
Daniel Chester French was an American sculptor of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. He is best known for his 1874 sculpture The Minute Man in Concord, Massachusetts, and his 1920 monumental statue of Abraham Lincoln in the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C.

Menkaure or Menkaura was a pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom. He is well known under his Hellenized names Mykerinos, in turn Latinized as Mycerinus, and Menkheres. According to Manetho, he was the throne successor of king Bikheris, but according to archaeological evidence, he was almost certainly the successor of Khafre. Africanus reports as rulers of the fourth dynasty Sôris, Suphis I, Suphis II, Mencherês (=Menkaure), Ratoisês, Bicheris, Sebercherês, and Thamphthis in this order. Menkaure became famous for his tomb, the Pyramid of Menkaure, at Giza and his statue triads, showing the king together with his wives Rekhetre and Khamerernebty and with various deities.

Paul Howard Manship was an American sculptor. He consistently created mythological pieces in a classical style, and was a major force in the Art Deco movement. He is well known for his large public commissions, including the iconic Prometheus in Rockefeller Center and the Celestial Sphere Woodrow Wilson Memorial in Geneva, Switzerland. He is also credited for designing the modern rendition of New York City's official seal.

The Museum of Fine Arts is an art museum in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. It is the 20th-largest art museum in the world, measured by public gallery area. It contains 8,161 paintings and more than 450,000 works of art, making it one of the most comprehensive collections in the Americas. With more than 1.2 million visitors a year, it is the 79th–most visited art museum in the world as of 2022.

Aspelta was a ruler of the kingdom of Kush. More is known about him and his reign than most of the rulers of Kush. He left several stelae carved with accounts of his reign.

Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal is a mesa or large rock outcrop located 400 km north of Khartoum, next to Karima in Northern State in Sudan, on the Nile River, in the region that is sometimes called Nubia. The jebel is 104 m tall, has a flat top, and came to have religious significance for both ancient Kush and ancient Egyptian occupiers. In 2003, the mountain, together with the extensive archaeological site at its base, were named as the center of a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. The Jebel Barkal area houses the Jebel Barkal Museum.

Nykara (Ni-ka-re) was an ancient Egyptian official of the Fifth Dynasty. His highest positions were that of an overseer of the double granaries and overseer of the granary of the residence. He was also priest at the sun-temple of king Niuserre. Nykara is known from a number of monuments all coming from his tomb at Saqqara. Its exact position is unknown.

Appeal to the Great Spirit is a 1908 equestrian statue by Cyrus Dallin, located in front of the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. It portrays a Native American on horseback facing skyward, his arms spread wide in a spiritual request to the Great Spirit. It was the last of Dallin's four prominent sculptures of Indigenous people known as The Epic of the Indian, which also include A Signal of Peace (1890), The Medicine Man (1899), and Protest of the Sioux (1904).
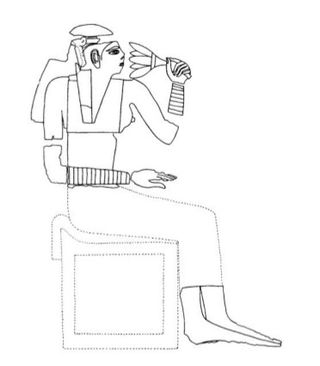
Hetepheres I was a queen of Egypt during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt who was a wife of one king, the mother of the next king, the grandmother of two more kings, and the figure who tied together two dynasties.

The painted limestone bust of Ankhhaf is an ancient Egyptian sculpture dating from the Old Kingdom. It is considered the work "of a master" of ancient Egyptian art, and can be seen at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. Its catalog number is Museum Expedition 27.442.

Water Lilies is a series of approximately 250 oil paintings by French Impressionist Claude Monet (1840–1926). The paintings depict his flower garden at his home in Giverny, and were the main focus of his artistic production during the last thirty years of his life. Many of the works were painted while Monet suffered from cataracts.

Exhibitions of artifacts from the tomb of Tutankhamun have been held at museums in several countries, notably the United Kingdom, Soviet Union, United States, Canada, Japan, and France.

Anlamani was a king of the Kingdom of Kush in Nubia, who ruled from 620 BC and died around 600 BC.

Atlanersa was a Kushite ruler of the Napatan kingdom of Nubia, reigning for about a decade in the mid-7th century BC. He was the successor of Tantamani, the last ruler of the 25th Dynasty of Egypt, and possibly a son of Taharqa or less likely of Tantamani, while his mother was a queen whose name is only partially preserved. Atlanersa's reign immediately followed the collapse of Nubian control over Egypt, which witnessed the Assyrian conquest of Egypt and then the beginning of the Late Period under Psamtik I. The same period also saw the progressive cultural integration of Egyptian beliefs by the Kushite civilization.

The Museum of Fine Arts of Lyon is a municipal museum of fine arts in the French city of Lyon. Located near the Place des Terreaux, it is housed in a former Benedictine convent which was active during the 17th and 18th centuries. It was restored between 1988, and 1998, remaining open to visitors throughout this time despite the ongoing restoration works. Its collections range from ancient Egyptian antiquities to the Modern art period, making the museum one of the most important in Europe. It also hosts important exhibitions of art, for example the exhibitions of works by Georges Braque and Henri Laurens in the second half of 2005, and another on the work of Théodore Géricault from April to July 2006. It is one of the largest art museums in France.

The colossal quartzite statue of Amenhotep III is an ancient Egyptian sculpture dating from the 18th Dynasty. It was found in the massive mortuary temple of the pharaoh Amenhotep III on the West Bank of the River Nile at Thebes (Luxor) in Egypt. Only the head of the broken colossal statue survives. It is part of the British Museum's Department of Ancient Egypt and Sudan collection.

The Temple of Amun is an archaeological site at Jebel Barkal in Northern State, Sudan. It is situated about 400 kilometres (250 mi) north of Khartoum near Karima. The temple stands near a large bend of the Nile River, in the region that was called Nubia in ancient times. The Temple of Amun, one of the largest temples at Jebel Barkal, is considered sacred to the local population. Not only was the Amun temple a main centre of what at one time was considered to be an almost universal religion, but, along with the other archaeological sites at Jebel Barkal, it was representative of the revival of Egyptian religious values. Up to the middle of the 19th century, the temple was subjected to vandalism, destruction, and indiscriminate plundering, before it came under state protection.

Wooden tomb models were deposited as grave goods in the tombs and burial shafts throughout early Egyptian History, most notably in the Middle Kingdom of Egypt. They included a wide variety of wooden figurines and scenes, such as boats, granaries, baking and brewing scenes and butchery scenes. These served as ways to preserve the action depicted for eternity in honor of the dead. The use of wood rather than other materials became popular in the first intermediate period. Over time the models of boats in particular went from life size to much smaller scale though they remained numerous, some boats being less than a meter in length and fleets at times being larger than 50 models. The 11th dynasty appears to be when there is a shift from making these burial boats river worthy to making them stand nicely for funerary display.

Amanimalel was a Kushite queen of the Napatan kingdom of Nubia, likely a spouse of king Senkamanisken living in the second half of the 7th century BC. She is mostly known from one or possibly two statues of her of very high quality.



















