The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a country in the eastern part of the Arabian Peninsula located on the southeastern coast of the Persian Gulf and the northwestern coast of the Gulf of Oman. The UAE consists of seven emirates and was founded on 2 December 1971 as a federation. Six of the seven emirates combined on that date. The seventh, Ras al Khaimah, joined the federation on 10 February 1972. The seven sheikdoms were formerly known as the Trucial States, in reference to the treaty relations established with the British in the 19th Century.

Umm Al Quwain is the least populous of the seven constituent emirates in the United Arab Emirates, located in the north of the country. The emirate is ruled by Saud bin Rashid Al Mualla. It had 72,000 inhabitants in 2007 and has an area of 770 km2 (300 sq mi).
The United Arab Emirates national cricket team is the team that represents the United Arab Emirates in international Cricket. They are governed by the Emirates Cricket Board (ECB) which became an affiliate member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) in 1989 and an associate member the following year. Since 2005, the ICC's headquarters have been located in Dubai.
Emiratisation is an initiative by the government of the United Arab Emirates to employ its citizens in a meaningful and efficient manner in the public and private sectors.

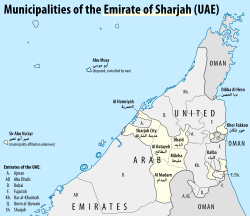
Sharjah is the third largest and third most populous city in the United Arab Emirates, forming part of the Dubai-Sharjah-Ajman metropolitan area. It is located along the southern coast of the Persian Gulf on the Arabian Peninsula.

Shimal is the name of a settlement in Ras Al Khaimah associated with the Shihuh tribe of the Northern UAE and Oman. It is also the location of an important archaeological site dating back to the Umm Al Nar culture. Tombs excavated and surveyed at Shimal include both the round Umm Al Nar type and the barrow tombs typical of the 'Wadi Suq' era. Grave goods found at Shimal have included large finds of pottery as well as beads and objects providing a link to the Harappan Indus Valley Civilisation.
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a diverse society. The country's historical population as a small tribal community has been changed with the arrival of other nationals, at first by Iranians and also from other Arab countries in the 1950s and 1960s. Furthermore, the country was a part of the British Empire up until 1971.
Most expatriates in the United Arab Emirates reside in Dubai and Abu Dhabi. A number of expatriates settled in the country prior to independence. The UAE is home to over 200 nationalities. Emiratis constitute roughly 20% of the total population, making UAE home to one of the world's highest percentage of immigrants. Indians and Pakistanis form the largest expatriate groups in the country, constituting 25% and 12% of the total population respectively.

Mleiha Archaeological Centre is a visitor centre and exhibition based around the history and archaeology of the areas surrounding the village of Mleiha in Sharjah, the United Arab Emirates. Built around a preserved Umm Al Nar era tomb, the centre details the excavations and discoveries made over the past 40 years at Mleiha and surrounding areas, particularly the important Faya North East find, which provides evidence that 'anatomically modern humans' were in the Mleiha area between 130,000 and 120,000 years ago. These finds point to the spread of humanity from Africa across the Red Sea to the Persian Gulf region, and onward to populate the world through Iran, India, Europe and Asia.

Ed-Dur or Ed-Dour is an Ancient Near Eastern City located in Umm Al Quwain, in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). One of the largest archaeological sites in the emirates, comprising an area of some 5 km2 (1.9 sq mi), the coastal settlement overlooks Al-Beidha Lake. One of the most important archaeological finds in the UAE, It has been dubbed 'one of the most significant lost cities of Arabia'.
Muweilah is an archaeological site in Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, in the suburb of Al Jurainah near Sharjah University City. A large, fortified settlement thought to have been occupied during the Iron Age II period (1,100-600BC), the site has been explored by archaeologists since an Australian expedition started work there in 1994 after the discovery of pottery shards by a local resident. It has yielded the oldest known example of writing found to date in the UAE, a pottery shard with an inscription, thought to be Sabean, with the letters 'bml'.

Al Madam is an inland town of the Emirate of Sharjah, the UAE. Located at the intersection of the Dubai-Hatta (E44) and Mleiha-Shwaib (E55) roads, its development has mainly centred around these road links and the road traffic through Hatta to Oman. The volume of traffic to Oman through Madam and Hatta has lessened since the closure of the 'soft' Omani border at Mahda in 2016, although traffic volumes remain at some 5,000 travellers daily. The road from Madam to Hatta is now only open to UAE or Omani nationals and permit holders.

Jebel Buhais is a geological feature, an extensive rocky outcrop, as well as an archaeological site located near Madam, in Sharjah, UAE. The area contains an extensive necropolis, consisting of burial sites spanning the Stone, Bronze, Iron and Hellenistic ages of human settlement in the UAE. Burials at Jebel Buhais date back to the 5th Millennium BCE. The site is located to the side of a limestone outcrop rising to some 340 metres above sea level and which runs almost contiguously from the town of Madam north to the town of Mleiha, itself an important archaeological site.
The area currently known as the United Arab Emirates (UAE) was formerly populated by inhabitants of a number of coastal and inland settlements, with human remains pointing to a pattern of transmigration and settlement as far back as 125,000 years. Prehistoric settlement in the UAE spanned the Neolithic, with a number of distinctive eras of ancient settlement including the Stone Age Arabian Bifacial and Ubaid cultures from 5,000 to 3,100 BCE; the Hafit period with its distinctive beehive shaped tombs and Jemdet Nasr pottery, from 3,200 to 2,600 BCE; the Umm Al-Nar period from 2,600 to 2,000 BCE; the Wadi Suq Culture from 2,000–1,300 BCE and the three Iron Ages of the UAE.
The territory currently known as the United Arab Emirates was home to three distinct Iron Age periods. Iron Age I spanned 1,200–1,000 BCE, Iron Age II from 1,000–600 BCE, and Iron Age III from 600–300 BCE. This period of human development in the region was followed by the Mleiha or Late Pre-Islamic era, from 300 BCE onwards through to the Islamic era which commenced with the culmination of the 7th century Ridda Wars.
The Sharjah Investment and Development Authority, also known as Shurooq, is responsible for the development of the emirate of Sharjah, one of the seven emirates of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) as a investment, tourism, and business destination.