisms encompass a range of some of the planet's smallest to largest multicellular animals in both the present day and in the past billion years; basking sharks and copepods are just two examples of giant and microscopic organisms that feed upon plankton.

Pterois is a genus of venomous marine fish, commonly known as the lionfish, native to the Indo-Pacific. It is characterized by conspicuous warning coloration with red or black bands and ostentatious dorsal fins tipped with venomous spines. Pterois radiata, Pterois volitans, and Pterois miles are the most commonly studied species in the genus. Pterois species are popular aquarium fish. P. volitans and P. miles are recent and significant invasive species in the west Atlantic, Caribbean Sea and Mediterranean Sea.
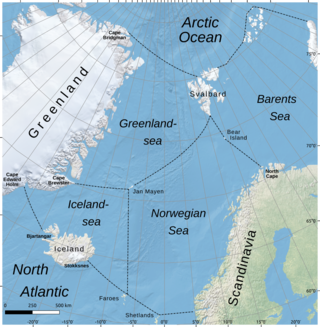
The Iceland Sea, a relatively small body of water, is bounded by Iceland. It is characterized by its proximity to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which transforms into the Kolbeinsey Ridge, and the Greenland-Scotland Ridge, and it lies just south of the Arctic Circle. This region is typically delineated by Greenland to the west, the Denmark Strait, and the continental shelf break south of Iceland to the south. Next in the boundary line are Jan Mayen, being a small Norwegian volcanic island, and the Jan Mayen fracture zone to the north, with the Jan Mayen Ridge to the east of the sea. This ridge serves as the northern boundary of the Iceland Sea, acting as the dividing line from the Greenland Sea. To the immediate south of Jan Mayen, the Iceland-Jan Mayen Ridge stretches towards the Iceland-Faroe Ridge, creating a boundary between the Iceland Sea and the Norwegian Sea to the east.
The Northeastern United States Continental Shelf (NEUS) is the large marine ecosystem designated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration that occupies the portion of the continental shelf of the Atlantic Ocean. The NEUS is defined as extending roughly from the Canadian province of Nova Scotia to Cape Hatteras in the US state of North Carolina. This large marine ecosystem is notable for its proximity to the Gulf Stream current, meridional variation of climate, and commercial fisheries.




















