Molecular surface may refer to one of the following.
- The Van der Waals surface
- Accessible surface area or Connolly surface
- Any of isosurfaces for a molecule
Molecular surface may refer to one of the following.

Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. It is essential because, apart from relatively recent results concerning the hydrogen molecular ion, the quantum many-body problem cannot be solved analytically, much less in closed form. While computational results normally complement the information obtained by chemical experiments, it can in some cases predict hitherto unobserved chemical phenomena. It is widely used in the design of new drugs and materials.
Deposition may refer to:
Emission may refer to:

Molecular nanotechnology (MNT) is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials. Based on Richard Feynman's vision of miniature factories using nanomachines to build complex products, this advanced form of nanotechnology would make use of positionally-controlled mechanosynthesis guided by molecular machine systems. MNT would involve combining physical principles demonstrated by biophysics, chemistry, other nanotechnologies, and the molecular machinery of life with the systems engineering principles found in modern macroscale factories.
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. A more generalized description of nanotechnology was subsequently established by the National Nanotechnology Initiative, which defined nanotechnology as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). This definition reflects the fact that quantum mechanical effects are important at this quantum-realm scale, and so the definition shifted from a particular technological goal to a research category inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with the special properties of matter which occur below the given size threshold. It is therefore common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to the broad range of research and applications whose common trait is size.

Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic and microscopic phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics such as motion, energy, force, time, thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics, analytical dynamics and chemical equilibria.

Theoretical chemistry is the branch of chemistry which develops theoretical generalizations that are part of the theoretical arsenal of modern chemistry: for example, the concepts of chemical bonding, chemical reaction, valence, the surface of potential energy, molecular orbitals, orbital interactions, and molecule activation.
Chip may refer to:

Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to liquid water when in contact with a liquid or solid surface or cloud condensation nuclei within the atmosphere. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition.

The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the protein to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries.

An atmosphere is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules.
Apical means "pertaining to an apex". It may refer to:
Oh, OH, or Oh! is an interjection, often proclaiming surprise. It may refer to:

Molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE) is an epitaxy method for thin-film deposition of single crystals. MBE is widely used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, including transistors, and it is considered one of the fundamental tools for the development of nanotechnologies. MBE is used to fabricate diodes and MOSFETs at microwave frequencies, and to manufacture the lasers used to read optical discs.
Knob or KNOB may refer to:

In the field of molecular modeling, docking is a method which predicts the preferred orientation of one molecule to a second when a ligand and a target are bound to each other to form a stable complex. Knowledge of the preferred orientation in turn may be used to predict the strength of association or binding affinity between two molecules using, for example, scoring functions.
Bioadhesives are natural polymeric materials that act as adhesives. The term is sometimes used more loosely to describe a glue formed synthetically from biological monomers such as sugars, or to mean a synthetic material designed to adhere to biological tissue.
Asphalt most often refers to:
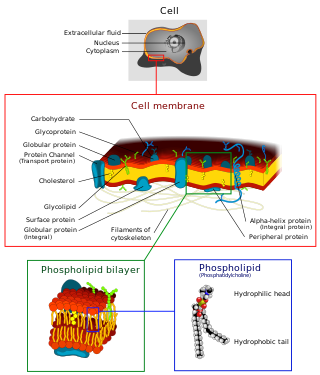
The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules. In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity, and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall and the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx, as well as the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. In the field of synthetic biology, cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.