
In the field of complex analysis in mathematics, the Cauchy–Riemann equations, named after Augustin Cauchy and Bernhard Riemann, consist of a system of two partial differential equations which, together with certain continuity and differentiability criteria, form a necessary and sufficient condition for a complex function to be holomorphic. This system of equations first appeared in the work of Jean le Rond d'Alembert. Later, Leonhard Euler connected this system to the analytic functions. Cauchy then used these equations to construct his theory of functions. Riemann's dissertation on the theory of functions appeared in 1851.

In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations are certain partial differential equations which describe the motion of viscous fluid substances, named after French engineer and physicist Claude-Louis Navier and Anglo-Irish physicist and mathematician George Gabriel Stokes. They were developed over several decades of progressively building the theories, from 1822 (Navier) to 1842–1850 (Stokes).
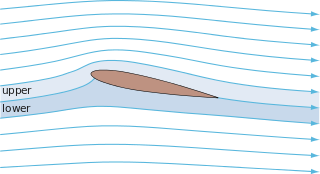
In fluid dynamics, potential flow describes the velocity field as the gradient of a scalar function: the velocity potential. As a result, a potential flow is characterized by an irrotational velocity field, which is a valid approximation for several applications. The irrotationality of a potential flow is due to the curl of the gradient of a scalar always being equal to zero.
In continuum mechanics, vorticity is a pseudovector field that describes the local spinning motion of a continuum near some point, as would be seen by an observer located at that point and traveling along with the flow. It is an important quantity in the dynamical theory of fluids and provides a convenient framework for understanding a variety of complex flow phenomena, such as the formation and motion of vortex rings.
In 1851, George Gabriel Stokes derived an expression, now known as Stokes law, for the frictional force – also called drag force – exerted on spherical objects with very small Reynolds numbers in a viscous fluid. Stokes' law is derived by solving the Stokes flow limit for small Reynolds numbers of the Navier–Stokes equations.
In fluid mechanics, the Taylor–Proudman theorem states that when a solid body is moved slowly within a fluid that is steadily rotated with a high angular velocity , the fluid velocity will be uniform along any line parallel to the axis of rotation. must be large compared to the movement of the solid body in order to make the Coriolis force large compared to the acceleration terms.

Large eddy simulation (LES) is a mathematical model for turbulence used in computational fluid dynamics. It was initially proposed in 1963 by Joseph Smagorinsky to simulate atmospheric air currents, and first explored by Deardorff (1970). LES is currently applied in a wide variety of engineering applications, including combustion, acoustics, and simulations of the atmospheric boundary layer.
In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds stress is the component of the total stress tensor in a fluid obtained from the averaging operation over the Navier–Stokes equations to account for turbulent fluctuations in fluid momentum.

Stokes flow, also named creeping flow or creeping motion, is a type of fluid flow where advective inertial forces are small compared with viscous forces. The Reynolds number is low, i.e. . This is a typical situation in flows where the fluid velocities are very slow, the viscosities are very large, or the length-scales of the flow are very small. Creeping flow was first studied to understand lubrication. In nature this type of flow occurs in the swimming of microorganisms, sperm and the flow of lava. In technology, it occurs in paint, MEMS devices, and in the flow of viscous polymers generally.

In applied mathematics, the Joukowsky transform, named after Nikolai Zhukovsky, is a conformal map historically used to understand some principles of airfoil design.
The Kutta–Joukowski theorem is a fundamental theorem in aerodynamics used for the calculation of lift of an airfoil and any two-dimensional bodies including circular cylinders translating in a uniform fluid at a constant speed large enough so that the flow seen in the body-fixed frame is steady and unseparated. The theorem relates the lift generated by an airfoil to the speed of the airfoil through the fluid, the density of the fluid and the circulation around the airfoil. The circulation is defined as the line integral around a closed loop enclosing the airfoil of the component of the velocity of the fluid tangent to the loop. It is named after Martin Kutta and Nikolai Zhukovsky who first developed its key ideas in the early 20th century. Kutta–Joukowski theorem is an inviscid theory, but it is a good approximation for real viscous flow in typical aerodynamic applications.

For a pure wave motion in fluid dynamics, the Stokes drift velocity is the average velocity when following a specific fluid parcel as it travels with the fluid flow. For instance, a particle floating at the free surface of water waves, experiences a net Stokes drift velocity in the direction of wave propagation.
In fluid dynamics, Airy wave theory gives a linearised description of the propagation of gravity waves on the surface of a homogeneous fluid layer. The theory assumes that the fluid layer has a uniform mean depth, and that the fluid flow is inviscid, incompressible and irrotational. This theory was first published, in correct form, by George Biddell Airy in the 19th century.

A Taylor column is a fluid dynamics phenomenon that occurs as a result of the Coriolis effect. It was named after Geoffrey Ingram Taylor. Rotating fluids that are perturbed by a solid body tend to form columns parallel to the axis of rotation called Taylor columns.
In mathematics, a line integral is an integral where the function to be integrated is evaluated along a curve. The terms path integral, curve integral, and curvilinear integral are also used; contour integral is used as well, although that is typically reserved for line integrals in the complex plane.

In mathematics, potential flow around a circular cylinder is a classical solution for the flow of an inviscid, incompressible fluid around a cylinder that is transverse to the flow. Far from the cylinder, the flow is unidirectional and uniform. The flow has no vorticity and thus the velocity field is irrotational and can be modeled as a potential flow. Unlike a real fluid, this solution indicates a net zero drag on the body, a result known as d'Alembert's paradox.

In fluid dynamics, the radiation stress is the depth-integrated – and thereafter phase-averaged – excess momentum flux caused by the presence of the surface gravity waves, which is exerted on the mean flow. The radiation stresses behave as a second-order tensor.
In the science of fluid flow, Stokes' paradox is the phenomenon that there can be no creeping flow of a fluid around a disk in two dimensions; or, equivalently, the fact there is no non-trivial steady-state solution for the Stokes equations around an infinitely long cylinder. This is opposed to the 3-dimensional case, where Stokes' method provides a solution to the problem of flow around a sphere.
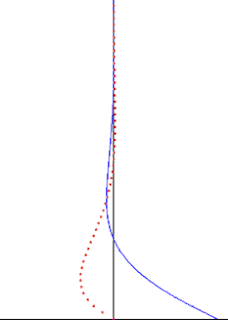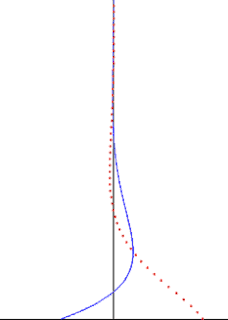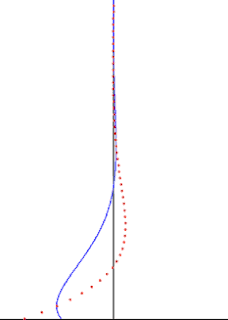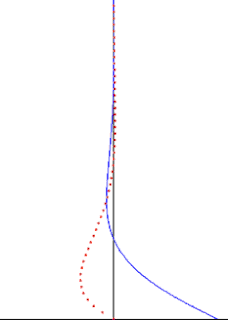
In fluid dynamics, Stokes problem also known as Stokes second problem or sometimes referred to as Stokes boundary layer or Oscillating boundary layer is a problem of determining the flow created by an oscillating solid surface, named after Sir George Stokes. This is considered one of the simplest unsteady problem that have exact solution for the Navier-Stokes equations. In turbulent flow, this is still named a Stokes boundary layer, but now one has to rely on experiments, numerical simulations or approximate methods in order to obtain useful information on the flow.
In fluid dynamics, Blasius theorem states that the force experienced by a two-dimensional fixed body in a steady irrotational flow is given by






















