Mitte is a district in Berlin.
Mitte (German for middle, i.e., city centre or downtown) may refer to:
Mitte is a district in Berlin.
Mitte (German for middle, i.e., city centre or downtown) may refer to:
Osnabrück is a district (Landkreis) in the southwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. With 2,122 km² it is the second largest district of Lower Saxony.
Neustadt may refer to:

Bremen Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the city of Bremen in northwestern Germany. It is the most important rail station for both the city and state of Bremen; InterCityExpress, Intercity, EuroCity, CityNightLine and DB NachtZug services call at the station, which is situated to the Northeast of the city centre. The train services are operated by Deutsche Bahn, NordWestBahn, Metronom and Erixx.

Germany has an extensive number of tramway networks. Some of these networks have been upgraded to light rail standards, called Stadtbahn in German. Straßenbahn and Stadtbahn schemes are usually operated on the legal foundation of the BOStrab, the Tramways Act of Germany.

Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station of the city of Hamburg, Germany. Opened in 1906 to replace four separate terminal stations, today Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is operated by DB Station&Service AG. With an average of 550,000 passengers a day, it is Germany's busiest railway station and the second-busiest in Europe after the Gare du Nord in Paris. It is classed by Deutsche Bahn as a category 1 railway station.

The approximately 5,400 railway stations in Germany that are owned and operated by the Deutsche Bahn subsidiary DB Station&Service are divided into seven categories, denoting the service level available at the station.
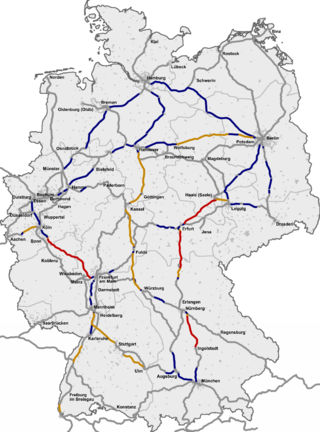
Construction of the first high-speed rail in Germany began shortly after that of the French LGVs. However, legal battles caused significant delays, so that the German Intercity-Express (ICE) trains were deployed ten years after the TGV network was established.
The Bundesfinanzdirektionen were the German federal funding agencies with responsibility to the Federal Ministry of Finance that operated between 2008-2015. On January 1, 2016 it was replaced by the newly established German federal government's General Directorate Generalzolldirektion.

Rapid transit in Germany consists of four U-Bahn systems and fourteen S-Bahn systems. The U-Bahn commonly understood to stand for Untergrundbahn are conventional rapid transit systems that run mostly underground, while the S-Bahn or Stadtschnellbahn are commuter rail services, that may run underground in the city center and have metro-like characteristics in Munich, Hamburg and Berlin which they only have to a lesser extent in other cities. There are also over a dozen premetro or Stadtbahn systems that are rapid transit in the city center and light rail outside.

This article shows a list of railway stations in Germany. The list is subdivided per federal state. Due to the number of railway stations it shows a selection of the principal stations and links to related state articles. Where there are 2 or more passenger stations in a large town or city, the most important is often designated by the Deutsche Bahn as the Hauptbahnhof, of which there are 122 in total.

Münster Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station in the city of Münster in Germany.
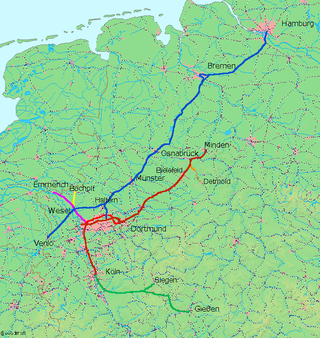
The Cologne-Minden Railway Company was along with the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company and the Rhenish Railway Company one of the railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia.

The Hanover–Brunswick Railway is a German main line railway in Lower Saxony and is one of the oldest lines in Germany, opened in 1843 and 1844. It was the first railway line linking to the city of Hanover and the first operating line of the Royal Hanoverian State Railways. It is now one of the main routes for east-west traffic. The main intermediate station is Peine.

Osnabrück Hauptbahnhof is a railway station located in Osnabrück, Germany. The station was opened in 1895 and is located on the Wanne-Eickel–Hamburg, Löhne–Rheine, Osnabrück–Bielefeld and the Oldenburg–Osnabrück lines. The train services are operated by Deutsche Bahn, Hamburg-Köln-Express, NordWestBahn, Eurobahn and WestfalenBahn. The station features two levels, with lines at right angles to each other.

Intercity is the second-highest train classification in Germany, after the ICE. Intercity services are loco-hauled express train services, usually over long-distances. There are Intercity routes throughout Germany, and routes generally operate with a two-hour frequency, with multiple routes giving a more frequent service on core routes. Intercity services are operated by the DB Fernverkehr sector of Deutsche Bahn.

Altenbeken station is in the municipality of Altenbeken in the Paderborn district of the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The station has a great importance as a hub for local and long-distance transport due to its location on the line from the Ruhr area to Warburg and Kassel, as well as to Holzminden–Kreiensen, Hanover and Herford. Its importance has increased recently because of the lack of Intercity-Express/Intercity services on the so-called Mid-Germany Railway.