Shareware is a type of proprietary software that is initially shared by the owner for trial use at little or no cost. Often the software has limited functionality or incomplete documentation until the user sends payment to the software developer. Shareware is often offered as a download from a website. Shareware differs from freeware, which is fully-featured software distributed at no cost to the user but without source code being made available; and free and open-source software, in which the source code is freely available for anyone to inspect and alter.

A text editor is a type of computer program that edits plain text. Such programs are sometimes known as "notepad" software. Text editors are provided with operating systems and software development packages, and can be used to change files such as configuration files, documentation files and programming language source code.
A music sequencer is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling note and performance information in several forms, typically CV/Gate, MIDI, or Open Sound Control, and possibly audio and automation data for digital audio workstations (DAWs) and plug-ins.
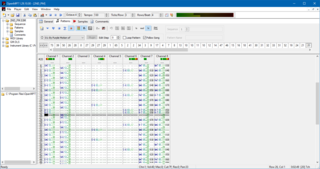
A music tracker is a type of music sequencer software for creating music. The music is represented as discrete musical notes positioned in several channels at chronological positions on a vertical timeline. A music tracker's user interface is traditionally number based. Notes, parameter changes, effects and other commands are entered with the keyboard into a grid of fixed time slots as codes consisting of letters, numbers and hexadecimal digits. Separate patterns have independent timelines; a complete song consists of a master list of repeated patterns.
In information theory, linguistics, and computer science, the Levenshtein distance is a string metric for measuring the difference between two sequences. The Levenshtein distance between two words is the minimum number of single-character edits required to change one word into the other. It is named after Soviet mathematician Vladimir Levenshtein, who defined the metric in 1965.

PC-Write was a computer word processor and was one of the first three widely popular software products sold via the marketing method that became known as shareware. It was originally written by Bob Wallace in early 1983.

OpenMPT is an open-source audio module tracker for Windows. It was previously called ModPlug Tracker, and was first released by Olivier Lapicque in September 1997.

FastTracker 2 is a music tracker created by Fredrik "Mr. H" Huss and Magnus "Vogue" Högdahl, two members of the demogroup Triton who set about releasing their own tracker after breaking into the scene in 1992 and winning several demo competitions. The source code of FastTracker 2 is written in Pascal using Borland Pascal 7 and TASM. The program works natively under MS-DOS.
MOD is a computer file format used primarily to represent music, and was the first module file format. MOD files use the “.MOD” file extension, except on the Amiga which doesn't rely on filename extensions; instead, it reads a file's header to determine filetype. A MOD file contains a set of instruments in the form of samples, a number of patterns indicating how and when the samples are to be played, and a list of what patterns to play in what order.

UltraEdit is a text editor for Microsoft Windows, Linux, and MacOS. It was initially developed in 1994 by Ian D. Mead, the founder of IDM Computer Solutions Inc., and was acquired by Idera Inc. in the August of 2021. Originally called MEDIT, it was first designed to run on Windows 3.1. A version called UltraEdit-32 was later created to run on Windows NT and Windows 95. The last 16-bit UltraEdit program version was 6.20b. UltraEdit-32 was later renamed to UltraEdit in version 14.00. Version 22.2 was the first native 64-bit version of the text editor. Starting with 2022.0, versioning had become year-based.

Module file is a family of music file formats originating from the MOD file format on Amiga systems used in the late 1980s. Those who produce these files and listen to them form the worldwide MOD scene, a part of the demoscene subculture.

PCBoard (PCB) was a bulletin board system (BBS) application first introduced for DOS in 1983 by Clark Development Company. Clark Development was founded by Fred Clark. PCBoard was one of the first commercial BBS packages for DOS systems, and was considered one of the "high end" packages during the rapid expansion of BBS systems in the early 1990s. Like many BBS companies, the rise of the Internet starting around 1994 led to serious downturns in fortunes, and Clark Development went bankrupt in 1997. Most PCB sales were of two-line licenses; additional line licenses were also available.
EmEditor is a lightweight extensible commercial text editor for Microsoft Windows. It was developed by Yutaka Emura of Emurasoft, Inc. It includes full Unicode support, 32-bit and 64-bit builds, syntax highlighting, find and replace with regular expressions, vertical selection editing, editing of large files, and is extensible via plugins and scripts. The software has free trial and after that it downgrades to free version, which still can handle huge files and regex.

The MC-808 is a groovebox introduced by Roland in 2006. It is the successor to the late Roland MC-303, Roland MC-307, Roland MC-505 and Roland MC-909.

Game-Maker is an MS-DOS-based suite of game design tools, accompanied by demonstration games, produced between 1991 and 1995 by the Amherst, New Hampshire based Recreational Software Designs and sold through direct mail in the US by KD Software. Game-Maker also was sold under various names by licensed distributors in the UK, Korea, and other territories including Captain GameMaker and Create Your Own Games With GameMaker!. Game-Maker is notable as one of the first complete game design packages for DOS-based PCs, for its fully mouse-driven graphical interface, and for its early support for VGA graphics, Sound Blaster sound, and full-screen four-way scrolling.

TreeDraw is a genealogy program for computers running Microsoft Windows. The program is a chart editor which aids family historians in creating and printing family trees. Developed by SpanSoft, Scotland, the software is distributed as shareware with a free trial period.

MilkyTracker is a free software multi-platform music tracker for composing music in the MOD and XM module file formats.
Multi-Edit is a commercial text editor for Microsoft Windows created in the 1980s by Todd Johnson. Multi Edit Software obtained ownership rights for the product in October 2002. Multi-Edit contains tools for programmers, including macros, configurable syntax highlighting, code folding, file type conversions, project management, regular expressions, three block highlight modes including column, stream and line modes, remote editing of files via FTP and interfaces for APIs or command lines of choice. The editor uses a tabbed document interface and sessions can be saved.

SunVox, also known as SunVox Modular Music Creation Studio, is a 2008 music creation tool built around the SunVox Engine, a software-based modular synthesizer and tracker-based sequencer. It is available for multiple platforms including Windows, MacOS, Linux on the desktop and iOS, Android in the mobile sphere. The desktop versions are freely available for download on the developer's website while a paid version for iOS and Android apps, respectively, is purchasable from those platforms' official app stores. There was also, at one time, a release for Palm OS devices.










