
Keystroke logging, often referred to as keylogging or keyboard capturing, is the action of recording (logging) the keys struck on a keyboard, typically covertly, so that a person using the keyboard is unaware that their actions are being monitored. Data can then be retrieved by the person operating the logging program. A keystroke recorder or keylogger can be either software or hardware.
Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems.
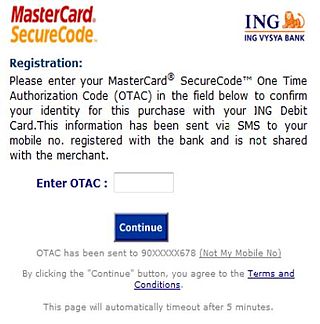
A one-time password (OTP), also known as a one-time PIN, one-time authorization code (OTAC) or dynamic password, is a password that is valid for only one login session or transaction, on a computer system or other digital device. OTPs avoid several shortcomings that are associated with traditional (static) password-based authentication; a number of implementations also incorporate two-factor authentication by ensuring that the one-time password requires access to something a person has as well as something a person knows.

An electronic identification ("eID") is a digital solution for proof of identity of citizens or organizations. They can be used to view to access benefits or services provided by government authorities, banks or other companies, for mobile payments, etc. Apart from online authentication and login, many electronic identity services also give users the option to sign electronic documents with a digital signature.
A transaction authentication number (TAN) is used by some online banking services as a form of single use one-time passwords (OTPs) to authorize financial transactions. TANs are a second layer of security above and beyond the traditional single-password authentication.

Keychain is the password management system in macOS, developed by Apple. It was introduced with Mac OS 8.6, and has been included in all subsequent versions of the operating system, now known as macOS. A Keychain can contain various types of data: passwords, private keys, certificates, and secure notes.
A password manager is a computer program that allows users to store and manage their passwords for local applications and online services like a web applications, online shops or social media. Password managers usually simplify authentication by reducing interaction from many steps like “recall-enter-submit” to one step “submit”.
A Google Account is a user account that is required for access, authentication and authorization to certain online Google services. It is also often used as single sign on for third party services.
Electronic authentication is the process of establishing confidence in user identities electronically presented to an information system. Digital authentication, or e-authentication, may be used synonymously when referring to the authentication process that confirms or certifies a person's identity and works. When used in conjunction with an electronic signature, it can provide evidence of whether data received has been tampered with after being signed by its original sender. Electronic authentication can reduce the risk of fraud and identity theft by verifying that a person is who they say they are when performing transactions online.
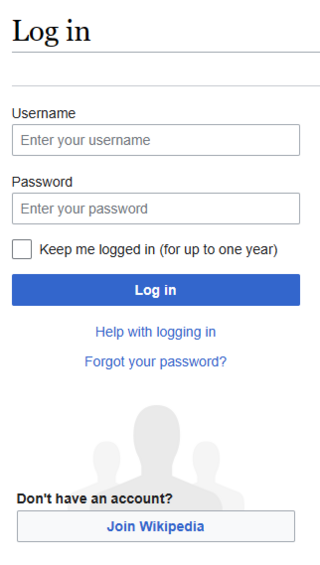
In computer security, logging in is the process by which an individual gains access to a computer system by identifying and authenticating themselves. The user credentials are typically some form of username and a matching password, and these credentials themselves are sometimes referred to as alogin. In practice, modern secure systems often require a second factor such as email or SMS confirmation for extra security. Social login allows a user to use existing user credentials from a social networking service to sign in to or create an account on a new website.
The Agency for Public Management and eGovernment or Difi is a government agency subordinate to the Norwegian Ministry of Government Administration and Reform.

Multi-factor authentication is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism: knowledge, possession, and inherence. MFA protects user data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password.
All European countries show eGovernment initiatives, mainly related to the improvement of governance at the national level. Significant eGovernment activities also take place at the European Commission level as well. There is an extensive list of eGovernment Fact Sheets maintained by the European Commission.
SAP Logon Tickets represent user credentials in SAP systems. When enabled, users can access multiple SAP applications and services through SAP GUI and web browsers without further username and password inputs from the user. SAP Logon Tickets can also be a vehicle for enabling single sign-on across SAP boundaries; in some cases, logon tickets can be used to authenticate into 3rd party applications such as Microsoft-based web applications.
Phone hacking is the practice of exploring a mobile device often using computer exploits to analyze everything from the lowest memory and central processing unit levels up to the highest file system and process levels. Modern open source tooling has become fairly sophisticated as to be able to "hook" into individual functions within any running App on an unlocked device and allow deep inspection and modification of their functions.

A Microsoft account or MSA is a single sign-on Microsoft user account for Microsoft customers to log in to Microsoft services, devices running on one of Microsoft's current operating systems, and Microsoft application software.
Identity-based security is a type of security that focuses on access to digital information or services based on the authenticated identity of an individual. It ensures that the users of these digital services are entitled to what they receive. The most common form of identity-based security involves the login of an account with a username and password. However, recent technology has evolved into fingerprinting or facial recognition.
Digital identity is used in Australia by residents to validate who they are over digital media, such as over the Internet.
The national identity number is a unique eleven-digit unique identifier issued to residents and citizens of Norway. The issuing of the identity number corresponds to being registered in the national population register. The ID number is used throughout government administration and a number of private sector services, in particular banking and insurance. All official IDs, including passports, national ID cards, driving licenses and bank cards contain the National Identity Number.
Smart-ID is an electronic authentication tool developed by SK ID Solutions, an Estonian company. Users can log in to various electronic services and sign documents with an electronic signature.





