Related Research Articles

The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. The network was assisted by abolitionists and others sympathetic to the cause of the escapees. The enslaved who risked escape and those who aided them are also collectively referred to as the "Underground Railroad". Various other routes led to Mexico, where slavery had been abolished, and to islands in the Caribbean that were not part of the slave trade. An earlier escape route running south toward Florida, then a Spanish possession, existed from the late 17th century until approximately 1790. However, the network now generally known as the Underground Railroad began in the late 18th century. It ran north and grew steadily until the Emancipation Proclamation was signed by President Abraham Lincoln. One estimate suggests that by 1850, approximately 100,000 enslaved people had escaped via the network.

Harriet Tubman was an American abolitionist and social activist. Born into slavery, Tubman escaped and subsequently made some 13 missions to rescue approximately 70 enslaved people, including family and friends, using the network of antislavery activists and safe houses known as the Underground Railroad. During the American Civil War, she served as an armed scout and spy for the Union Army. In her later years, Tubman was an activist in the movement for women's suffrage.

Black studies, or Africana studies, is an interdisciplinary academic field that primarily focuses on the study of the history, culture, and politics of the peoples of the African diaspora and Africa. The field includes scholars of African-American, Afro-Canadian, Afro-Caribbean, Afro-Latino, Afro-European, Afro-Asian, African Australian, and African literature, history, politics, and religion as well as those from disciplines, such as sociology, anthropology, cultural studies, psychology, education, and many other disciplines within the humanities and social sciences. The field also uses various types of research methods.

The Cyrus Gates Farmstead is located in Maine, New York. Cyrus Gates was a cartographer and map maker for New York State, as well as an abolitionist. The great granddaughter of Cyrus-Louise Gates-Gunsalus has stated that from 1848 until the end of slavery in the United States in 1865, the Cyrus Gates Farmstead was a station or stop on the Underground Railroad. Its owners, Cyrus and Arabella Gates, were outspoken abolitionists as well as active and vital members of their community. Historian Shirley L. Woodward states that through those years escaped slaves came through the Gates' station.
Kate Clifford Larson is an American historian and Harriet Tubman scholar. Her 2003 biography of Harriet Tubman, Bound for the Promised Land was one of the first non-juvenile Tubman biographies published in six decades. Larson is the consultant for the Harriet Tubman Special Resource Study of the National Park Service and serves on the advisory board of the Historic Context on the Underground Railroad in Delaware, Underground Railroad Coalition of Delaware.

Beriah Green, Jr. was an American reformer, abolitionist, temperance advocate, college professor, minister, and head of the Oneida Institute. He was "consumed totally by his abolitionist views". He has been described as "cantankerous". Former student Alexander Crummell described him as a "bluff, kind-hearted man," a "master-thinker".
Dorothy Sterling was an American writer and historian. After college, she worked as a journalist and writer in New York for several years, including work for the Federal Writers’ Project.
Earl Conrad, birth name Cohen, was an American author who penned at least twenty works of biography, history, and criticism, including books in collaboration. At least one that he 'ghost' wrote was the autobiography of actor Errol Flynn, titled My Wicked, Wicked Ways.
Catherine Clinton is the Denman Professor of American History at the University of Texas at San Antonio. She specializes in American History, with an emphasis on the history of the South, the American Civil War, American women, and African American history.

St. James AME Zion Church is a historic African Methodist Episcopal Zion church located at Ithaca in Tompkins County, New York. It is a two-story, frame church structure set on a high foundation and featuring a four-story entrance tower. The church structure was begun in the 1830s and modified many times since. The original stone meetinghouse was built in 1836 and is believed to be Ithaca's oldest church and one of the oldest in the AME Zion system.
The following is a bibliography of New York. New York is a U.S. state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the Northeastern United States. New York is commonly known as the "Empire State" and sometimes the "Excelsior State". It is the nation's third most populous state at over 19 million people. The capital of the state is Albany and its most populous city is New York City. New York is often referred to as New York State to distinguish it from New York City.

The Oneida Institute was a short-lived (1827–1843) but highly influential school that was a national leader in the emerging abolitionist movement. It was the most radical school in the country, the first at which black men were just as welcome as whites. "Oneida was the seed of Lane Theological Seminary, Western Reserve College, Oberlin and Knox colleges."
Hiram Wilson was an anti-slavery abolitionist who worked directly with escaped and former slaves in southwestern Ontario. He attempted to improve their living conditions and help them to be integrated into society by providing education and practical working skills. He established ten schools to educate free blacks in southwestern Ontario. Wilson worked extensively with Josiah Henson to establish the British-American Institute and the Dawn Settlement in 1841. He was a delegate to the World Anti-Slavery Convention of 1843 in London, England. He resigned from the British-American Institute and moved to St. Catharines, Ontario, where his home was a final terminal for the Underground Railroad.
The Department of African American Studies (AAS) at Syracuse University is an academic department supporting Africana studies. It is located at Syracuse University in Syracuse, New York. It is part of the Syracuse University College of Arts and Sciences. The Department supports an external community based unit that is a part of the department and has played a central role in shaping culture and arts in the Syracuse city community - Community Folk Art Center (CFAC). It has also supported the Paul Robeson Performing Arts Company (PRPAC) in the past. These are both independent units that were housed or founded by the department The department also houses the award-winning library, the Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial Library. It currently oversees the internationally recognized university wide initiative "Africa Initiative". Its other projects include the nationally recognized "Paris Noir" and the Ford Foundation Environmental Justice and Gender Project. It has had a long history of activism within the university, surrounding community, and abroad through its strong international network. The AAS department has housed many renowned scholars in African, Afro-Caribbean, African-American, Afro-Latin American, and Afro-European studies.
Greene Smith (1842–1886) was an American amateur scientist and taxidermist with a specific interest in ornithology. His father was Gerrit Smith.
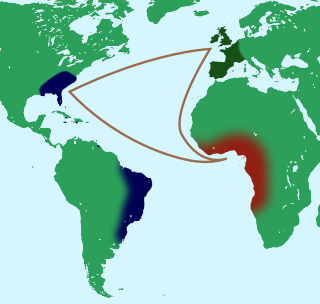
Flying Africans are figures of African diaspora legend who escape enslavement by a magical passage back over the ocean. Most noted in Gullah culture, they also occur in wider African-American folklore, and in that of some Afro-Caribbean peoples.

A statue of Harriet Tubman created by artist Jane DeDecker honors the life of abolitionist Harriet Tubman. The bronze statue depicts Tubman walking and holding the hand of a young boy.

Noted Negro Women: Their Triumphs and Activities is an anthology of biographies of African-American women edited by Monroe Alpheus Majors published in 1893 in Chicago. Majors sketched the lives of nearly 300 women, including Edmonia Lewis, Amanda Smith, Ida B. Wells, and Sojourner Truth. Majors began to compile the book in Waco, Texas, in 1890. He hoped to show the worth of black women for themselves and as an expression of the value of all African Americans. A significant omission from the book was Harriet Tubman. The book sought to shape contemporary attitudes and historian Milton C. Sernett hypothesizes that including Tubman would invoke memories of the pain of slavery.

Fern Cunningham was an American sculptor. One of her best known works is the Harriet Tubman Memorial, which was the first statue honoring a woman on city-owned land in Boston.
The Empire State Federation of Women's Clubs (ESFWC) was founded in 1908 and is an umbrella organization for African-American women's groups in New York. The organization worked to help improve the lives of young women and helped care for Harriet Tubman until her death in 1913. The organization was affiliated with the National Association of Colored Women's Clubs, and worked with the NAACP.
References
- 1 2 Books, Used, New, and Out of Print Books - We Buy and Sell - Powell's. "Harriet Tubman: Myth, Memory, and History by Milton C. Sernett". Powells.com. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
- 1 2 "Milton C. Sernett, Professor Emeritus, History and African American Studies". Maxwell.syr.edu. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
- ↑ "Harriet Tubman Talk Draws Overflow Crowd" (PDF). Northcountryundergroundrailroad.com. Retrieved 2017-08-20.
- ↑ Pan African Studies Newsletter, 'Milton C. Sernett' - Pan African Studies at Syracuse University Newsletter, Special Edition, 2004/2005 p4
- ↑ Pan African Studies Newsletter, 'Milton C. Sernett ' - Pan African Studies at Syracuse University Newsletter, Special Edition, 2004/2005 p4
- ↑ Books, Used, New, and Out of Print Books - We Buy and Sell - Powell's. "Harriet Tubman: Myth, Memory, and History by Milton C. Sernett". Powells.com. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
- ↑ Knoblauch, Edward H. "The Antislavery Alliance of Gerrit Smith and Beriah Green - New York History Net". Nyhistory.com. Retrieved 20 August 2017.