This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2020) |
| Communication |
|---|
 |
| General aspects |
| Fields |
| Disciplines |
| Categories |
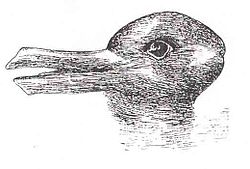

Miscommunication ("mis" + "communication") is the failure of communicating clearly the intended message or idea. [1] It may be a social inability to communicate adequately and properly, and it is one of many types of communication barriers.
It is an instance where either the speaker is unable to provide the proper and adequate information to the hearer or the hearer misperceived and couldn't recognise the communication from the speaker. The cases of miscommunication vary depending on the situation and persons included in it, but often result in confusion and frustration. In some cases, miscommunication may even open up the triangle of other factors that inevitably leads to a conflict.
Miscommunication is a lack of alignment of agents' intellectual state, especially when they diverge on the outcomes of communication. [2] The type of miscommunication can now be classified as to the source of the non-alignment about the communicative act. [3]