
The miR-9 microRNA, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. The mature ~21nt miRNAs are processed from hairpin precursor sequences by the Dicer enzyme. The dominant mature miRNA sequence is processed from the 5' arm of the mir-9 precursor, and from the 3' arm of the mir-79 precursor. The mature products are thought to have regulatory roles through complementarity to mRNA. In vertebrates, miR-9 is highly expressed in the brain, and is suggested to regulate neuronal differentiation. A number of specific targets of miR-9 have been proposed, including the transcription factor REST and its partner CoREST.

mir-133 is a type of non-coding RNA called a microRNA that was first experimentally characterised in mice. Homologues have since been discovered in several other species including invertebrates such as the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster. Each species often encodes multiple microRNAs with identical or similar mature sequence. For example, in the human genome there are three known miR-133 genes: miR-133a-1, miR-133a-2 and miR-133b found on chromosomes 18, 20 and 6 respectively. The mature sequence is excised from the 3' arm of the hairpin. miR-133 is expressed in muscle tissue and appears to repress the expression of non-muscle genes.
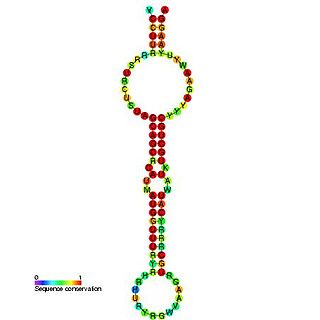
The miR-15 microRNA precursor family is made up of small non-coding RNA genes that regulate gene expression. The family includes the related mir-15a and mir-15b sequences, as well as miR-16-1, miR-16-2, miR-195 and miR-497. These six highly conserved miRNAs are clustered on three separate chromosomes. In humans miR-15a and miR-16 are clustered within 0.5 kilobases at chromosome position 13q14. This region has been found to be the most commonly affected in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), with deletions of the entire region in more than half of cases. Both miR-15a and miR-16 are thus frequently deleted or down-regulated in CLL samples with 13q14 deletions; occurring in more than two thirds of CLL cases. The expression of miR-15a is associated with survival in triple negative breast cancer.
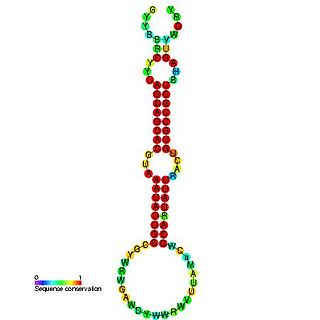
The miR-16 microRNA precursor family is a group of related small non-coding RNA genes that regulates gene expression. miR-16, miR-15, mir-195 and miR-497 are related microRNA precursor sequences from the mir-15 gene family. This microRNA family appears to be vertebrate specific and its members have been predicted or experimentally validated in a wide range of vertebrate species.

The miR-1 microRNA precursor is a small micro RNA that regulates its target protein's expression in the cell. microRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give products at ~22 nucleotides. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 3' arm of the precursor. The mature products are thought to have regulatory roles through complementarity to mRNA. In humans there are two distinct microRNAs that share an identical mature sequence, these are called miR-1-1 and miR-1-2.
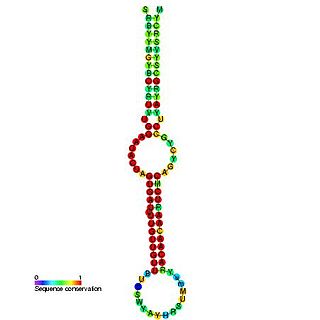
This family represents the microRNA (miRNA) precursor mir-7. This miRNA has been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. miRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 5' arm of the precursor. The extents of the hairpin precursors are not generally known and are estimated based on hairpin prediction. The involvement of Dicer in miRNA processing suggests a relationship with the phenomenon of RNA interference.
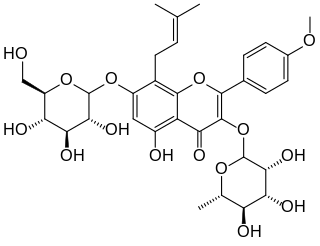
Icariin is a chemical compound classified as a prenylated flavonol glycoside, a type of flavonoid. It is the 8-prenyl derivative of kaempferol 3,7-O-diglucoside. The compound has been isolated from several species of plant belonging to the genus Epimedium which are commonly known as horny goat weed, Yin Yang Huo, and Herba epimedii. Extracts from these plants are reputed to produce aphrodisiac effects, and are used in traditional Chinese medicine to enhance erectile function. However, clinical trial data are lacking to support these claims.

mir-127 microRNA is a short non-coding RNA molecule with interesting overlapping gene structure. miR-127 functions to regulate the expression levels of genes involved in lung development, placental formation and apoptosis. Aberrant expression of miR-127 has been linked to different cancers.

In molecular biology mir-22 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs are an abundant class of molecules, approximately 22 nucleotides in length, which can post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression by binding to the 3' UTR of mRNAs expressed in a cell.

In molecular biology miR-375 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNAs that regulate genes post-transcriptionally by inhibiting translation and/or causing mRNA degradation. miR-375 is found on human chromosome 2 in between the CRYBA2 and CCDC108 genes.

miR-27 is a family of microRNA precursors found in animals, including humans. MicroRNAs are typically transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. The excised region or, mature product, of the miR-27 precursor is the microRNA mir-27.
miR-144 is a family of microRNA precursors found in mammals, including humans. The ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA sequence is excised from the precursor hairpin by the enzyme Dicer. In humans, miR-144 has been characterised as a "common miRNA signature" of a number of different tumours.

miR-338 is a family of brain-specific microRNA precursors found in mammals, including humans. The ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA sequence is excised from the precursor hairpin by the enzyme Dicer. This sequence then associates with RISC which effects RNA interference.
In molecular biology mir-340 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-370 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-484 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. The precursor hairpin of miR-484 is transcribed directly and contains a 7-methylguanylated cap. The biogenesis of miR-484 is independent of Drosha.
In molecular biology mir-503 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-153 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-198 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-872 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.













