
Salta is a province of Argentina, located in the northwest of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the east clockwise Formosa, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Tucumán and Catamarca. It also surrounds Jujuy. To the north it borders Bolivia and Paraguay and to the west lies Chile.

San Salvador de Jujuy, commonly known as Jujuy and locally often referred to as San Salvador, is the capital and largest city of Jujuy Province in northwest Argentina. Also, it is the seat of the Doctor Manuel Belgrano Department. It lies near the southern end of the Humahuaca Canyon where wooded hills meet the lowlands.

Paraná is the capital city of the Argentine province Entre Ríos, located on the eastern shore of the Paraná River, opposite the city of Santa Fe, capital of the neighbouring Santa Fe Province. The city has a population of 268,889 inhabitants with its metropolitan area, Greater Paraná, having 391,962 inhabitants.

Trelew is a city in the eastern part of the Chubut Province of Argentina. Located in Patagonia, the city is the largest and most populous in the low valley of the Chubut River, with 97,915 inhabitants as of 2010. The Trelew municipality is part of the Rawson Department, whose capital, Rawson, is also the provincial capital.

Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego also formerly Isla de Xátiva is an island near the southern tip of South America from which it is separated by the Strait of Magellan. The western portion (61.4%) of the island is in Chile, while the eastern portion is in Argentina. It forms the major landmass in an extended group of islands or archipelago also known as Tierra del Fuego.

Cape Virgenes is the southeastern promontory of continental Argentina in South America. A little to the south-west,the southernmost point of land is Punta Dúngeness. Ferdinand Magellan reached it on 21 October 1520 during the Spanish expedition to East Asia and discovered a strait, now called the Strait of Magellan in his honor. As 21 October was the feast day of Saint Ursula and the Eleven Thousand Virgins, he named the cape in their honor.
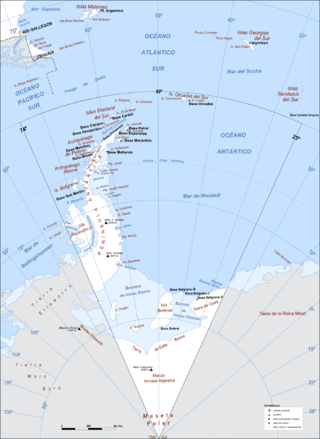
Argentine Antarctica is an area on Antarctica claimed by Argentina as part of its national territory. It consists of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel. This region overlaps with British and Chilean claims in Antarctica. None of these claims have widespread international recognition.
La Quiaca is a small city in the north of the province of Jujuy, Argentina, on the southern bank of the La Quiaca River, opposite the town of Villazón, Bolivia. It lies at the end of National Route 9, 289 km (180 mi) from San Salvador de Jujuy, and at an altitude of 3,442 m (11,293 ft) above mean sea level.

Gobernador Gregores is a town in Santa Cruz Province, Argentina, formerly known as Cañadón León. Ramón Outerello, one of the leaders of the massive strike known as Patagonia rebelde was executed there by a firing squad of the Argentine Army in November 1921.

Tartagal is a tropical city in northern Argentina, in the province of Salta. It is located in the northeast of the province, within the General José de San Martín Department, of which it is the capital. It is located in the Yungas jungle, at the foot of the sub-Andean mountain ranges to the west and the Salta plains to the east. This location gives it a wide variety of flora and fauna, and its territory is home to eight indigenous communities. It stands out for the large density of large trees in its streets and squares, such as mangoes, algarrobos and lapachos. It is one of the few places in the world where the green macaw is not extinct in the wild.

San Ramón de la Nueva Orán is a city in northwest province of Salta, Argentina, about 270 km (170 mi) from the provincial capital, Salta. It is the head town of the Orán Department, and it has about 73,000 inhabitants as per the 2001 census [INDEC], which makes it the second-most populated in the province.

The climate of Argentina varies from region to region, as the vast size of the country and wide variation in altitude make for a wide range of climate types. Summers are the warmest and wettest season in most of Argentina, except for most of Patagonia, where it is the driest season. The climate is warm in the north, cool in the center, and cold in the southern parts, that experience frequent frost and snow. Because the southern parts of the country are moderated by the surrounding oceans, the cold is less intense and prolonged than areas at similar latitudes in the northern hemisphere. Spring and autumn are transition seasons that generally feature mild weather.

San Antonio de los Cobres is a small town of population 5,482 in northwestern Argentina. It is the capital of the Los Andes Department of the Salta Province.

Puerto Santa Cruz is a town and municipality in Santa Cruz Province in southern Argentina. It lies near the Atlantic coast on the northern bank of the estuary of Santa Cruz River. It is the second oldest city in the province, being founded in 1878. It was the capital of the Santa Cruz National Territory until Río Gallegos took over the position in 1888. The town is a local centre for sheep and cattle farming. The presence of fresh water in an otherwise semi-arid environment allows for orchards and a local horticulture.

Gobernador Costa (Chubut) is a village and municipality in Chubut Province in southern Argentina.
General Conesa is a village and municipality in Río Negro Province in Argentina. It is also the antipode to Beijing, China.

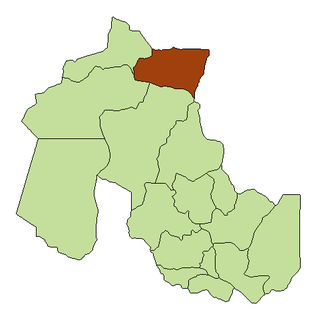
Los Andes is a department located in Salta Province, Argentina. It is the second largest by area in the province, after Rivadavia Department, and its capital is the town of San Antonio de los Cobres.

Salar de Arizaro is a large salt flat of the Andes in north-western Argentina. It is located between the villages of Tolar Grande and Caipe and near Mina La Casualidad, in Los Andes Department, Salta Province.

Due to its vast size and range of altitudes, Argentina possesses a wide variety of climatic regions, ranging from the hot subtropical region in the north to the cold subantarctic in the far south. The Pampas region lies between those and featured a mild and humid climate. Many regions have different, often contrasting, microclimates. In general, Argentina has four main climate types: warm, moderate, arid, and cold in which the relief features, and the latitudinal extent of the country, determine the different varieties within the main climate types.

Corrida de Cori is a mountain range in Argentina and Chile. It consists of several aligned volcanoes, including Cerro Escorial, which exceed 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) in elevation. The range, together with several local volcanoes, forms an alignment that may be controlled by a fault system. The volcanoes erupted mainly andesite and basaltic andesite, they were active in the Plio-Pleistocene with the most recent activity occurring at Cerro Escorial and at a cinder cone east of the range. There are two mines in the area, with a weather station nearby.


















