The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity,fracture,prosperity,and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Yellow River valley,which along with the Yangtze basin constitutes the geographic core of the Chinese cultural sphere. China maintains a rich diversity of ethnic and linguistic people groups. The traditional lens for viewing Chinese history is the dynastic cycle:imperial dynasties rise and fall,and are ascribed certain achievements. Throughout pervades the narrative that Chinese civilization can be traced as an unbroken thread many thousands of years into the past,making it one of the cradles of civilization. At various times,states representative of a dominant Chinese culture have directly controlled areas stretching as far west as the Tian Shan,the Tarim Basin,and the Himalayas,as far north as the Sayan Mountains,and as far south as the delta of the Red River.

Nanjing is the capital of Jiangsu province in eastern China. The city,which is located in the southwestern corner of the province,has 11 districts,an administrative area of 6,600 km2 (2,500 sq mi),and as of 2021 a population of 9,423,400 Situated in the Yangtze River Delta region,Nanjing has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture,having served as the capital of various Chinese dynasties,kingdoms and republican governments dating from the 3rd century to 1949,and has thus long been a major center of culture,education,research,politics,economy,transport networks and tourism,being the home to one of the world's largest inland ports. The city is also one of the fifteen sub-provincial cities in the People's Republic of China's administrative structure,enjoying jurisdictional and economic autonomy only slightly less than that of a province. It has also been awarded the title of 2008 Habitat Scroll of Honor of China,Special UN Habitat Scroll of Honor Award and National Civilized City. Nanjing is also considered a Beta city classification,together with Chongqing,Hangzhou and Tianjin by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network,and ranked as one of the world's top 100 cities in the Global Financial Centres Index.
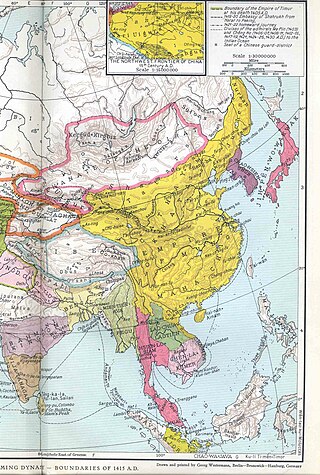
The Ming dynasty,officially the Great Ming,was an imperial dynasty of China,ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Han people,the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng,numerous rump regimes ruled by remnants of the Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662.

The Grand Canal is a system of interconnected canals linking various major rivers in North and East China,serving as an important waterborne transport infrastructure between the north and the south during Medieval and premodern China. It is the longest artificial waterway in the world and a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Amur River or Heilong River is a perennial river in Northeast Asia,forming the natural border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China. The Amur proper is 2,824 km (1,755 mi) long,and has a drainage basin of 1,855,000 km2 (716,000 sq mi). If including its main stem tributary,the Argun,the Amur is 4,444 km (2,761 mi) long,making it the world's tenth longest river.

The Crisis of the Tumu Fortress,also known as the Tumu Crisis,or the Jisi Incident,was a frontier conflict between the Northern Yuan and Ming dynasties. The Oirat ruler of the Northern Yuan,Esen,captured the Emperor Yingzong of Ming on September 1,1449.

The Yongle Emperor,personal name Zhu Di,was the third emperor of the Ming dynasty,reigning from 1402 to 1424.

Dongting Lake is a large,shallow lake in northeastern Hunan Province,China. It is a flood basin of the Yangtze River,so its volume depends on the season. The provinces of Hubei and Hunan are named after their location relative to the lake:Hubei means "North of the Lake" and Hunan,"South of the Lake".

Jiangnan is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River,including the southern part of its delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai,the southern part of Jiangsu Province,the southeastern part of Anhui Province,the northern part of Jiangxi Province and the northern part of Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing,Changzhou,Hangzhou,Nanjing,Ningbo,Shaoxing,Suzhou,Wuxi,Wenzhou,Yangzhou and Zhenjiang.

Lujiazui is a locality in Shanghai,a peninsula formed by a bend in the Huangpu River. Since the early 1990s,Lujiazui has been developed specifically as a new financial district of Shanghai. The decision to earmark Lujiazui for this purpose reflects its location:it is located on the east side of the Huangpu River in Pudong,and sits directly across the river from the old financial and business district of the Bund.
Imperial Tombs of the Ming and Qing Dynasties is the designation under which the UNESCO has included several tombs and burial complexes in the list of World Heritage Sites. These tombs date from the Ming and Qing dynasties of China.

LêLợi,also known by his temple name as LêThái Tổ (黎太祖) and by his pre-imperial title Bình Định vương,was a Vietnamese rebel leader who founded the Later Lêdynasty and became the first king of the restored kingdom of Đại Việt after the country was conquered by the Ming dynasty. In 1418,LêLợi and his followers rose up against Ming rule. He was known for his effective guerrilla tactics,including constantly moving his camps and using small bands of irregulars to ambush the larger Ming forces. Nine years later,his resistance movement successfully drove the Ming armies out of Vietnam and restored Vietnamese independence. LêLợi is among the most famous figures of Vietnamese history and one of its greatest heroes.

The Great Wall of China is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic groups from the Eurasian Steppe. Several walls were built from as early as the 7th century BC,with selective stretches later joined by Qin Shi Huang (220–206 BC),the first emperor of China. Little of the Qin wall remains. Later on,many successive dynasties built and maintained multiple stretches of border walls. The best-known sections of the wall were built by the Ming dynasty (1368–1644).

She County,or Shexian,is a county in the southeast of Anhui Province,China,bordering Zhejiang Province to the east. It is the easternmost county-level division of the prefecture-level city of Huangshan City. It has a population of 363,000 as of 2021,and an area of 2,236 square kilometres (863 sq mi).

The Northern Yuan was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later Jin dynasty in 1635. The Northern Yuan dynasty began with the retreat of the Yuan imperial court led by Toghon Temür to the Mongolian steppe. This period featured factional struggles and the often only nominal role of the Great Khan.

The Nine Garrisons,or Nine Defense Areas,was a system implemented during the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) to protect the northern border and the Great Wall. Originally consisting of nine garrisons,the system was later expanded to eleven. Each garrison was controlled from a fortified garrison town,strategically located at important passages and reinforced militarily. The leadership of the garrisons was divided among three supreme commanders:Jiliao,Xuanda,and Shaanxi sanbian. Each garrison had a military commander,as well as a civilian administration. In total,approximately 300,000 soldiers and officers were deployed in the garrisons.

The Ming Ancestors Mausoleum,Ming Ancestor Tomb,or Zuling Tomb was the first imperial mausoleum complex of the Ming dynasty,constructed at a geomantically advantageous site near the inlet of the Huai River into the west side of Hongze Lake in present-day Xuyi County,Huai'an Prefecture,Jiangsu Province,China. Built between 1386 and 1413 by Zhu Yuanzhang—the Hongwu Emperor who founded the Ming—and his son Zhu Di the Yongle Emperor to display their filial piety,it was located north of the town of Sizhou,where the ancestors of the dynasty had lived. The remains of the Hongwu Emperor's grandfather Zhu Chuyi are known to have been disintered and moved to the site. He,his father Zhu Sijiu,and his grandfather Zhu Bailiu were posthumously revered at the site as honorary emperors,Zhu Chuyi as the Xi Ancestor of the Ming (Xizu),Zhu Sijiu as the Yi Ancestor of the Ming (Yizu),and Zhu Bailiu as the De Ancestor of the Ming (Dezu).

The Yongle Emperor's campaigns against the Mongols happened from 1410 to 1424. It comprised five aggressive military expeditions by Ming China's armies against the Eastern Mongols,Oirat Mongols,and other Mongol tribes.

Manchuria under Ming rule refers to the domination of the Ming dynasty of China over the greater region of Manchuria,including today's Northeast China and Outer Manchuria. The Ming rule of Manchuria began with its conquest of Manchuria in the late 1380s after the fall of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty,and reached its peak in the early 15th century with the establishment of the Nurgan Regional Military Commission. With the dissolution of the Nurgan Regional Military Commission the Ming power waned considerably in Manchuria. Starting in the 1580s,Nurhaci,the Jianzhou Jurchen chieftain who had been a Ming vassal,began to take control of most of Manchuria over the next several decades,and in 1616 he established the Later Jin and openly renounced Ming overlordship with the Seven Grievances. The Qing dynasty established by his son Hong Taiji would eventually conquer the Ming and take control of China proper.
















