
In molecular biology, a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule, resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. Thus, an mRNA that contains a riboswitch is directly involved in regulating its own activity, in response to the concentrations of its effector molecule. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins, catalyze reactions, or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules.

The YdaO/YuaA leader is a conserved RNA structure found upstream of the ydaO and yuaA genes in Bacillus subtilis and related genes in other bacteria. Its secondary structure and gene associations were predicted by bioinformatics.

The PreQ1-I riboswitch is a cis-acting element identified in bacteria which regulates expression of genes involved in biosynthesis of the nucleoside queuosine (Q) from GTP. PreQ1 (pre-queuosine1) is an intermediate in the queuosine pathway, and preQ1 riboswitch, as a type of riboswitch, is an RNA element that binds preQ1. The preQ1 riboswitch is distinguished by its unusually small aptamer, compared to other riboswitches. Its atomic-resolution three-dimensional structure has been determined, with the PDB ID 2L1V.
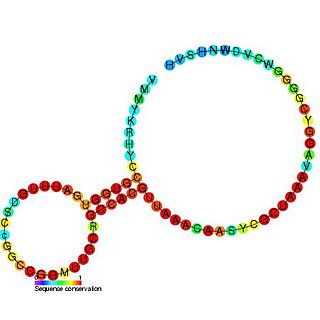
The SAM-II riboswitch is a RNA element found predominantly in alpha-proteobacteria that binds S-adenosyl methionine (SAM). Its structure and sequence appear to be unrelated to the SAM riboswitch found in Gram-positive bacteria. This SAM riboswitch is located upstream of the metA and metC genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and other methionine and SAM biosynthesis genes in other alpha-proteobacteria. Like the other SAM riboswitch, it probably functions to turn off expression of these genes in response to elevated SAM levels. A significant variant of SAM-II riboswitches was found in Pelagibacter ubique and related marine bacteria and called SAM-V. Also, like many structured RNAs, SAM-II riboswitches can tolerate long loops between their stems.
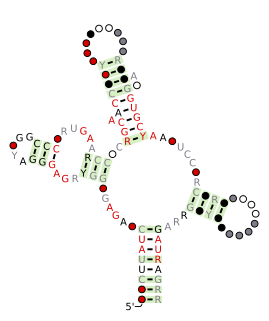
The SAM riboswitch is found upstream of a number of genes which code for proteins involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis in Gram-positive bacteria. Two SAM riboswitches in Bacillus subtilis that were experimentally studied act at the level of transcription termination control. The predicted secondary structure consists of a complex stem-loop region followed by a single stem-loop terminator region. An alternative and mutually exclusive form involves bases in the 3' segment of helix 1 with those in the 5' region of helix 5 to form a structure termed the anti-terminator form. When SAM is unbound, the anti-terminator sequence sequesters the terminator sequence so the terminator is unable to form, allowing the polymerase read-through the downstream gene. When the SAM is bound to the aptamer, the anti-terminator is sequestered by an anti-anti-terminator; the terminator forms and terminates the transcription. However, many SAM riboswitches are likely to regulate gene expression at the level of translation.

The TPP riboswitch, also known as the THI element and Thi-box riboswitch, is a highly conserved RNA secondary structure. It serves as a riboswitch that binds directly to thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) to regulate gene expression through a variety of mechanisms in archaea, bacteria and eukaryotes. TPP is the active form of thiamine (vitamin B1), an essential coenzyme synthesised by coupling of pyrimidine and thiazole moieties in bacteria. The THI element is an extension of a previously detected thiamin-regulatory element, the thi box, there is considerable variability in the predicted length and structures of the additional and facultative stem loops represented in dark blue in the secondary structure diagram Analysis of operon structures has identified a large number of new candidate thiamin-regulated genes, mostly transporters, in various prokaryotic organisms. The x-ray crystal structure of the TPP riboswitch aptamer has been solved.
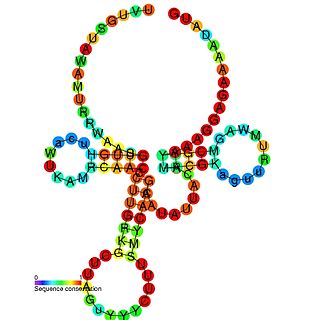
PreQ1-II riboswitches form a class of riboswitches that specifically bind pre-queuosine1 (PreQ1), a precursor of the modified nucleoside queuosine. They are found in certain species of Streptococcus and Lactococcus, and were originally identified as a conserved RNA secondary structure called the "COG4708 motif". All known members of this riboswitch class appear to control members of COG4708 genes. These genes are predicted to encode membrane-bound proteins and have been proposed to be a transporter of preQ1, or a related metabolite, based on their association with preQ1-binding riboswitches. PreQ1-II riboswitches have no apparent similarities in sequence or structure to preQ1-I riboswitches, a previously discovered class of preQ1-binding riboswitches. PreQ1 thus joins S-adenosylmethionine as the second metabolite to be found that is the ligand of more than one riboswitch class.

Cyclic di-GMP-I riboswitches are a class of riboswitch that specifically bind cyclic di-GMP, which is a second messenger that is used in a variety of microbial processes including virulence, motility and biofilm formation. Cyclic di-GMP-I riboswitches were originally identified by bioinformatics as a conserved RNA-like structure called the "GEMM motif". These riboswitches are present in a wide variety of bacteria, and are most common in Clostridia and certain varieties of Proteobacteria. The riboswitches are present in pathogens such as Clostridium difficile, Vibrio cholerae and Bacillus anthracis. Geobacter uraniumreducens is predicted to have 30 instances of this riboswitch in its genome. A bacteriophage that infects C. difficile is predicted to carry a cyclic di-GMP-I riboswitch, which it might use to detect and exploit the physiological state of bacteria that it infects.

The crcB RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in a wide variety of bacteria and archaea. These RNAs were later shown to function as riboswitches that sense fluoride ions. These "fluoride riboswitches" increase expression of downstream genes when fluoride levels are elevated, and the genes are proposed to help mitigate the toxic effects of very high levels of fluoride.

The Downstream-peptide motif refers to a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics in the cyanobacterial genera Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus and one phage that infects such bacteria. It was also detected in marine samples of DNA from uncultivated bacteria, which are presumably other species of cyanobacteria.

The glutamine riboswitch is a conserved RNA structure that was predicted by bioinformatics. It is present in a variety of lineages of cyanobacteria, as well as some phages that infect cyanobacteria. It is also found in DNA extracted from uncultivated bacteria living in the ocean that are presumably species of cyanobacteria.

The pfl RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure present in some bacteria and originally discovered using bioinformatics. pfl RNAs are consistently present in genomic locations that likely correspond to the 5' untranslated regions of protein-coding genes. This arrangement in bacteria is commonly associated with cis-regulatory elements. Moreover, they are in presumed 5' UTRs of multiple non-homologous genes, suggesting that they function only in these locations. Additional evidence of cis-regulatory function came from the observation that predicted rho-independent transcription terminators overlap pfl RNAs. This overlap suggests that the alternate secondary structures of pfl RNA and the transcription terminator stem-loops compete with each other, and this is a common mechanism for cis gene control in bacteria.

The potC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure discovered using bioinformatics. The RNA is detected only in genome sequences derived from DNA that was extracted from uncultivated marine bacteria. Thus, this RNA is present in environmental samples, but not yet found in any cultivated organism. potC RNAs are located in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of genes predicted to encode either membrane transport proteins or peroxiredoxins. Therefore, it was hypothesized that potC RNAs are cis-regulatory elements, but their detailed function is unknown.

The yjdF RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified using bioinformatics. Most yjdF RNAs are located in bacteria classified within the phylum Firmicutes. A yjdF RNA is found in the presumed 5' untranslated region of the yjdF gene in Bacillus subtilis, and almost all yjdF RNAs are found in the 5' UTRs of homologs of this gene. The function of the yjdF gene is unknown, but the protein that it is predicted to encode is classified by the Pfam Database as DUF2992.

Tetrahydrofolate riboswitches are a class of homologous RNAs in certain bacteria that bind tetrahydrofolate (THF). It is almost exclusively located in the probable 5' untranslated regions of protein-coding genes, and most of these genes are known to encode either folate transporters or enzymes involved in folate metabolism. For these reasons it was inferred that the RNAs function as riboswitches. THF riboswitches are found in a variety of Firmicutes, specifically the orders Clostridiales and Lactobacillales, and more rarely in other lineages of bacteria. The THF riboswitch was one of many conserved RNA structures found in a project based on comparative genomics. The 3-d structure of the tetrahydrofolate riboswitch has been solved by separate groups using X-ray crystallography. These structures were deposited into the Protein Data Bank under accessions 3SD1 and 3SUX, with other entries containing variants.

The FuFi-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Such RNA "motifs" are often the first step to elucidating the biological function of a novel RNA. FuFi-1 motif RNAs are found in Firmicutes AND Fusobacteria.
The nadA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The nadA motif is found in Acidobacteria.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Firmicutes and Gammaproteobacteria.

The Zeta-pan RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Zeta-pan motif RNAs are found in Zetaproteobacteria.























