
Airborne forces are ground combat units carried by aircraft and airdropped into battle zones, typically by parachute drop. Parachute-qualified infantry and support personnel serving in airborne units are also known as paratroopers.
Mission Chicago was a pre-dawn glider-borne combat assault in the American airborne landings in Normandy, made by elements of the 101st Airborne Division on the early morning of June 6, 1944 during the Normandy landings of World War II. It was part of Operation Neptune, the assault portion of the Allied invasion of Normandy, codenamed Operation Overlord. Originally slated to be the main assault for the 101st Airborne Division, the glider operation instead became the first reinforcement mission after the main parachute combat assault, Mission Albany. Because the area of responsibility for the division was in close proximity to Utah Beach, the use of glider reinforcement was limited in scale, with most division support units transported by sea.

Operation Tonga was the codename given to the airborne operation undertaken by the British 6th Airborne Division between 5 June and 7 June 1944 as a part of Operation Overlord and the D-Day landings during the Second World War.

Operation Ladbroke was a glider landing by British airborne troops during the Second World War near Syracuse, Sicily, that began on 9 July 1943 as part of Operation Husky, the Allied invasion of Sicily. The first Allied mission using large numbers of the aircraft, the operation was carried out from Tunisia by glider infantry of the British 1st Airlanding Brigade, commanded by Brigadier Philip Hicks, with a force of 136 Hadrians and eight Airspeed Horsas. The objective was to establish a large invasion force on the ground near the town of Syracuse, secure the Ponte Grande Bridge and ultimately take control of the city itself with its strategically vital docks, as a prelude to the full-scale invasion of Sicily.

Operation Fustian was an airborne forces operation undertaken during the Allied invasion of Sicily in July 1943 in the Second World War. The operation was carried out by Brigadier Gerald Lathbury's 1st Parachute Brigade, part of the British 1st Airborne Division. Their objective was the Primosole Bridge across the Simeto River. The intention was for the brigade, with glider-borne forces in support, to land on both sides of the river. They would then capture the bridge and secure the surrounding area until relieved by the advance of British XIII Corps, which had landed on the south eastern coast three days previously. Because the bridge was the only crossing on the river and would give the British Eighth Army access to the Catania plain, its capture was expected to speed the advance and lead to the defeat of the Axis forces in Sicily.
During World War II, Mission Elmira was the landing of a significant part of the 82nd Airborne Division’s glider train in Normandy on the evening of 6 June 1944 as part of Operation Neptune, the assault phase of Operation Overlord.

The 1st Airborne Division was an airborne infantry division of the British Army during the Second World War. The division was formed in late 1941 during the Second World War, after the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill, demanded an airborne force, and was initially under command of Major-General Frederick A. M. "Boy" Browning. The division was one of two airborne divisions raised by the British Army during the war, with the other being the 6th Airborne Division, created in May 1943, using former units of the 1st Airborne Division.

The Airspeed AS.51 Horsa was a British troop-carrying glider used during the Second World War. It was developed and manufactured by Airspeed Limited, alongside various subcontractors; the type was named after Horsa, the legendary 5th-century conqueror of southern Britain.

Glider infantry was a type of airborne infantry in which soldiers and their equipment were inserted into enemy-controlled territory via military glider. Initially developed in the late 1930s by Germany, glider infantry units were used extensively during World War II but are no longer used by any modern military.

Military gliders have been used by the militaries of various countries for carrying troops and heavy equipment to a combat zone, mainly during the Second World War. These engineless aircraft were towed into the air and most of the way to their target by military transport planes, e.g., C-47 Skytrain or Dakota, or bombers relegated to secondary activities, e.g., Short Stirling. Most military gliders do not soar, although there were attempts to build military sailplanes as well, such as the DFS 228.

The 1st Airlanding Brigade was an airborne infantry brigade of the British Army during the Second World War and the only glider infantry formation assigned to the 1st Airborne Division, serving alongside the 1st Parachute Brigade and 4th Parachute Brigade.
The 1st Airborne Task Force was a short-lived Allied airborne unit that was active during World War II created for Operation Dragoon–the invasion of Southern France. Formed in July 1944, under the command of Major General Robert T. Frederick, it took part in the "Dragoon" landings on 15 August 1944, securing the area north-west of the landing beaches, before moving towards the French–Italian border as part of the United States Seventh Army. The unit was disbanded in November 1944.

American airborne landings in Normandy were a series of military operations carried by the United States as part of Operation Overlord, the invasion of Normandy by the Allies on June 6, 1944, during World War II. In the opening maneuver of the Normandy landings, about 13,100 American paratroopers from the 82nd and 101st Airborne Divisions, then 3,937 glider infantrymen, were dropped in Normandy via two parachute and six glider missions.

The Waco CG-4 was the most widely used American troop/cargo military glider of World War II. It was designated the CG-4A by the United States Army Air Forces, and given the service name Hadrian by the British.

Operation Mallard was the codename for an airborne forces operation, which was conducted by the British Army on 6 June 1944, as part of the Normandy landings during the Second World War.

The 51st Troop Carrier Wing is an inactive United States Air Force unit. The wing was formed during World War II and was the first troop carrier wing in the Army Air Forces (AAF) organized for deployment overseas. During the war, it served in the Mediterranean Theater of Operations, and its elements participated in every airborne assault in the theater. The wing also transported personnel and supplies within the theater. Its units also performed the majority of special operations flights by AAF units in the theater. Following V-E Day, the wing moved to Germany, where it became part of the occupation forces, operating as the European Air Transport Service until inactivating in January 1948. In August 1946, two of its planes were shot down by Yugoslav Air Force fighters near Yugoslavia's border with Austria and Italy.
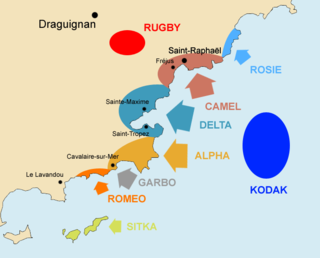
The British 2nd Parachute Brigade was part of the Operation Rugby airborne landings in August 1944. The operation was carried out by an ad hoc airborne formation called the 1st Airborne Task Force. Operation Rugby was itself part of the Operation Dragoon invasion of Southern France by the American 7th Army. The airborne task force landed in the River Argens valley with the objective of preventing German reinforcements from reaching the landing beaches. The landings were mainly an American operation and the brigade was the only British Army formation involved.

The capture of the Caen canal and Orne river bridges was an operation by airborne forces of the British Army that took place in the early hours of 6 June 1944 as part of the Normandy landings of the Second World War. The objective was to capture intact two road bridges in Normandy across the River Orne and the Caen canal, providing the only exit eastwards for British forces from their landing on Sword Beach. Intelligence reports said both bridges were heavily defended by the Germans and wired for demolition. Once captured, the bridges had to be held against any counter-attack, until the assault force was relieved by commandos and other infantry advancing from the landing beach.
Operation Turkey Buzzard, also known as Operation Beggar, was a British supply mission to North Africa that took place between March and August 1943, during the Second World War. The mission was undertaken by No. 2 Wing, Glider Pilot Regiment and No. 295 Squadron Royal Air Force, prior to the Allied invasion of Sicily. Unusually, the mission was known by different names in different branches of the British Armed Forces: the British Army called the operation "Turkey Buzzard", while in the Royal Air Force it was known as "Beggar".

The Battle of Merville Gun Battery was a series of British assaults beginning 6 June 1944, as part of Operation Tonga, part of the Normandy landings, during the Second World War. Allied intelligence believed the Merville Gun Battery was composed of heavy-calibre 150 mm (5.9 in) guns that could threaten the British landings at Sword Beach, only 8 miles (13 km) away.















